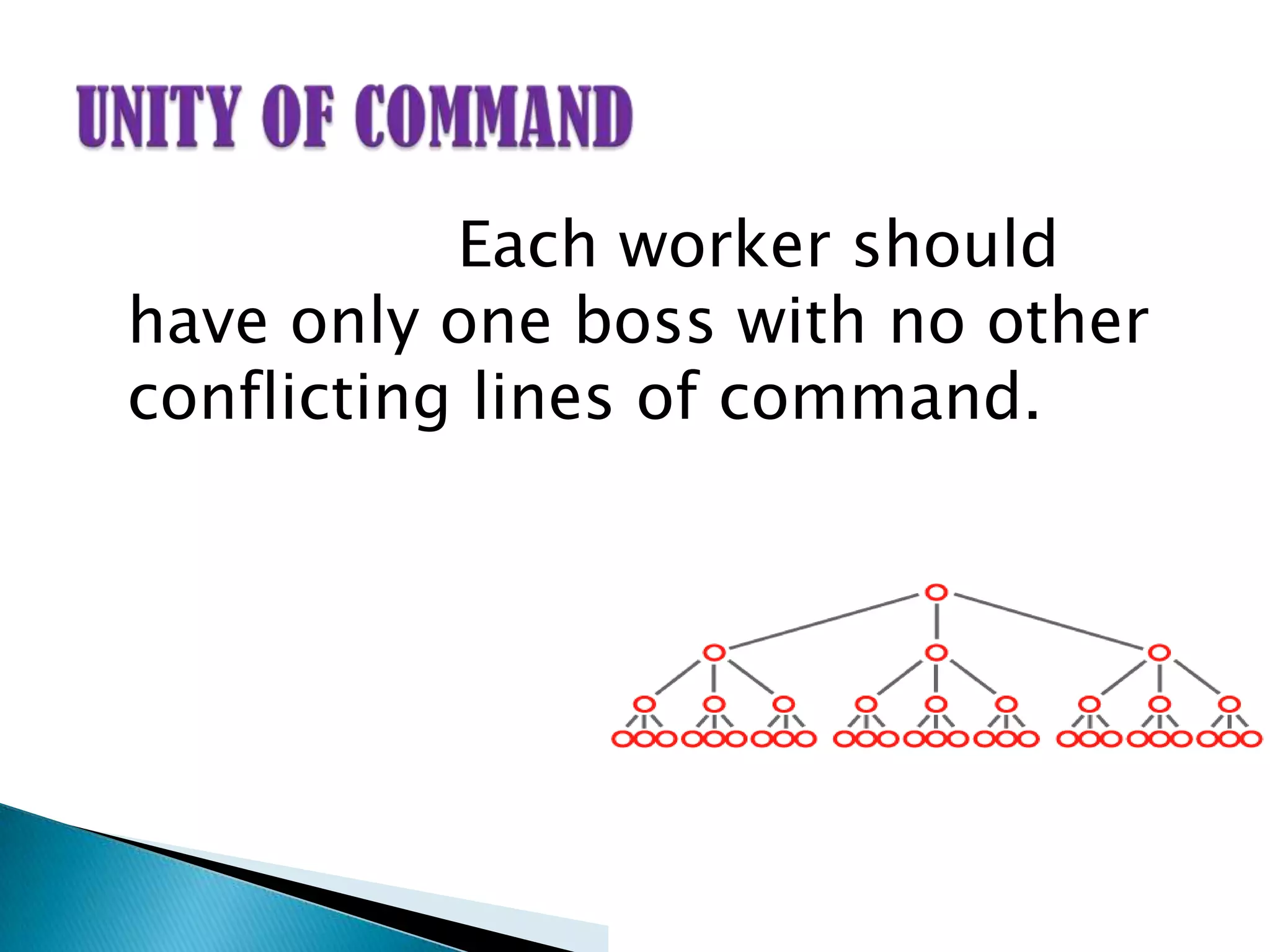
This document discusses 14 principles of management according to Henri Fayol. It summarizes each principle in 1-2 sentences. The principles include specialization, authority and responsibility, unity of command, unity of direction, kindness and justice, material order and social order, discipline, initiative, remuneration, stability of tenure, hierarchy, order, esprit de corps, and subordination of individual interests. Management must balance these principles to effectively lead an organization.