The document outlines a prenatal program in Brazil that develops preventive and corrective actions for pregnant women to ensure better health for mothers and their newborns. It highlights the importance of testing for infectious diseases such as HIV, syphilis, and others, using filter-paper kits for efficient sample collection and diagnosis. Additionally, the document addresses the challenges faced in providing quality prenatal care and the need for improved access to laboratory examinations in vulnerable populations.
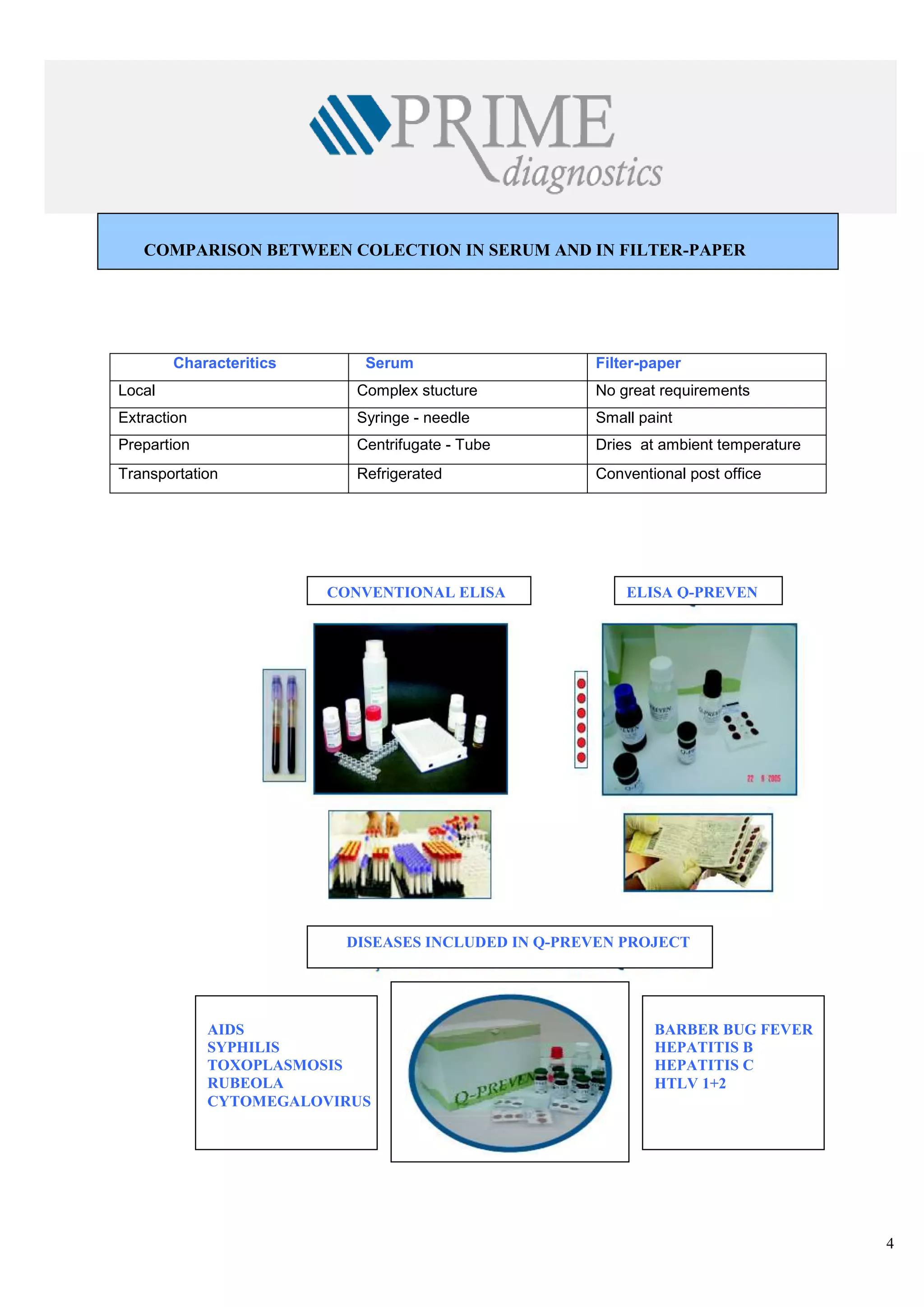
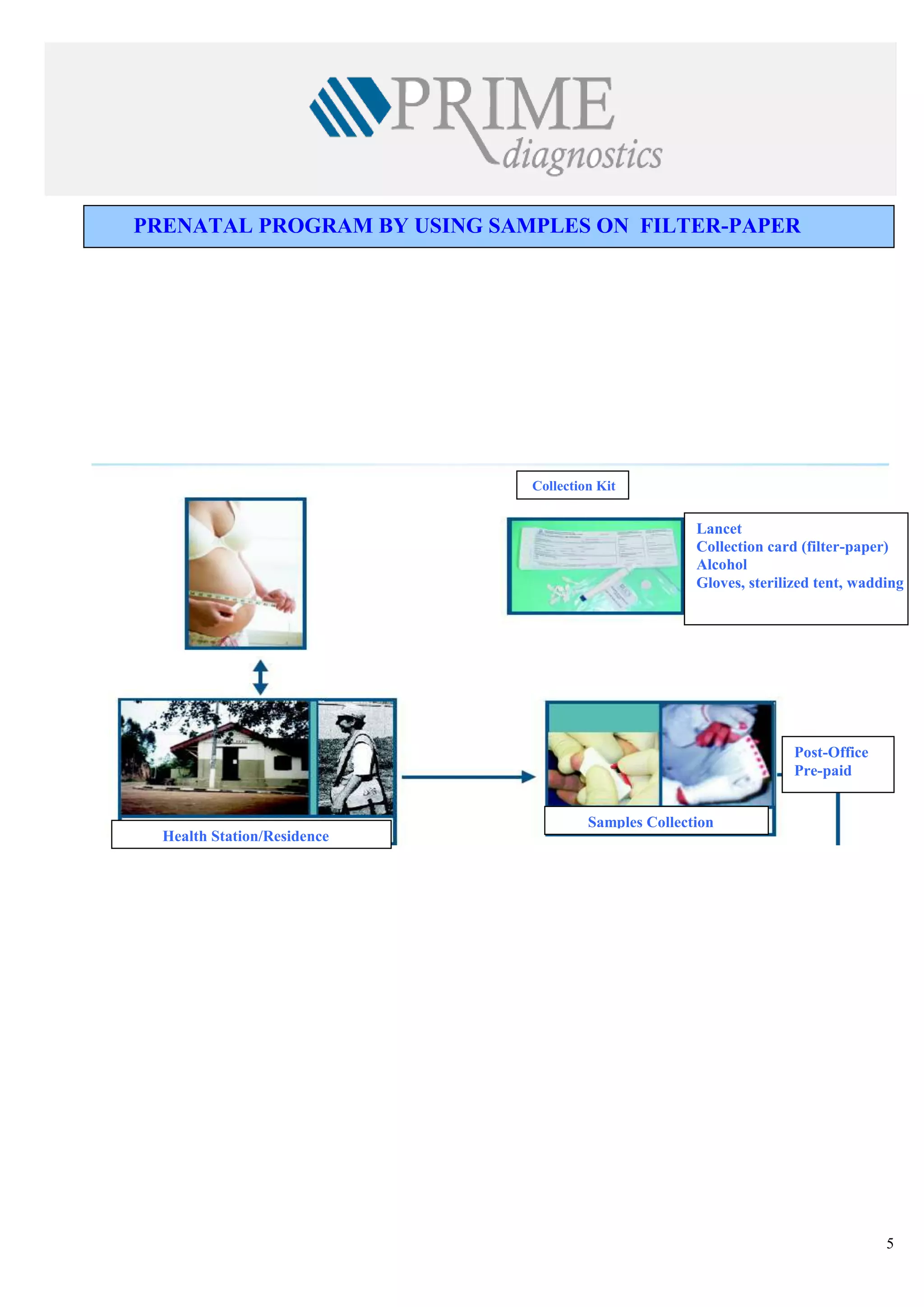
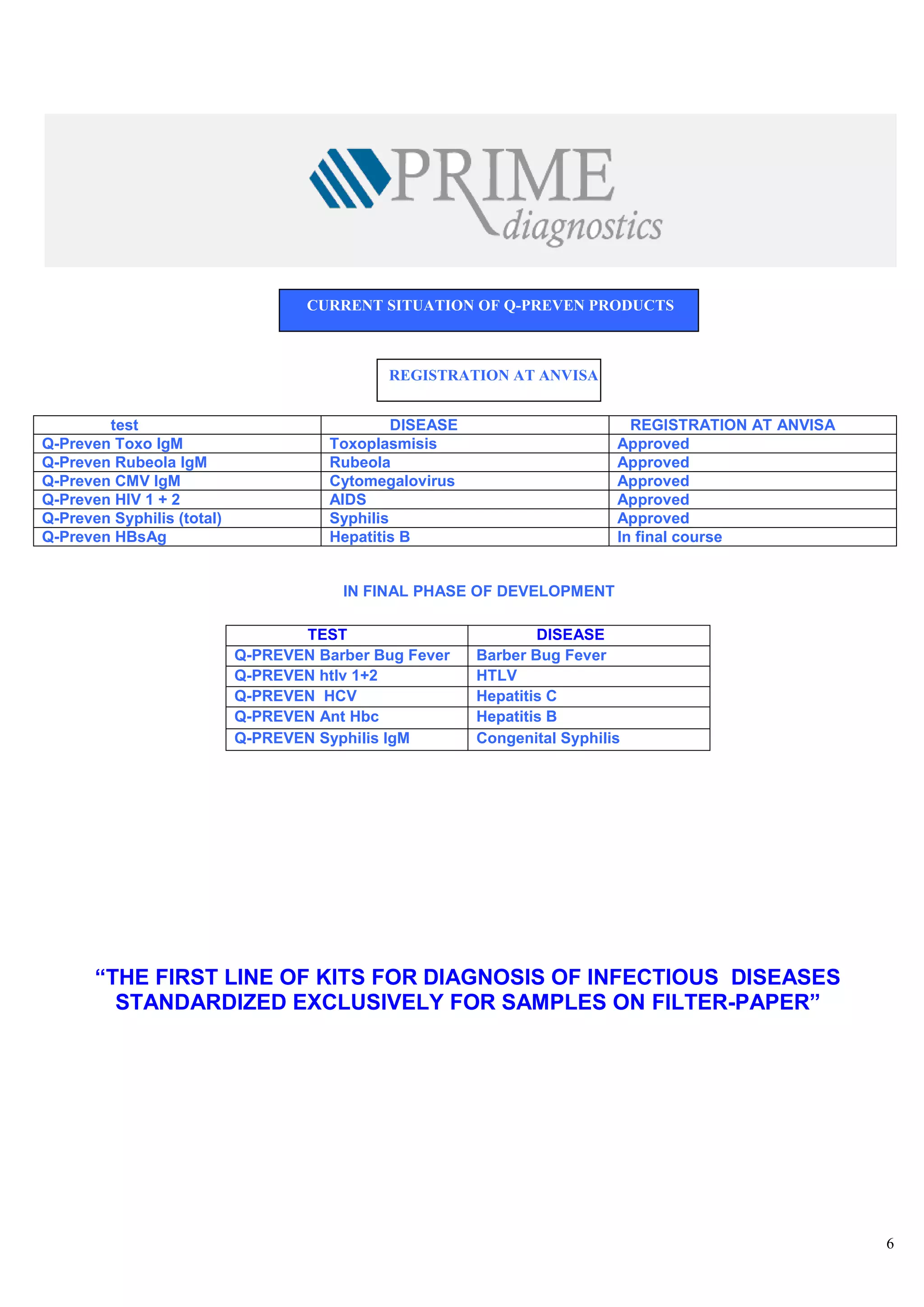
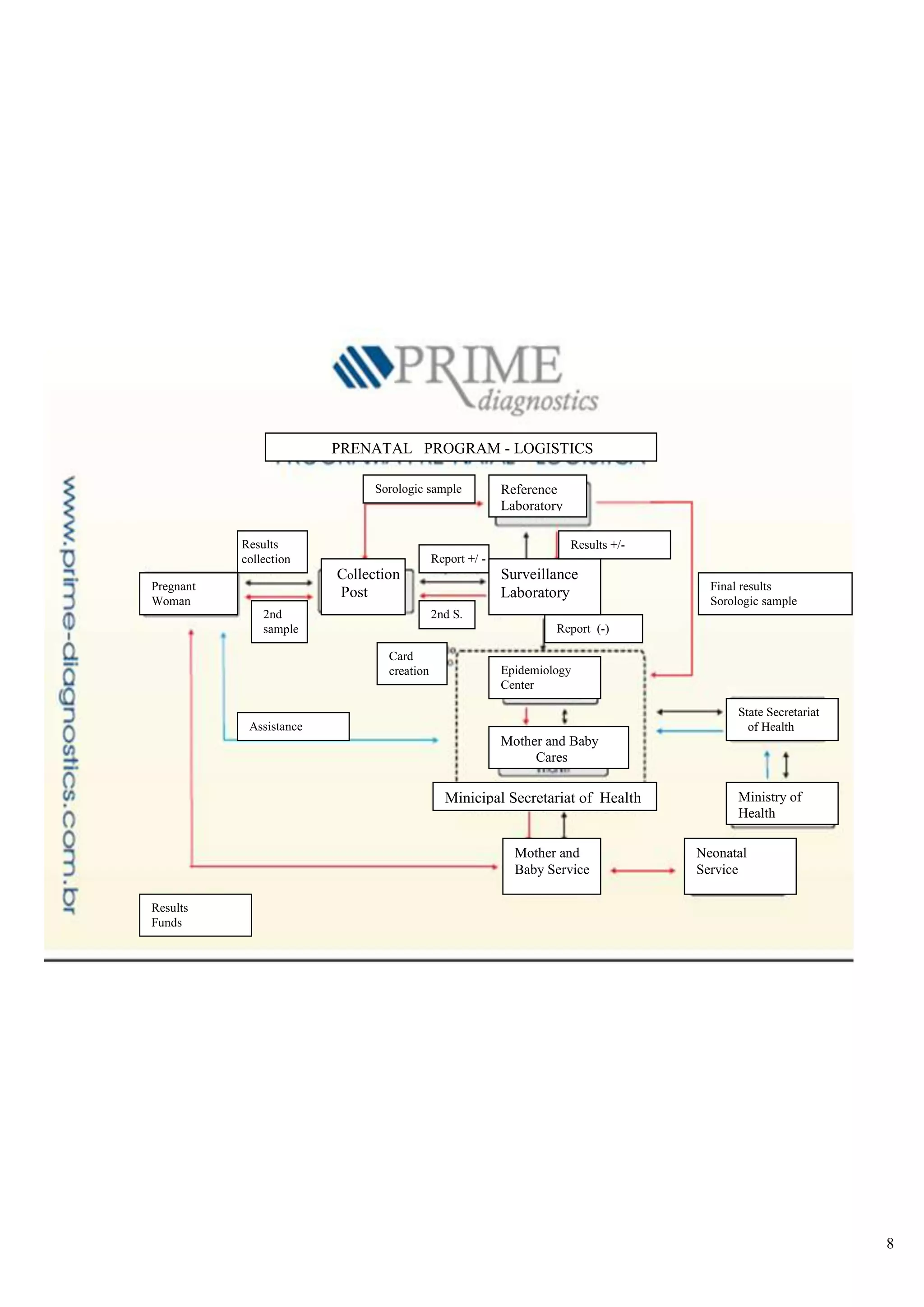
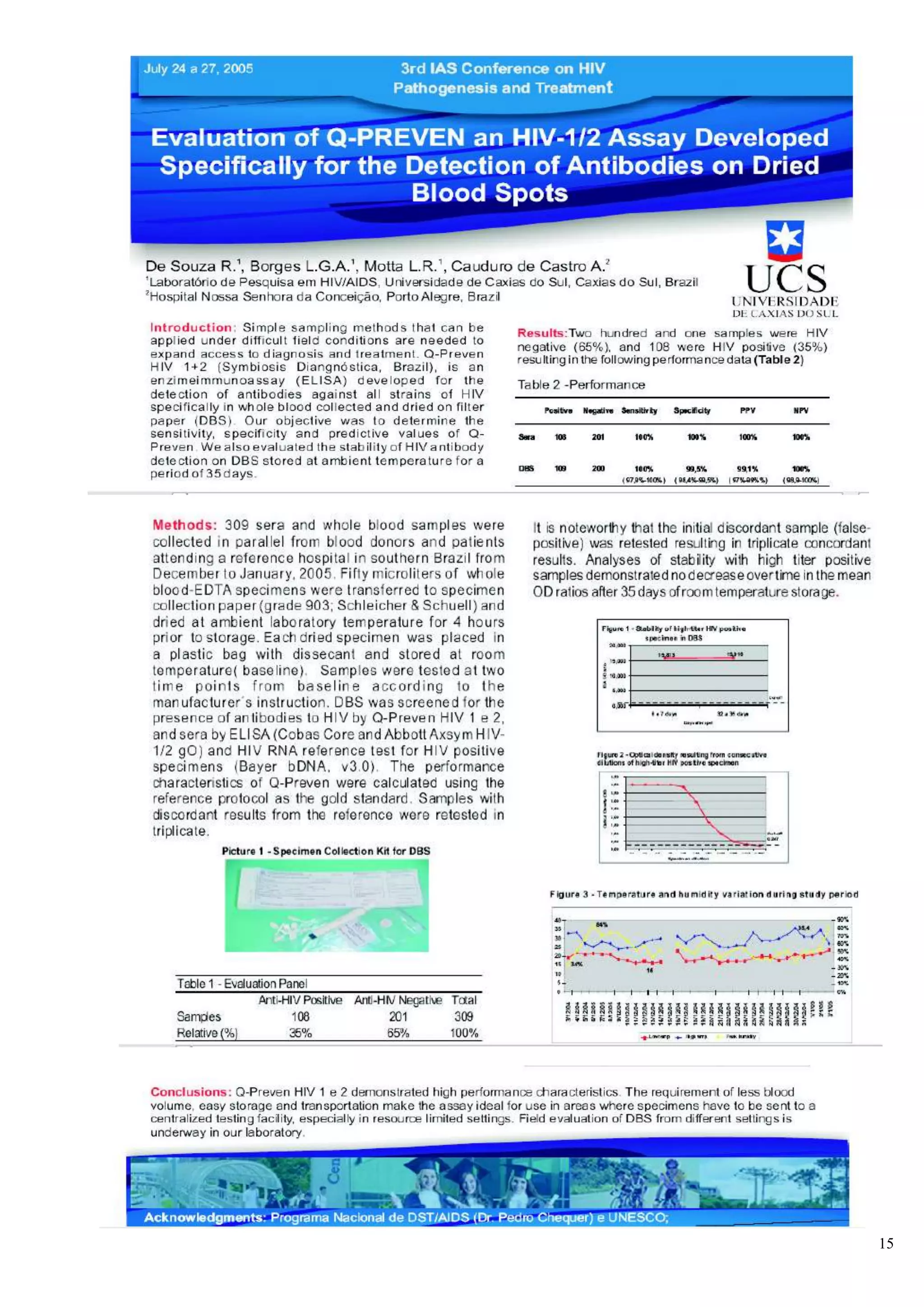
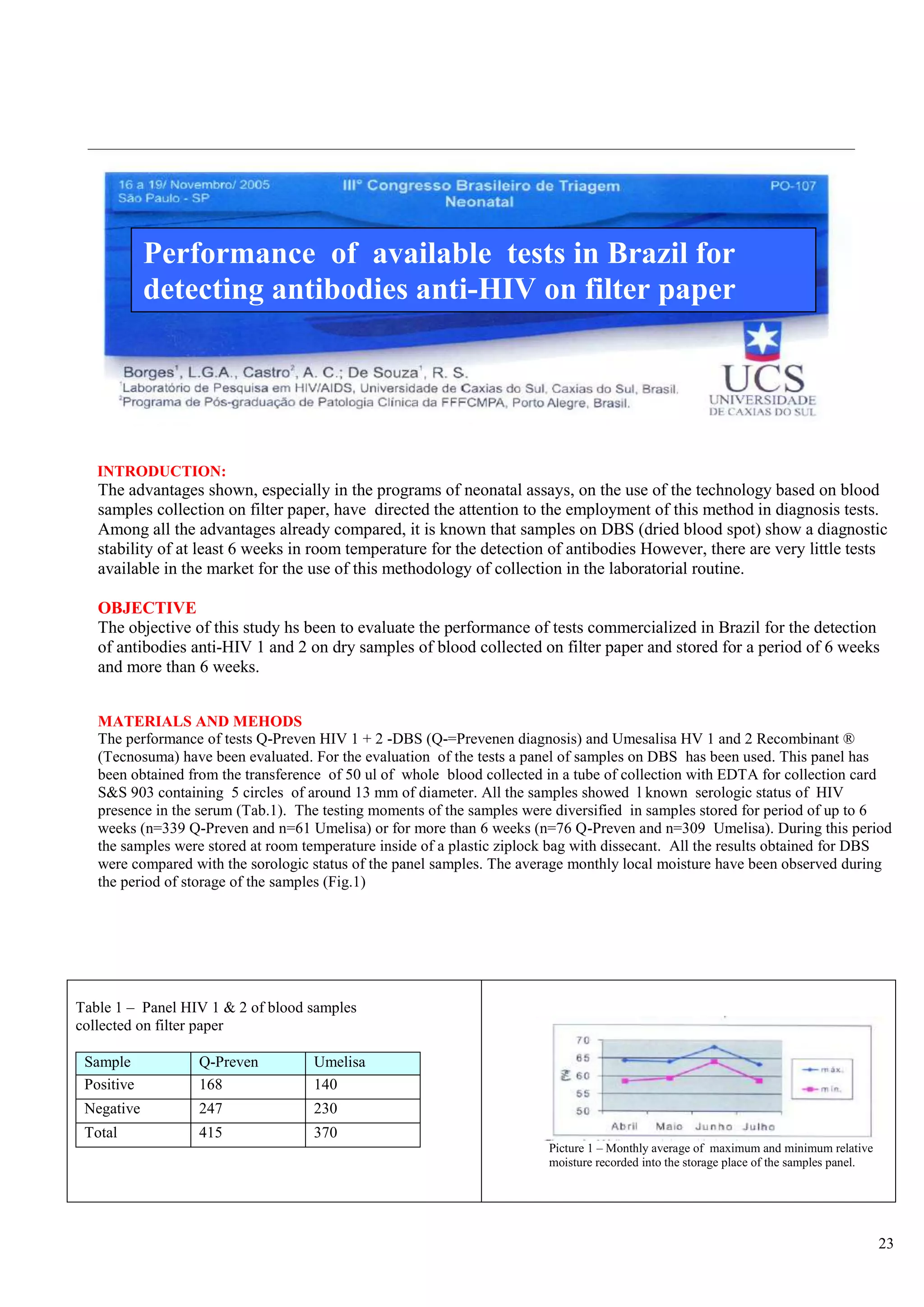
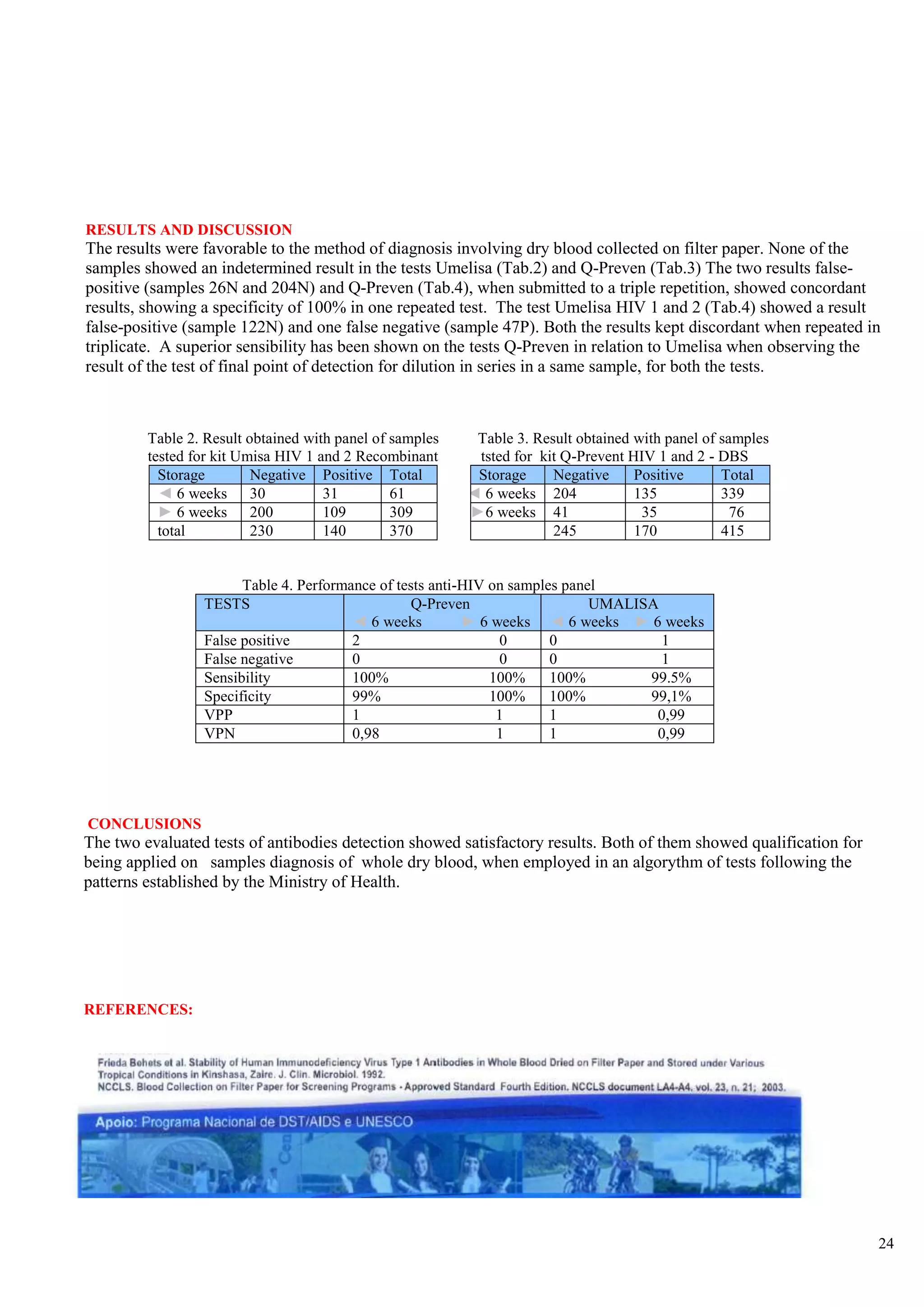
![<br /> PRENATAL DIAGNOSISCHARACTERISTICS OF THE KITS◙EASY DELIVERY AND HANDLING OF SAMPLES ◙STANDARDIZED EXCLUSIVELY FOR FILTER-PAPER ◙HIGH SENSIBILITY AND SPECIFICITY ◙MANUAL AND AUTOMATIZED PROCEDURE . ◙SAME COST OF SOROLOGIC TECHNIQUES ◙FORMAT FOR SMALL, MEDIUM AND BIG ROUTINE ◙VALIDATED AT NATIONAL AND INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTIONS<br /> DISEASES THAT MAY BE DETECTEDAIDSHTLV SYPHILISBARBER BUG FEVERRUBEOLA HEPATITIS BHEPATITIS CTOXOPLASMOSISCYTOMEGALOVIRUS <br />The Prenatal Program is characterized by the development of preventive and corrective actions through the frequent and planned contact of the pregnant woman with the health services, making possible the precocious intervention to problems that affect pregnancy and the future new-born baby. The main goals of the Prenatal Program are:<br />-to prepare a pregnant woman to maternity by giving instructions on the parturition and on child cares.<br />- to give orientations on hygienic habits during the pregnancy and Prenatal moments <br />- to avoid medicines or actions that may damage the fetus<br />- to treat the small usual disturbs of pregnancy<br />- to make prophylaxis, diagnosis and treatment of illness and diseases that are peculiar to pregnancy<br />-to give psychologic assistance to the pregnant woman. <br />In Brazil, one of the current main concerns of Health Institutions related to women and child is to assure a better access, a treatment and a good quality of the Prenatal assistance, especially in relation to laboratorial examinations for controlling infectious deseases that may be transmitted from mother to her new-born son before, during and after the pregnancy. <br />Although the main priorities of Health autorities and institutions are especially concentrated on AIDS and Syphilis problems in Brazil, hospitals are still in great difficulty to provide laboratorial diagnosis of HIV infection and the number of pregnant women examined is scarce, especially in the places where population is more vulnerable to HIV and undergoing a bad prenatalsituation.<br /> <br /> <br /> SITUATION OF AIDS AND SYPHILIS IN BRAZIL<br />-80% of HIV contaminations in people with 13 years of age occur by vertical transmission<br />-65% of vertical transmission of HIV occur during parturition work<br />-The assistance of diagnosis of HIV during prenatal period in lower than 60% and in the case of syphilis it is <br /> only 10%<br />-The prevalence of Syphilis during pregnancy attains 2%<br />-The rate of Syphilis vertical transmission is higher than 70%<br />-In 2006 Brazil has shown a rate of 3.141 congenital syphilis cases <br />-The mortality rate for congenital Syphilis disease is high and it rather attains 40% of the cases.<br />At present, a few factors related with the lack of health infra-structure out of the large cities are limiting the implementation, assistance and efficiency of field epidemiologic studies and programs of population diagnosis in countries under development, starting from the difficulty to obtain the samples through the traditional means of collection (periferic blood), that requires nurses or qualified personnel, as also discarding articles like test-tubes, syringes, injection needles and the blood samples obtained through veins must be centrifugated and refrigerated.<br /> PROJECT Q-PREVEN<br />The use of filter-paper is a cheap and a convenient method for collecting , stocking, conveying, handling and keeping for long periods blood samples to be used in populational studies and in programs of sociologic assistance . This has been demonstrated by the experience and by the results of the new-born diagnosis programs carried out during the last 40 years with a group of great diseases <br />which included heredo-metabolic illness and infectious illness. Thanks to the use of this kind of samples, these programs have shown a good performance, even in less developed countries and in remote regions with no laboratorial support, so it has been possible to make diagnosis of several congenital and hereditary diseases, affording the elimination or diminution of the associated sequels of each single illness, thus representing a great goal in Prevention Health Programs<br />With a view to attain theses goals, a team of researchers highly experienced in the incrementation of products for diagnosis of blood collected on filter paper, together with producers of material for diagnosis in vitro, started, in 2002, the development of diagnosis kits lines based on the methodology of ELISA (immunization-test), that utilizes samples of human blood collected on filter-paper S & S903 for analysis of infectious diseases.<br /> COMPARISON BETWEEN COLECTION IN SERUM AND IN FILTER-PAPER<br />Characteritics SerumFilter-paperLocalComplex stuctureNo great requirementsExtractionSyringe - needleSmall paintPrepartionCentrifugate - TubeDries at ambient temperatureTransportationRefrigeratedConventional post office<br /> <br />ELISA Q-PREVEN CONVENTIONAL ELISA <br />AIDSSYPHILISTOXOPLASMOSISRUBEOLACYTOMEGALOVIRUSBARBER BUG FEVERHEPATITIS BHEPATITIS CHTLV 1+2 DISEASES INCLUDED IN Q-PREVEN PROJECT <br /> PRENATAL PROGRAM BY USING SAMPLES ON FILTER-PAPER <br /> <br /> Health Station/Residence Samples CollectionPost-OfficePre-paid Collection KitLancetCollection card (filter-paper)AlcoholGloves, sterilized tent, wadding <br /> <br /> test DISEASE REGISTRATION AT ANVISAQ-Preven Toxo IgMToxoplasmisisApprovedQ-Preven Rubeola IgMRubeolaApprovedQ-Preven CMV IgMCytomegalovirusApprovedQ-Preven HIV 1 + 2AIDSApprovedQ-Preven Syphilis (total)SyphilisApprovedQ-Preven HBsAgHepatitis BIn final course<br />REGISTRATION AT ANVISA CURRENT SITUATION OF Q-PREVEN PRODUCTS <br /> <br /> <br /> <br /> IN FINAL PHASE OF DEVELOPMENT<br /> <br /> TEST DISEASEQ-PREVEN Barber Bug FeverBarber Bug FeverQ-PREVEN htlv 1+2HTLVQ-PREVEN HCVHepatitis CQ-PREVEN Ant HbcHepatitis BQ-PREVEN Syphilis IgMCongenital Syphilis<br />“THE FIRST LINE OF KITS FOR DIAGNOSIS OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES<br />STANDARDIZED EXCLUSIVELY FOR SAMPLES ON FILTER-PAPER”<br /> PROGRAM PHILOSOPHY <br />● Conception: Mass analysis● Program target: 100% of pregnant women● Methodology: Dry blood collected on filter-paper● Purpose:Reduction of maternal-infantile morbi-natality● Justification:□ High rate of maternal mortality□ 1990: 47,8 / 100.000 parturitions□ 2000: 53,7 / 100.000 parturitions□ High rate of malformation, spontaneous abortion ● Essentially Preventive Program<br /> <br />SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES● To facilitate the access of pregnant women to Prenatal exams● To ameliorate the knowledge of epidemiologic profile of aggravations in this group, in order to help interventions● To ameliorate the quality of woman’s health,● To ameliorate the health quality of new-born children and reduce infantile mortality● To increase the quantity of pregnantwomen examined on Prenatal prioritary pathologies ● To reduce the prevalence and vertical transmission of the identified pathologies , especially: HIV,Syphilis,Hepatitis B, Toxoplasmosis, Cytomegalovirus, Rubeola, etc.●To improve the registrations and control of pregnant women<br />Mother and Baby Service PRENATAL PROGRAM - LOGISTICSResultsFundsCard creationReport (-)Final resultsSorologic sampleResults +/-Sorologic sampleReport +/ -2nd S.sample2nd sample Results collectionAssistanceMinicipal Secretariat of HealthState Secretariat of HealthMinistry of HealthNeonatalServiceMother and Baby CaresEpidemiologyCenterReferenceLaboratorySurveillance Laboratory Collection Post Pregnant Woman<br /> <br />TOXOPLASMOSIS<br />Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease caused by a protozoa called Toxoplasma gondii. This protozoa is easily found in the nature and it can cause infection in a great number of mammifers and birds all over the world. In human beings the infection is assymptomatic in 80 to 90% of the cases, namely, it does not cause any symptom and it may be ignored in patients with a normal immunity.<br />It is estimated that 60% of the Brazilian Pregnant women has already caught toxoplasmosis before pregnancy. The infection may be caught in several ways: by eating underdone meat, non-filtered water, vegetables and greens wrongly washed. However, The major source of transmission source of this infection is through a contact with animals (dogs and especially cats).<br />If this infection is caught during pregnancy, it may be transmitted to the baby. When this occurs, the greatest part of the babies stay healthy but a small part will show symptoms of the disease that will become serious if the infections has been caught precociously. Nevertheless, today there are exams that allow the doctor to know if the baby is infected or not and there are medicines that are efficient and heel the baby during the woman pregnancy, reducing the probability of occurring serious problems. <br /> <br /> RUBEOLA<br />It is an infectious disease caused by a virus (togavirus of Rubivirus type) that attacks children and adults, although it is considered a disease of children. Although it is considered a viral disease, generally a benign virus, when it occurs during the pregnancy it may be transmitted to the fetus, and become serious causing intra-uterine death or malformations. The diffusion Of vaccine diffusion has diminished the incidence of congenital rubeola that presently is estimated in 4/10.000 gestações.<br />Rubeola may be transmitted through the inalation of small drops of nose secretion of people bearing the virus, or via blood, in the case of afetus, during pregnancy. The disease in a baby is more serious when caught precociously in the pregnancy. During the three first months, more than 80% of maternal infections of rebeola are transmitted to the baby, and there is 20% of abortion risk or a serious congenital malformation in 90% of the risks. The risk of fetal transmission diminishes progressively after the 3rd month and the risks of malformation is practically null after the fourth month.<br />CYTOMEGALOVIRUS (CMV)<br />The cytomegalovirus is an timeserver human pathogene where the infection is particularly prevalent between children and young adults. The infection through CMV is an important health problem in certain groups of patients, as new-born babies, patients who have undergone solid organs or bone medule transplantation and bearers of AIDS.<br />The congenital cytomegalovirus is a most frequent infection. It is estimated that in Brazil 0,55% to 6,8% of the babies come<br />to life contaminated with cytomegalovirus and between the infected babies 5 to 20% show the symptoms when they are born (pneumonia,low weigh,prematurity, neo-natal ictericia). The infection may cause permanent problems in the baby, especially a delay in the development and a mental retardation.<br />The transmission of the virus to the baby occurs normally as a result of an acute mother infection. If there is a contact with the virus, confirmed through laboratorial exams, the Prenatal diagnosis of the fetal infection may be done through the amniotic exam that may be performed from the 6th month on of pregnancy<br />AIDS<br />The Syndrome of Acquired Imuno-Deficiency (AIDS) has been described for the first time in l981 and it is an infectious disease caused by the virus of human imuno-deficiency which leads to a progressive loss of immunity, ending in serious<br />Infections, malign tumours and other timeserver infections that may take to death.<br />From 1980 to June 2005, statistics have shown 371.827 cases of AIDS in Brazil. In general the incidence rate of AIDS (cases of disease per each 100 thousand inhabitants) keeps stable, but in 2004 it has attained - 17,2. The difference between men and women rates is changing considerably and today we have 1,5 male cases per 1 female case. In the beginning of the epidemy, the comparison was 16 male cases against 1 female case.<br />The HIV virus may be transmitted through sexual contact between infected people with HIV, through exposition to blood (including the shared use of contaminated injection needles) or through certain hemoderivated contaminations with HIV or then through mothers transmission to their fetus or baby during prenatal period.<br />The transmission of virus from mother to son stands for the majority of AIDS cases among children. A due treatment of<br />HIV+ in pregnant women allows to save up to 70% of the babies and they will have a good chance to come to life without<br />the virus.<br /> SYPHILIS<br />Syphilis is a chronic infectious disease caused by a fragile bacteria called Treponema Pallidum which grows in a chronic (slow) way and shows acute periods (it burst out acutely) alternated with latent period (with no manifestation). <br /> If it is not treated in time, it grows up and becomes chronic and ostensive, affecting multiple organs (skin, eyes,bones, cardiovascular system, nervous system). Its progression, according to the body injure degree, has been classified in several stages (primary, secondary and tertiary). The two first stages show stronger characteristics of infection with more symptoms and more risk of contamination. Syphilis may be caught by sexual contact, via placenta (congenital syphilis since foetus is attacked during intra-uterine life), via kiss or other intimate contact with an active wound (containing bacteria Treponema), via blood transfusion or other derivated ways.<br />Main aspects to be taken into account in the vertical transmission of syphilis:<br />● the maternal transmission may occur in any pregnancy period;<br />● The rate of vertical syphilis, in women without any treatment, stands between 70 to 100% during the first 4 years of the <br /> disease evolution;<br /> ●Prenatal death occurs in 40% of the infected babies <br />A correct treatment during pregnancy reduces to 1,5% the risk of syphilis transmission to the baby.<br />HEPATITIS B<br />Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by a virus which affects essentially the liver. Hepatitis B (HBV) virus may cause an infection for the rest of the life, like liver cirrhosis, liver cancer, hepatic failure and death. After the infection, <br />the virus concentrates almost totally into the cells of the liver.<br />Hepatitis B may be caught through blood transfusions or shared utilization of syringes, needles and other instruments <br />of drug users, or also in sexual relations,body contacts with secretions contaminated with the virus,mucus orwounded ]<br />skin and also by vertical transmission from the pregnant to the baby. <br />The transmission risk is little during the first and second quarter of pregnancy but it is high after the 7th month. Other vias of contamination are the contact with maternal blood or contaminated vaginal secretions during the parturition or through mother’s milk.<br />The incidence of Hepatitis B during pregnancy is around 0,5%. The baby may catch the infection from a pregnant woman with a strong infection or chronical carrier of hepatitis.<br /> BARBER BUG FEVER<br />Barber Bug Fever is as infectious and parasitary disease caused by the protozoe Trypanosoma Cruzi and transmitted by the insect Triatoma infetans (Triatomineo), commonly called Barber. It is an endemic disease of great part of Central and South America. According to the World Health Organization, around 17 million people are carriers of Barber Bug Fever and 50.000 of them die every year. In Brazil, approximately 5% of the population carries this disease and the statistics show 100.000 new cases per year.<br />The main vias of transmissions are:<br />Vectorial: prick of infected triatomineo<br />Transfusional: exposition to contaminated blood<br />Transplacentary: vertical transmission from a mother to the new-born baby.<br />A pregnant woman carrying this strong or chronical infection may transmit it to the foetus in any period of her<br />pregnancy, including during the first quarter, if the trophoblasto is thicker, and even in the channel of parturition through the contact of foetus mucus with his mother’s infected blood.<br />The incidence in pregnant women may vary from 2 to 11% in the urban centers and from 23 to 58% in the rural <br />areas. Studies have been published saying that in new-born babies the incidence may vary from 0,7% to 8% and<br /> the transmission is 1% among chronical carriers and 7,7% among premature babies of carriers women.<br />HEPATITIS C<br />Hepatitis C is a liver disease caught through the contact with infected blood or other body fluids. It is caused by<br />virus HCV and in the past it was called virus non-A/non-B. Hepatitis C is dangerous because in 85% of the cases it becomes chronic and may grow and become a liver cirrosis or cancer. The evolution period of the disease is estimated to be 20 to 30 years but each single organism react differently. This period depends on the cares and modus vivendi of the patient. It is estimated that among 2,5% to 4,9% of the Brazilian population, approximately 4.1 to 8 million people are carriers of Hepatitis C.<br />The transmission of Hepatitis C occurs through the contact with the blood or body contamined secretion: blood, mucus or wounded skin. Although recent reports mention the presence of this virus in other secretions (milk, spittle ,urine and sperma), the quantity of virus seems to be too little to cause infection and there are no data indicating transmission through these vias. The mother-foetus transmission is rare. In spite of the already known transmission means, 20 to 30% of the cases occur without revealing the contamination via. <br /> <br />HTLV 1+2<br />HTLV is a virus pertaining to the family of retrovirus (the same as HIV). HTLV 1 causes mainly a rare modality of leukaemia (Leukaemia of Cells T in adults) which is normally fatal and a serious chronical neurologic degenerative disease, myelopathy/paraparesis that affects the capacity of walking.<br />It is estimated that 15 to 20 million people in the world are carriers of HTLV-1. In Brazil, statistics show 2,5 million of infected people by this virus, especially in Bahia (1,35% to 1,80% of the population), Pará (1,61%) and Pernambuco (0,33% to 0,82%). Nevertheless, just as in the rest of the continent, these information is based on studies of specific groups like blood donors and pregnant women.<br />Among the strategies to diminish the incidence of HTLV in Brazil , there is the implantation of binding tests for detecting HTLV in milk banks and prenatal exams.<br />HTLV is transmitted similarly to HIV, namely through body fluids like sperma, vaginal secretions, blood, pregnant women to fetus and baby nursing.<br /> <br />Scientific Publications and ValidationsQ-PREVEN HIV 1+2 DBS<br /> <br />“EVALUATION OF Q-PREVEN HIV 1+2 TEST<br />SPECIFICALLY DEVELOPED FOR DETECTING<br />ANTIBODY TO HIV 1+2 IN SAMPLES OF DRY BLOOD”<br />Laboratory of HIV/AIDS Researches<br />UCS/ Caxias do Sul – RS<br />Caxias do Sul/February 2005<br /> <br /> <br />“EVALUATION OF THE PRENATAL EXAMS OF HIV<br />BY USING DRY BLOOD ON FILTER PAPER”<br />APAE – Associação de Pais e Amigos dos Excepcionais de Salvador<br />Salvador – Bahia State<br /> <br />APAE ASSOCIATION PRESENTS A NEW EXAM FOR DETECTING AIDS IN PREGNANT WOMEN<br />04/11/2005 – 09h50<br />the unique service entitled by the Ministry of Health to perform the child foot test may now become a reference <br />also in the detection of HIV virus in pregnant women. The Association of Parents and Friends of Anomalous – APAE – has presented yesterday, in Salvador city, the validation of a new technique of collection and analysis of exam that utilizes the same material as the one of child foot test: filter-paper. It reduces the time of diagnosis <br />(8 days instead of 60) , it costs 30% less and finally the procedure may increase the access of pregnant women to the exam and favour the tracing of other maternal diseases subject to vertical transmission.<br />The researchers of the Reference Service for Newborn Surveillance of APAE worked during 6 months for the validation of the technique created last year.In partnership with The Health Secretariat of the State of Bahia (Sesab) they have submitted to analysis 1.483 patients who asked for Prenatal assistance in 3 public Maternity hospitals (Albert Sabin, Tsylla Babino and Iprba) , as also in the Reference Center specialized in DST/AIDS of Salvador and in APAE. The results which included also tests with 25 blood tests of patients soropositive (sent by the Hospital Efgard Santos) showed that the traditional method matches 99,86% with the filter paper methodology.<br />Preconized by the Ministry of Health the serologic methodology for HIV detection in pregnant women is only favoured by the new technology. Any health station making the test of child foot is in a position to perform the material collection for the HIV exam with samples o dry blood and send it even by envelope to the laboratory of analysis. “The collection may be done in any place of the State, within the same routine of diagnosis of Prenatal cases. The facility and simplicity of the procedure favour what recommends the Ministry of Health: the universal access to the exam”, says the medical director of APAE, Dr Cleusa Zanetti.<br />Source: Correio da Bahia (journal)<br /> <br /> <br />Participation in the quality control of the<br /> Center of Diseases Control (CDC) - USA<br />DIAGNOSIS OF HIV<br /> 15/01/2005 – 09:45<br />Brazilian Researchers Point Out Advantages Of Filter-Paper in HIV Diagnosis<br />BRASILIA – Researchers of the University of Caxias do Sul (UCS) have developed a study for validating and evaluating the advantages of a “test with dry samples on filter paper”, a technology that allows to check if the patient has the virus HIV and other diseases by analysing a small sample of blood dropped on a paper from a prick<br />on a patient’s finger. The research, financed by the National Program of DST/AIDS and by the Orgnization of the United Nations for Science and Culture (UNESCO), examines the filter paper in different conditions of temperature and moisture, comparable to cities of other regions of the country, and this will serve for the government to analyse its utilization in regions of difficult access or with little laboratorial structure.<br />According to the Chief of the Researches Laboratory in HIV and AIDS of the University UCS, Dr Ricardo da Silva de Souza, the results of the first phase of research have been quite positive. The validation confirmed that filter paper has the same efficiency of the collection via veins injection and he pointed out other factors of security.The evalutation of the sensibility of filter paper for tests anti-HIV (capacity of giving positive results) showed 100% of efficiency and<br /> the one of specificity (capacity of identifying people without the virus) has showed 99,5% of favorable results.<br />The doctor who coordinated the research said that in the overall they have analysed 309 samples between the 3rd of<br />December 2004 and the 3rd of January 2005. “We have been able to certify that it is possible to make a diagnosis of HIV with filter paper and we could realize that it works. It has a stability of up to 35 days without special conditions of stockage, namely, it fits the ambient temperature”, he assures. Today only one company has the registry at National Sanitary Agency (ANVISA) for the utilization of filter paper as a method of blood collection and it is not binding to present a study of stability to the regulating agency.<br />ADVANTAGES<br />Beside validating the method, the researchers showed other positive points of this kind of sampling, like the easy collection and storage, the necessity of little structure and little human resources, as also the capacity of generating quick answers (via internet and post office) and the low .cost. “The transport of conventional samples of blood (via tubes of tests) may alterate the characteristics of blood if there is not an dequate refrigration and there is also the risk of accidents with the material. With filter paper the transport may be done by post office without any alteration of the results”, he says. In the traditional method, if the blood is not refrigerated right after the collection, says Ricardo, it is annulled . “We reproduce the conditions of collection and transport and we confirm that the exams may be tested with quality even after a long period after analysis and with variation of temperature and moisture.”<br />The variation of moisture is an important point because the sample is dry and if the weather is too humid, it may generate fungus and other problems that interfere in the result. Variations of temperature and moisture of Porto Alegre city have been compared to other seven capitals (Curitiba, João Pessoa, Manaus, Natal,Rio Branco,Salvador and Teresina), where it has been noticed a similarity between them and the absence of any difference in the results and in the quality of the samples due to the temperature and moisture aspects. Therefore, the samples can come from any place of the country without alterating the results of the exam.<br />Although it was not one of the objective of the research, the researchers made preliminary analysis of the results confirmation by comparing the initial information made through the method Elisa with the Western Blot, one of the exams that confirms HIV.” It was not our principal objective but we could confirm that the Elisa results are the same as the Western Blot ones. However, we saw in these preliminary results that it is important to have a higher quantity of dry blood than the one used in Elisa, leaving the test more sensible due to the size of the sample, namely the ideal is to use two samples of dry blood for each patient in the confirmatory” says the coordinator of the research.<br />PILOT<br />The researchers finalized the first phase of the project that started in April 2004 and are expecting to start the following phase still in the first semester of this year. At this stage will be performed a pilot-study in Prenatal hospitals and different regions of the country to check if the data shown in phase 1 are confirmed in phase 2. “We want to develop an algorythm specific for filter paper in testing HIV, namely we want to have a sequence of tests that would give 100% of chances to obtain the correct result with this method”, defends Ricardo.<br />Another objective of phase 2 is to implant the system of devolution of the results by internet and post office and offer training courses personally and at distance, in order to orient the professionals health on how to present the result to the patients.<br />According to the researcher, the idea is to associate the diagnosis via filter paper to other programs, such as the Family Health, and serve as instrument of diagnosis of other infections that attack pregnant women. “For this reason we have started to validate and test filter paper for toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, syphilis, herpes, rubeola and HTLV”. The intention of this study is to contribute for the reduction of the vertical transmission (when the virus passes from a mother<br />to her baby) and other prenatal infections through precocious diagnosis afforded by the test.<br /> <br /> HEALTH<br /> <br />‘PERFORMANCE OF TESTS AVAILABLE IN BRAZIL FOR THE DETECTION OF ANTIBODIES<br />ANTI-HIV 1 + 2 IN FILTER PAPER SAMPLES”<br />Laboratory of Research in HIV/AIDS UCS/Caxias do Sul-RS<br />Caxias do Sul / February 2005<br />Performance of available tests in Brazil for detecting antibodies anti-HIV on filter paper<br /> INTRODUCTION:<br />The advantages shown, especially in the programs of neonatal assays, on the use of the technology based on blood samples collection on filter paper, have directed the attention to the employment of this method in diagnosis tests. Among all the advantages already compared, it is known that samples on DBS (dried blood spot) show a diagnostic stability of at least 6 weeks in room temperature for the detection of antibodies However, there are very little tests available in the market for the use of this methodology of collection in the laboratorial routine.<br />OBJECTIVE<br />The objective of this study hs been to evaluate the performance of tests commercialized in Brazil for the detection of antibodies anti-HIV 1 and 2 on dry samples of blood collected on filter paper and stored for a period of 6 weeks and more than 6 weeks.<br />MATERIALS AND MEHODS<br />The performance of tests Q-Preven HIV 1 + 2 -DBS (Q-=Prevenen diagnosis) and Umesalisa HV 1 and 2 Recombinant ®<br />(Tecnosuma) have been evaluated. For the evaluation of the tests a panel of samples on DBS has been used. This panel has been obtained from the transference of 50 ul of whole blood collected in a tube of collection with EDTA for collection card S&S 903 containing 5 circles of around 13 mm of diameter. All the samples showed l known serologic status of HIV presence in the serum (Tab.1). The testing moments of the samples were diversified in samples stored for period of up to 6 weeks (n=339 Q-Preven and n=61 Umelisa) or for more than 6 weeks (n=76 Q-Preven and n=309 Umelisa). During this period the samples were stored at room temperature inside of a plastic ziplock bag with dissecant. All the results obtained for DBS were compared with the sorologic status of the panel samples. The average monthly local moisture have been observed during the period of storage of the samples (Fig.1)<br />Table 1 – Panel HIV 1 & 2 of blood samples collected on filter paperSampleQ-PrevenUmelisaPositive168140Negative247230Total415370 Picture 1 – Monthly average of maximum and minimum relative moisture recorded into the storage place of the samples panel.<br />RESULTS AND DISCUSSION<br />The results were favorable to the method of diagnosis involving dry blood collected on filter paper. None of the samples showed an indetermined result in the tests Umelisa (Tab.2) and Q-Preven (Tab.3) The two results false-positive (samples 26N and 204N) and Q-Preven (Tab.4), when submitted to a triple repetition, showed concordant results, showing a specificity of 100% in one repeated test. The test Umelisa HIV 1 and 2 (Tab.4) showed a result false-positive (sample 122N) and one false negative (sample 47P). Both the results kept discordant when repeated in triplicate. A superior sensibility has been shown on the tests Q-Preven in relation to Umelisa when observing the result of the test of final point of detection for dilution in series in a same sample, for both the tests.<br /> Table 2. Result obtained with panel of samples Table 3. Result obtained with panel of samples <br /> tested for kit Umisa HIV 1 and 2 Recombinant tsted for kit Q-Prevent HIV 1 and 2 - DBS<br />StorageNegativePositiveTotalStorageNegativePositiveTotal◄ 6 weeks303161◄ 6 weeks204135339► 6 weeks200109309 ►6 weeks41 35 76total230140370245170415<br /> Table 4. Performance of tests anti-HIV on samples panel<br />TESTS Q-Preven◄ 6 weeks ► 6 weeks UMALISA◄ 6 weeks ► 6 weeksFalse positive2 00 1False negative0 00 1Sensibility100% 100% 100% 99.5%Specificity99% 100%100% 99,1%VPP1 11 0,99VPN0,98 11 0,99<br /> CONCLUSIONS<br />The two evaluated tests of antibodies detection showed satisfactory results. Both of them showed qualification for being applied on samples diagnosis of whole dry blood, when employed in an algorythm of tests following the patterns established by the Ministry of Health.<br /> <br />REFERENCES:<br />CHILD FOOT TEST FOR PREGNANT WOMEN<br />Magazine “Crescer”, Edition 166, September 2007<br /> <br />ASK DR TABORDAEdition 166 – Sept./07 <br />Child foot Test for Pregnant Woman<br />The utilization of this alternative method is always more diffused and it consists in collecting<br /> blood samles of pregnant women and trace infection during prenatal period, so that it enables<br />to reduce de risk of transmitting HIV, syphilis,cytomegalovirus,toxoplasmosis and hepatitis B. <br />The blood is collected with only one prick in the finger – similarly to the process renown as <br />“child foot test” made in new-born children – and stored on filter paper.<br />The method is cheap and it dispenses with qualified professionals for collection, storage and <br />transport. The difficulty for obtaining blood samples is just one of the points that contributes<br />to the high Brazilian transmission of diseases from mother to child. The strategy consecrated <br />all over the world is to obtain prenatal exams in order to identify transmissible diseases but <br />unfortunately this does not attain great part of pregant women. Currently, around 80% of <br />teenagers under 13 years of age have been contaminated during the preganancy or parturition <br />or nursery. A shameful panorama. Several researches confirm the good application of filter<br />paper.<br />This technology has been used at APAE, in Bahia, to trace the HIV in approximately 1.500 <br />pregnant women and the result has been the same as those of traditional tests in 99,86% of <br />the cases.<br />Edition 166 09-2007<br />Wladimir Taboarda is Doctor in Medicine at the Federal University<br />of São Paulo, as also Consultant of the Hospital and Maternity São Camilo in São Paulo<br /> <br /> <br />Rua da Silva de Souza 1, L.G. Borges 1, L.do Amaral Inocêncio 2, D.de Souza 2, L.Motta 1,<br />Universidade de Caxias do Sul – Laboratório de Pesquisas em HIV/AIDS, Clinical Medicine,<br />Ca\xias do Sul, Brazil, 2 Programa Nacional de DST/AIDS, Ministério da Saúde, Brasília, Brazil<br /> <br /> <br />](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primediagnostics-110124001817-phpapp02/75/Prime-diagnostics-1-2048.jpg)