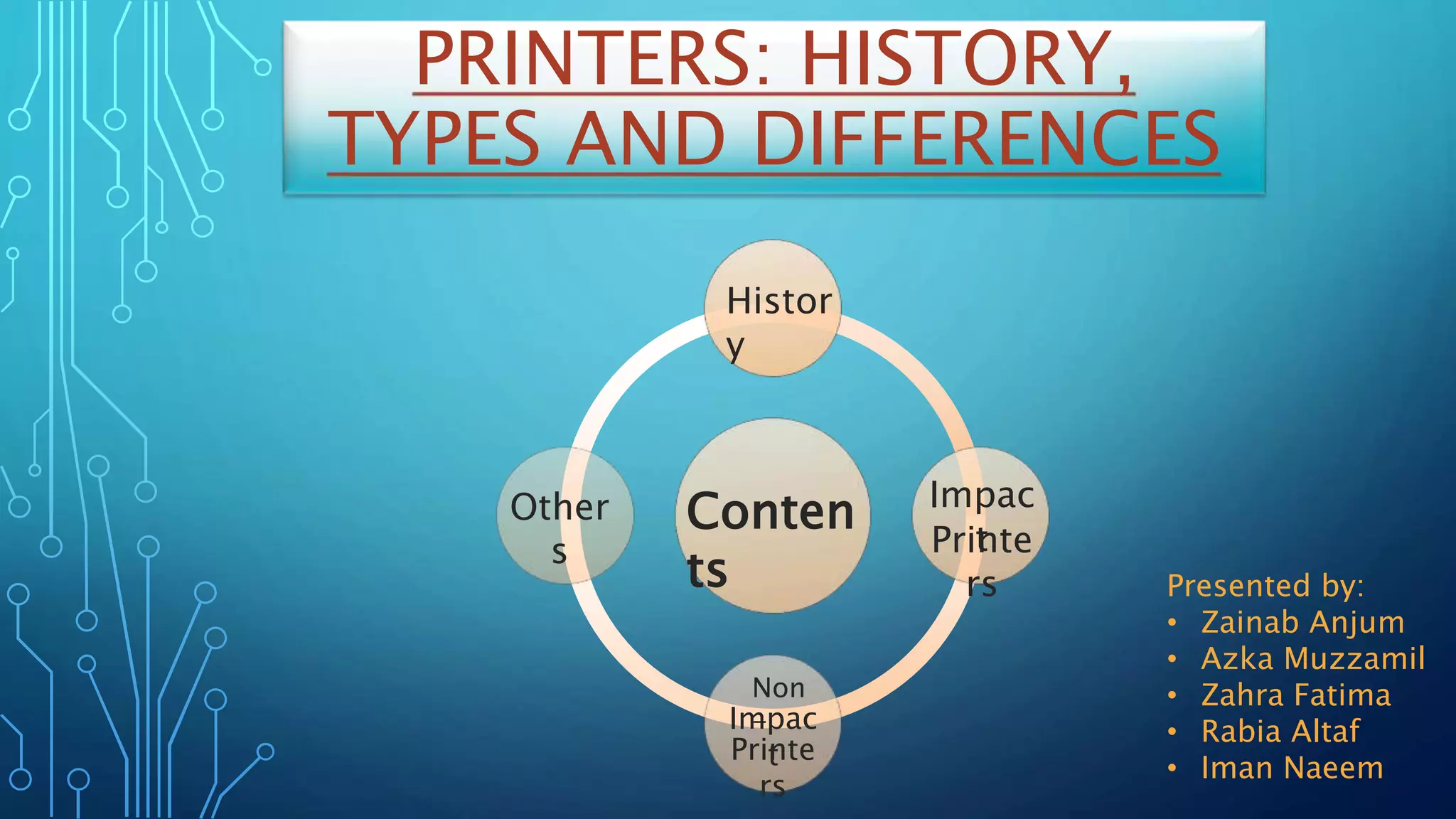
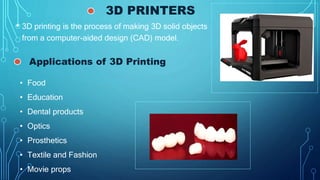
Printers have evolved significantly from early mechanical printers to modern digital printers. Early printers included mechanical printers invented by Charles Babbage in the 1800s and the first xerographic process invented by Chester Carlson in the 1930s. Printers are generally categorized as either impact printers, which use a mechanical mechanism to strike pins against paper, or non-impact printers, which use technologies like laser, inkjet, or thermal to print high quality text without noise. Common impact printers include dot matrix and daisy wheel printers while popular non-impact printers are laser and inkjet printers. 3D printers also represent an emerging technology that can print solid 3D objects from digital models.