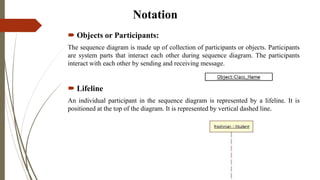
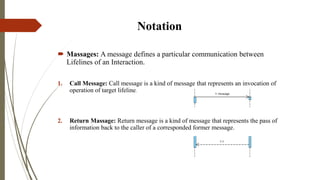
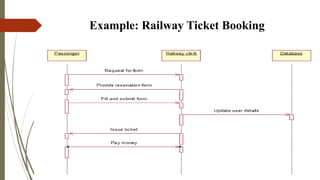
The presentation discusses sequence diagrams, which illustrate interactions between objects in a system sequentially. It covers their purpose, notation, and provides examples, highlighting key components like lifelines, activation, and various types of messages. In conclusion, sequence diagrams are valuable for documenting system requirements and designing interaction logic.