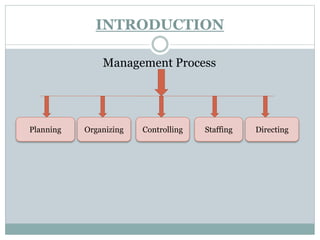
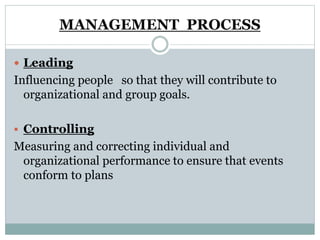
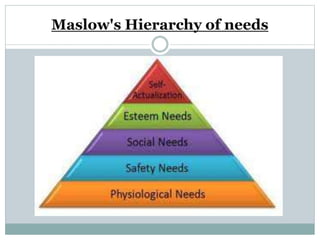
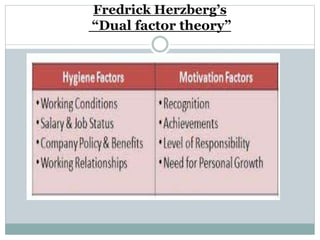
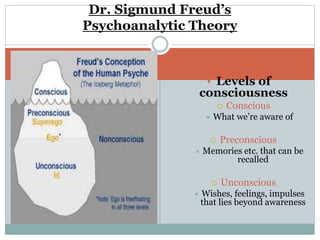
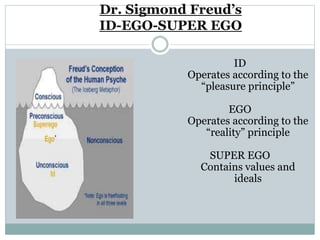
This document discusses management processes and issues at a management institute. It provides an overview of key management processes like planning, organizing, staffing, leading, and controlling. It then describes problems at a specific management institute, including high faculty turnover, unprofessional behavior by the dean, and lack of morale. It analyzes these issues through frameworks like Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's motivator-hygiene theory, and Freudian concepts. It outlines steps that should be taken for organizing, controlling, staffing, directing, and other management functions. The document aims to understand management challenges and apply management theories to a real-world case study.