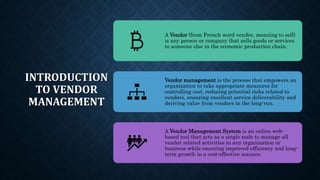
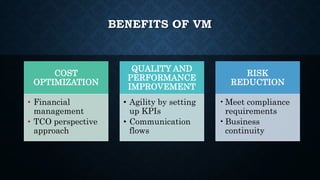
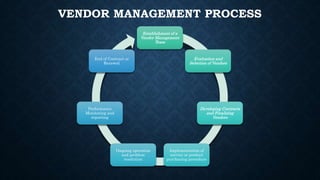
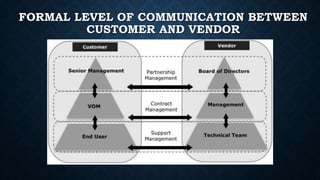
The document provides an overview of vendor management (VM), detailing its purpose in controlling costs, mitigating vendor-related risks, and ensuring service quality. It discusses various aspects of VM including the types of vendors, objectives, benefits, challenges, and the vendor management process, culminating in strategies for effective communication with vendors. The document emphasizes the importance of establishing a structured relationship that benefits both the supplier and the buyer, and outlines the necessary skills for managing vendor relationships.