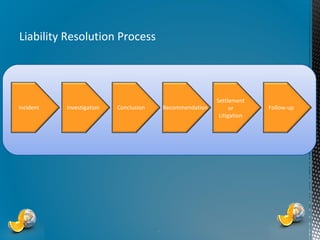
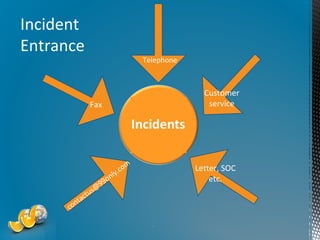
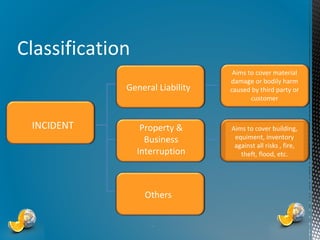
The document outlines the importance of proactive risk management and customer service strategies at Gestion d’incidents GRS, emphasizing the need to mitigate risks such as reputational and legal issues. It presents a comprehensive approach to incident management, advocating for the development of effective strategies that prioritize safety, evidence preservation, and legal compliance. The overall goal is to transition from reactive incident handling to a more proactive and integrated method to enhance customer satisfaction and operational stability.