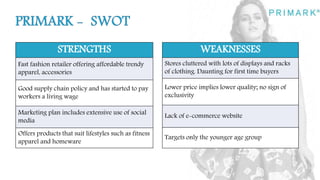
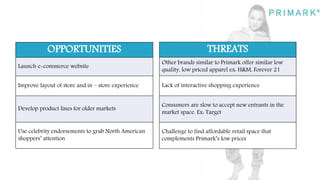
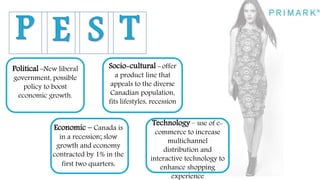
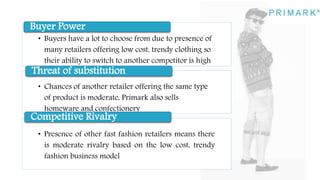
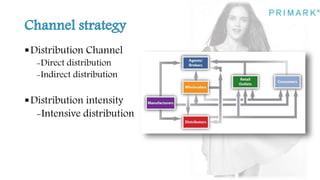
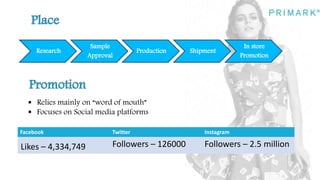
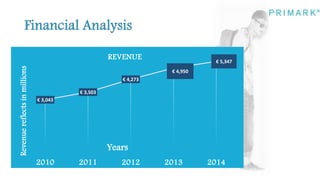
Primark is a fast fashion retailer known for its affordable trendy apparel and accessories. It has expanded successfully since opening its first store in 1969, now operating in several countries. Strengths include a good supply chain and social media marketing. Weaknesses include cluttered stores and lower perceived quality. Opportunities exist in improving the online and in-store shopping experience. Threats include competition from similar retailers. A SWOT analysis is provided.