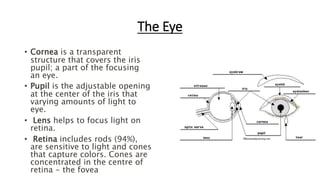
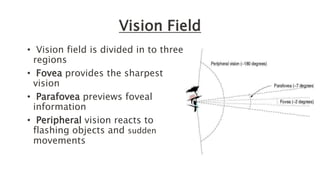
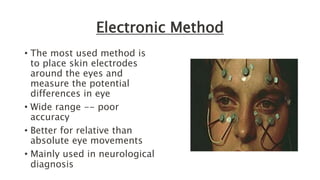
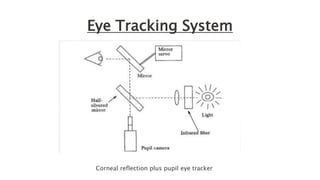
Eye movement-based human-computer interaction techniques allow computers to passively monitor users' eye movements to understand where their attention is focused without requiring explicit commands. The document discusses current eye tracking methods like electronic, mechanical, and optical/video techniques, how the eye works, applications like usability testing and medical diagnosis, advantages like speed and lack of training needed, and limitations like equipment expense.