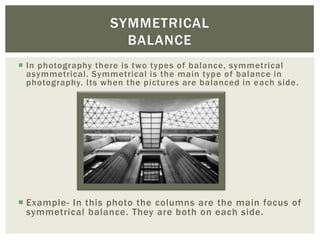
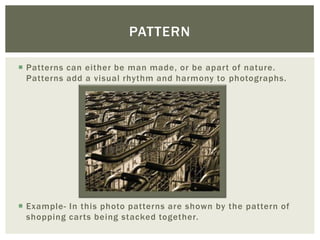
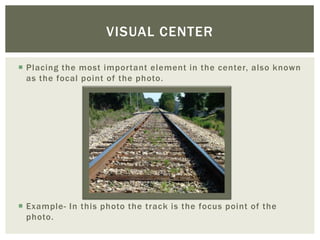
This document discusses key principles of photography including shape and form, leading lines, texture, color, symmetrical and asymmetrical balance, gradation, repetition, pattern, contrast, dominance, proportion, unity, negative space, rule of thirds, and visual center. Each principle is defined and an example photo is provided to illustrate it.