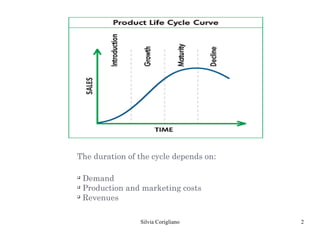
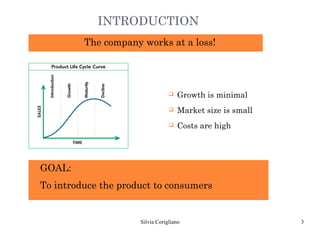
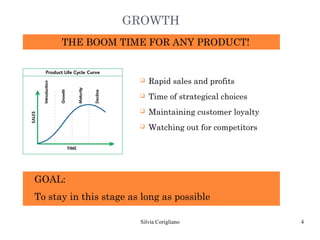
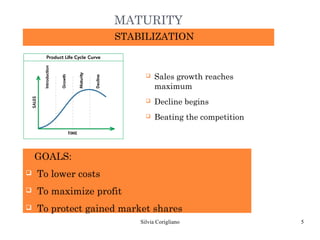
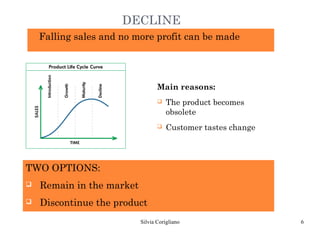
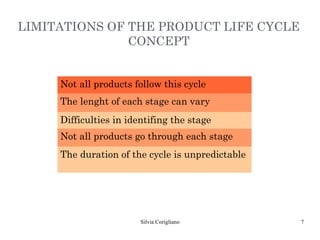
The document outlines Raymond Vernon's product life cycle theory, which describes the typical stages a product goes through: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. The duration of each stage depends on demand, production costs, and revenues. During introduction, the company operates at a loss due to small market size and high costs. The growth stage sees rapid sales and profits increases. In maturity, sales reach their maximum but decline begins. During decline, the product becomes obsolete or tastes change, leading companies to either remain in the market or discontinue the product. However, not all products follow the exact stages or timeline.