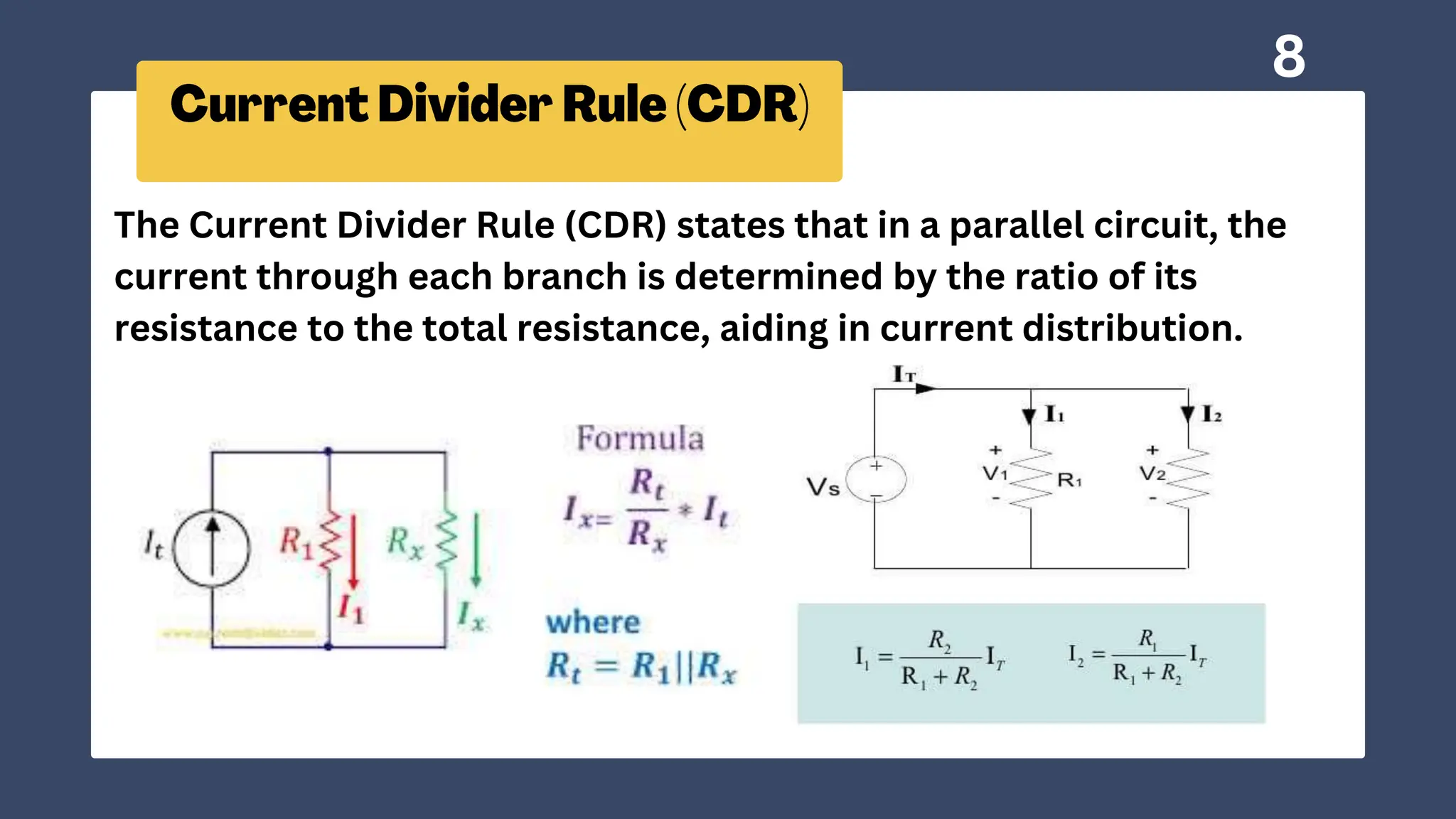
The document discusses essential electrical circuit principles such as Ohm's Law, Kirchhoff's Laws, and the current and voltage divider rules. These principles are crucial for electrical engineers in designing, analyzing, and troubleshooting circuits across various applications. Practical suggestions for testing circuit designs with batteries and lightbulbs are also included.