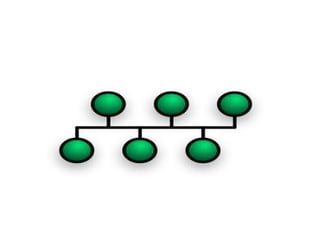
Network topology defines the arrangement of components in a network, encompassing both physical layouts and logical structures. Common types include bus, star, ring, mesh, tree, and hybrid topologies, each with distinct advantages and disadvantages regarding installation, performance, and troubleshooting. Understanding these topologies is crucial for designing effective and reliable networks.