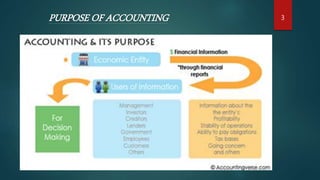
This document provides an overview of accounting principles and financial statements. It discusses that accounting involves recording business transactions in monetary terms and interpreting the results. The main purposes of accounting are to provide quantitative financial information to help with economic decision making. Key users of financial statements are identified such as owners, management, lenders and the government. The document then discusses accounting principles like the revenue recognition principle and matching principle. It defines the objectives of financial reporting and elements of financial statements. Finally, it provides details on the nature of accounting systems and how they communicate financial information to stakeholders through financial reports.