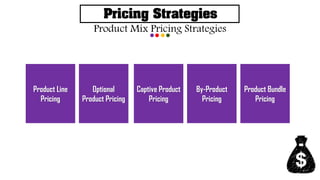
This document discusses pricing strategies and considerations. It defines price as the amount charged for a product or service. Major pricing strategies discussed include customer value-based pricing, cost-based pricing, good-value pricing, value-added pricing, competition-based pricing, and market skimming versus market penetration pricing for new products. Both internal factors like costs and external factors like competitors' prices and customer perceptions must be considered when setting prices.