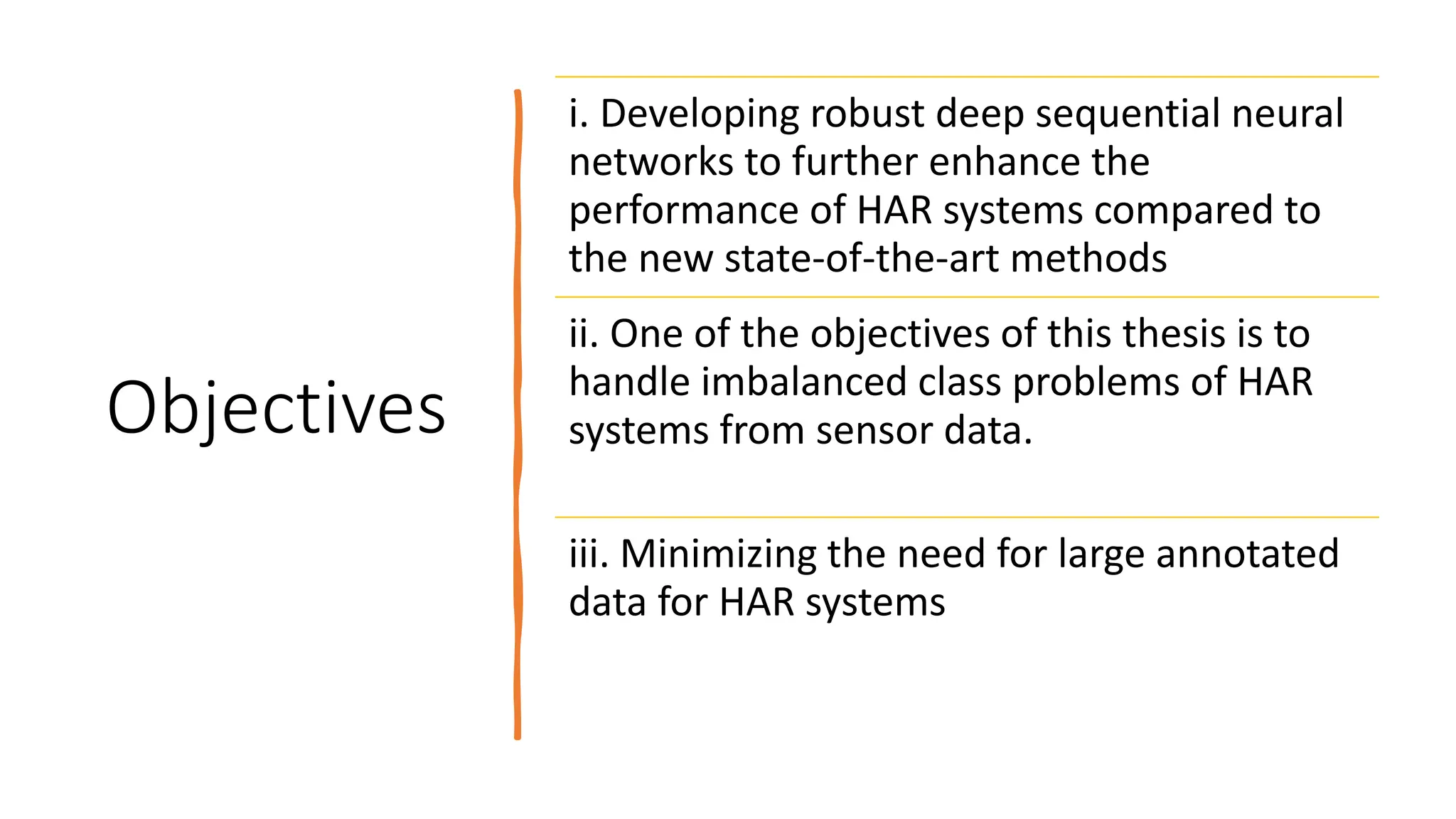
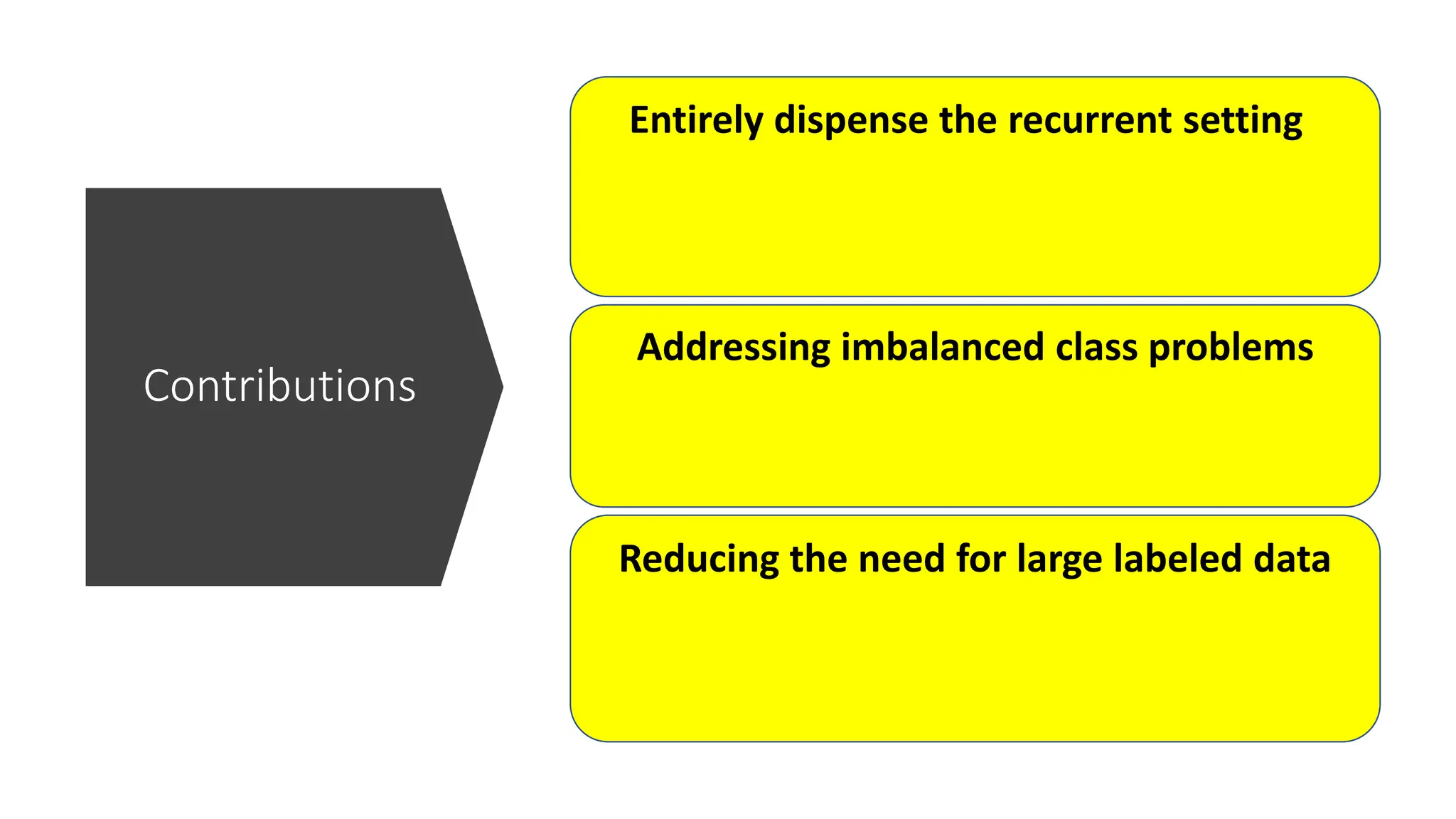
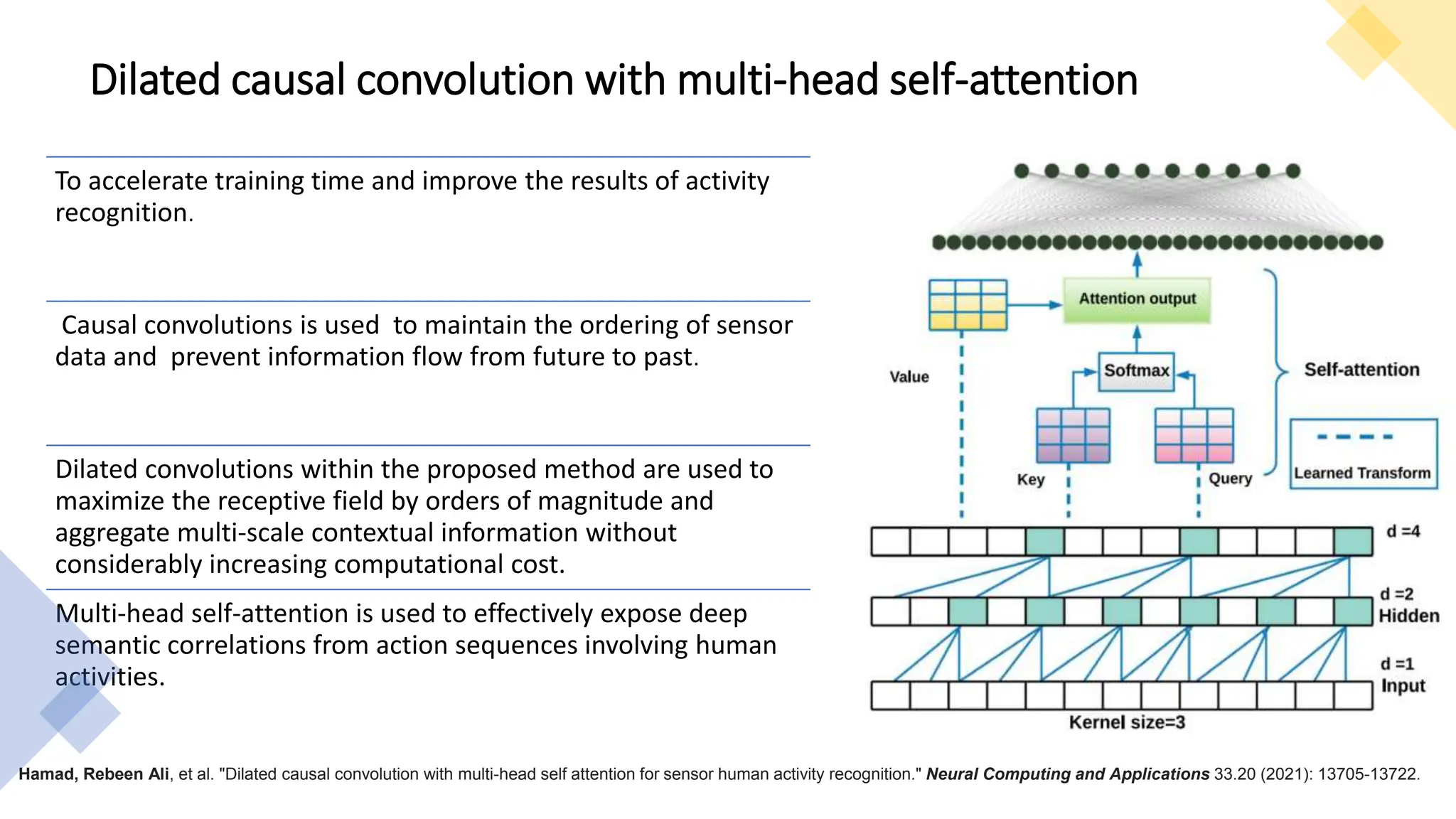
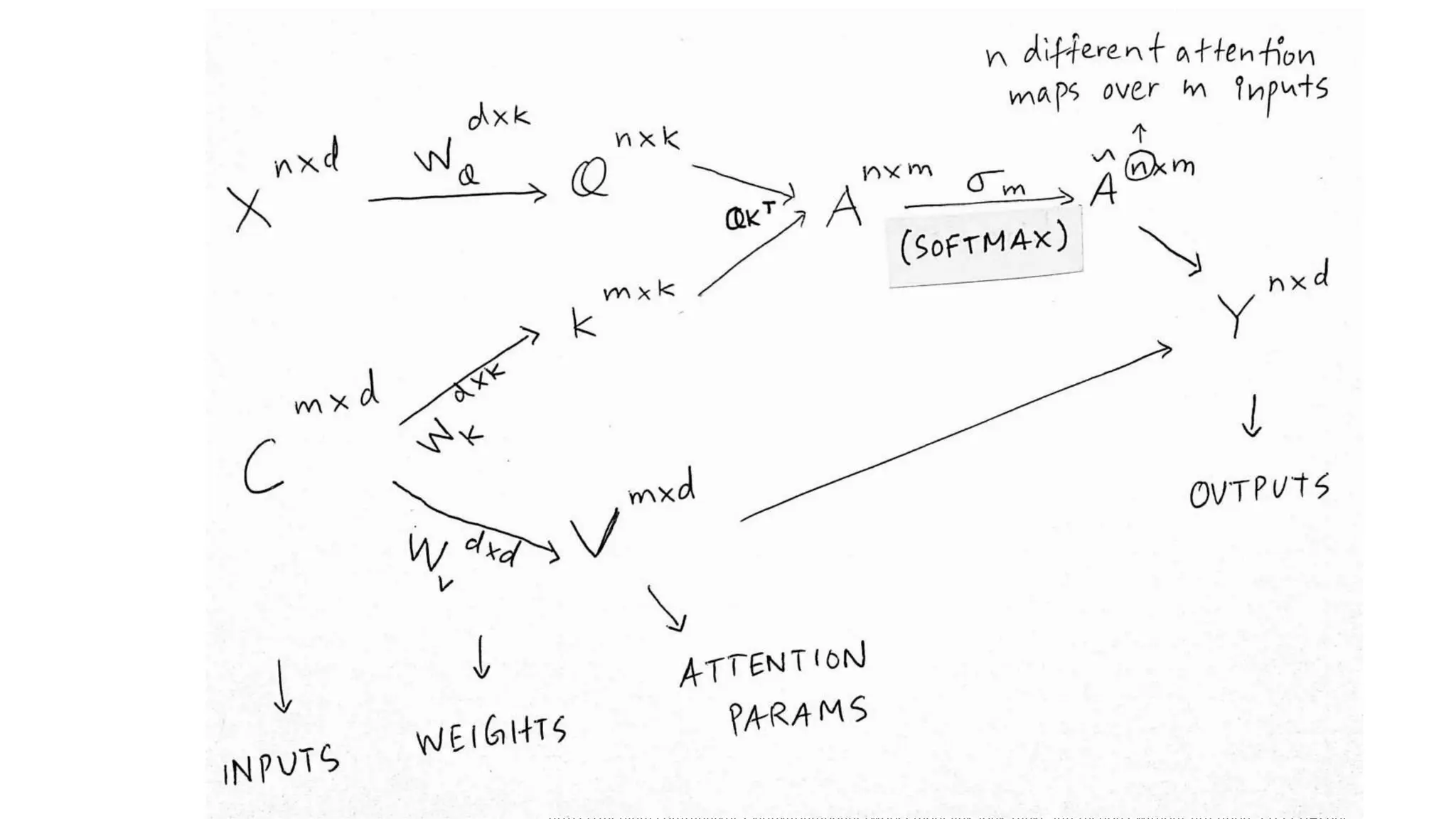
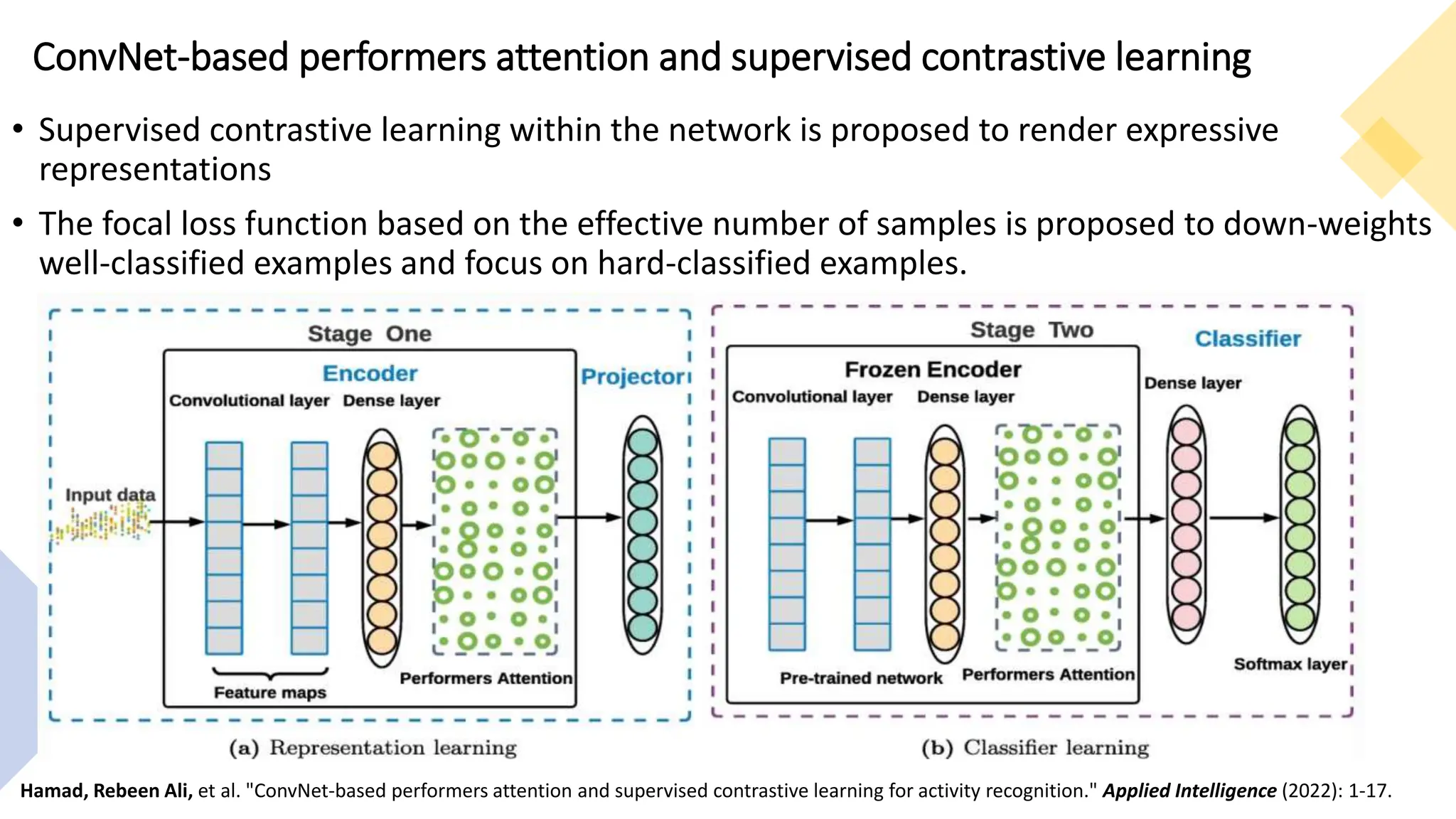
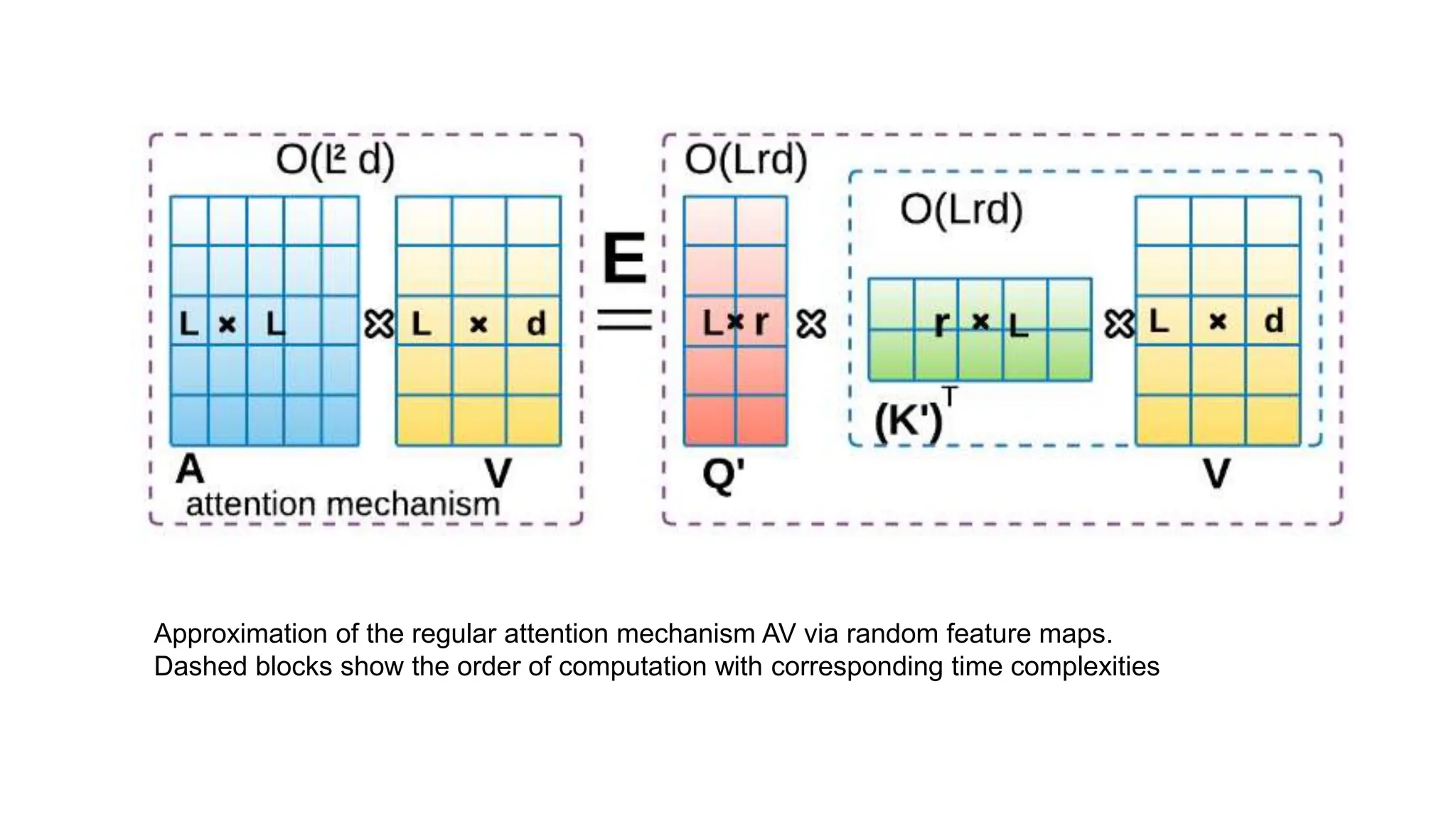
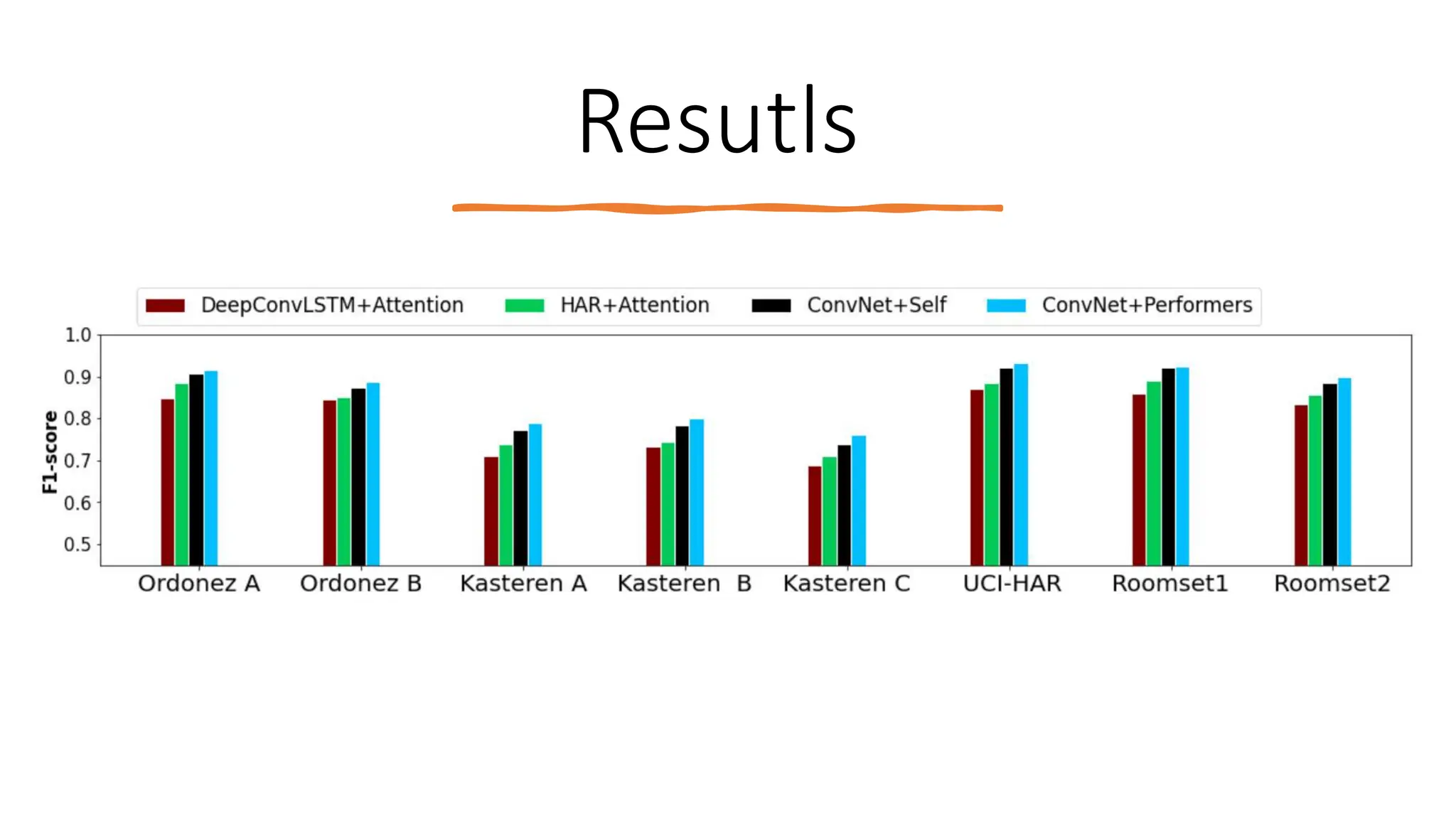
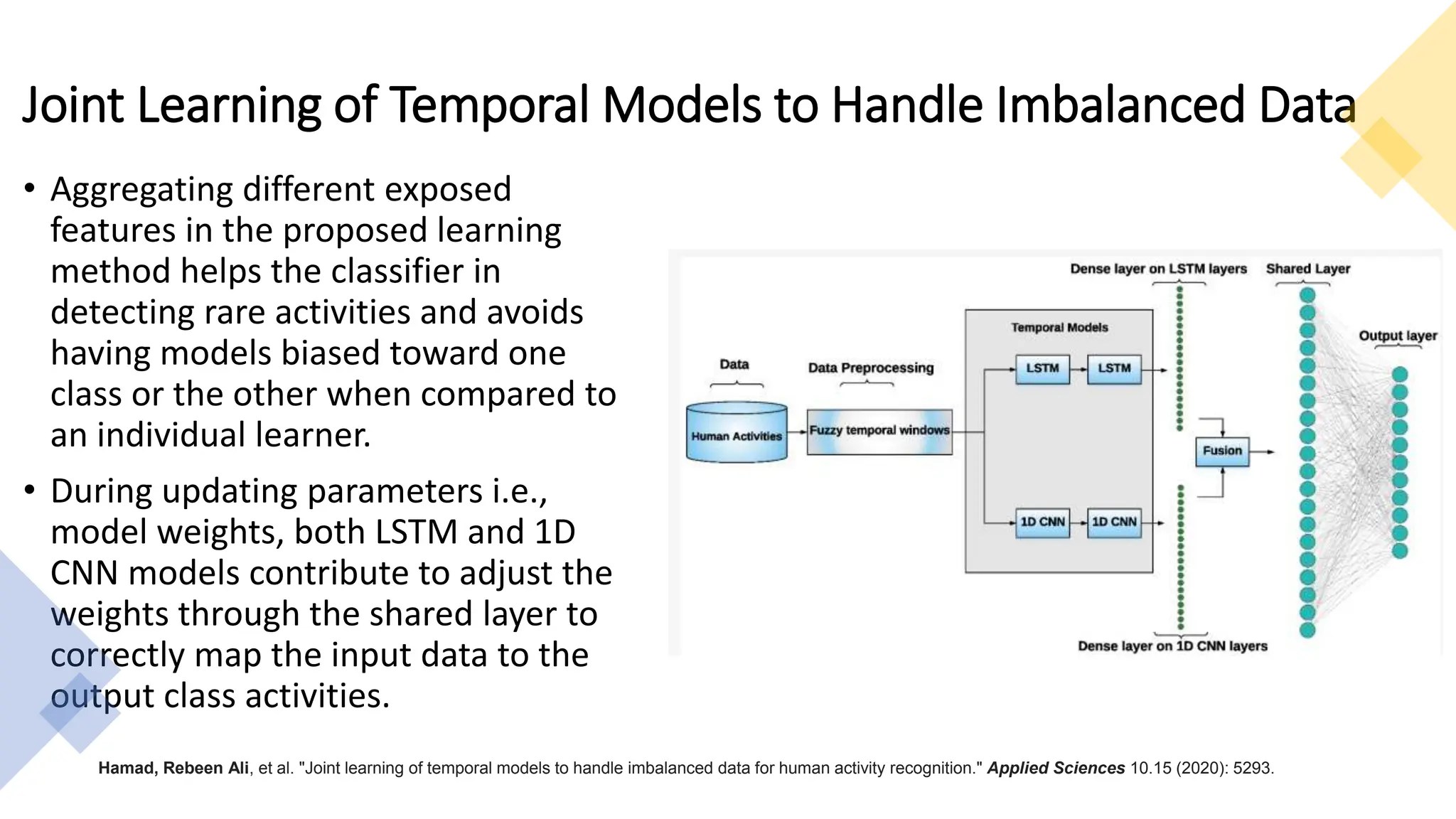
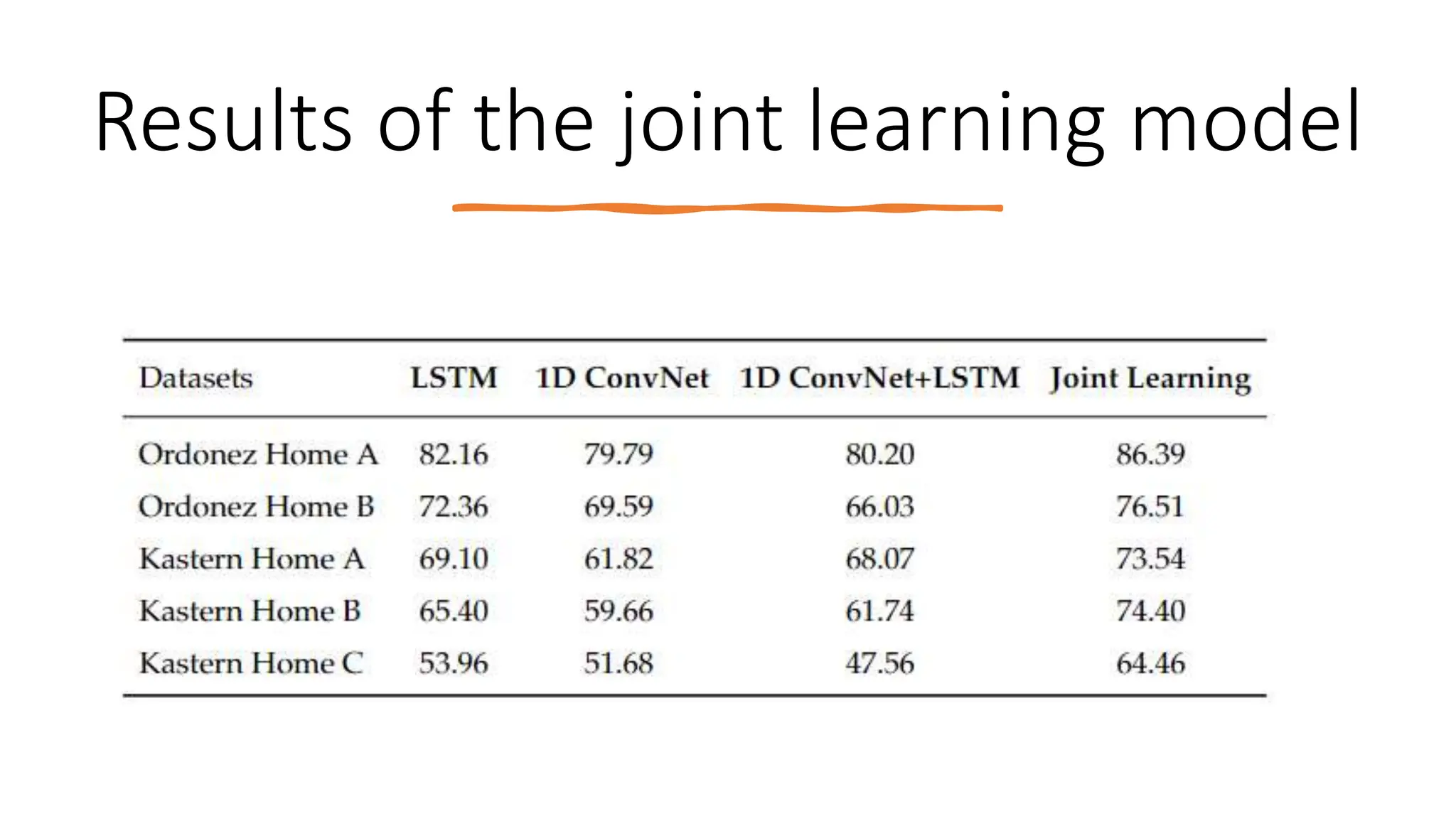
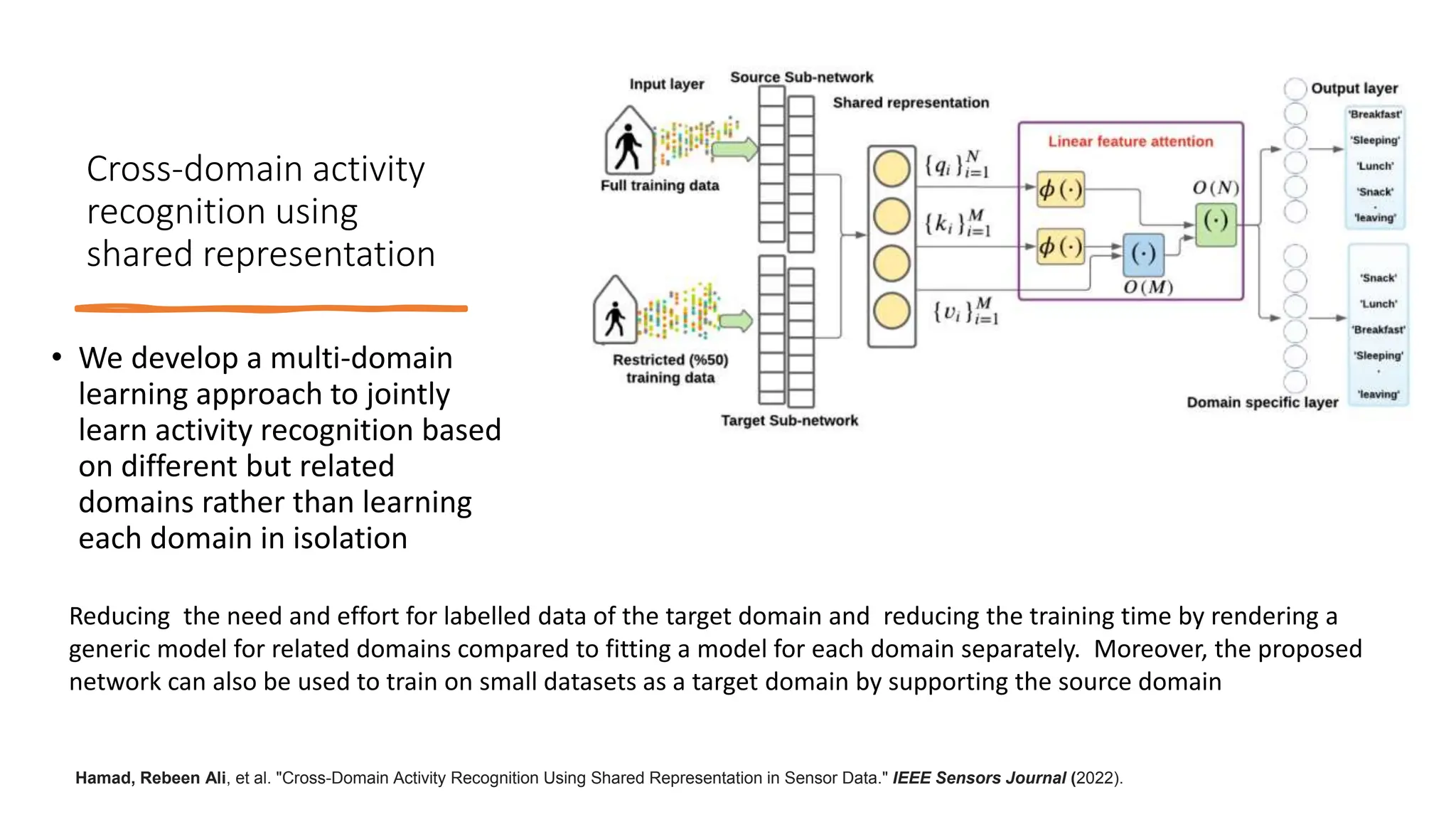
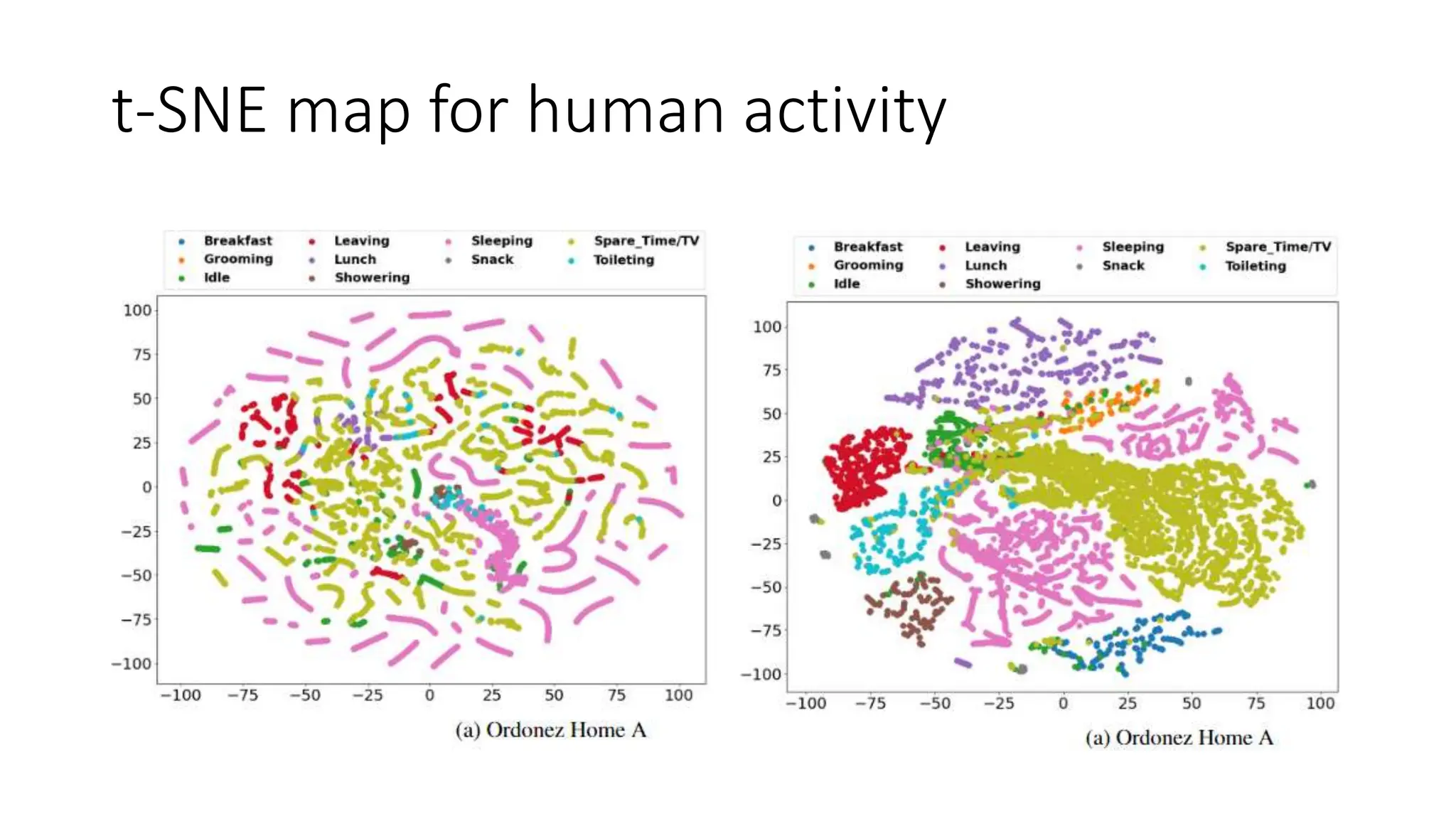
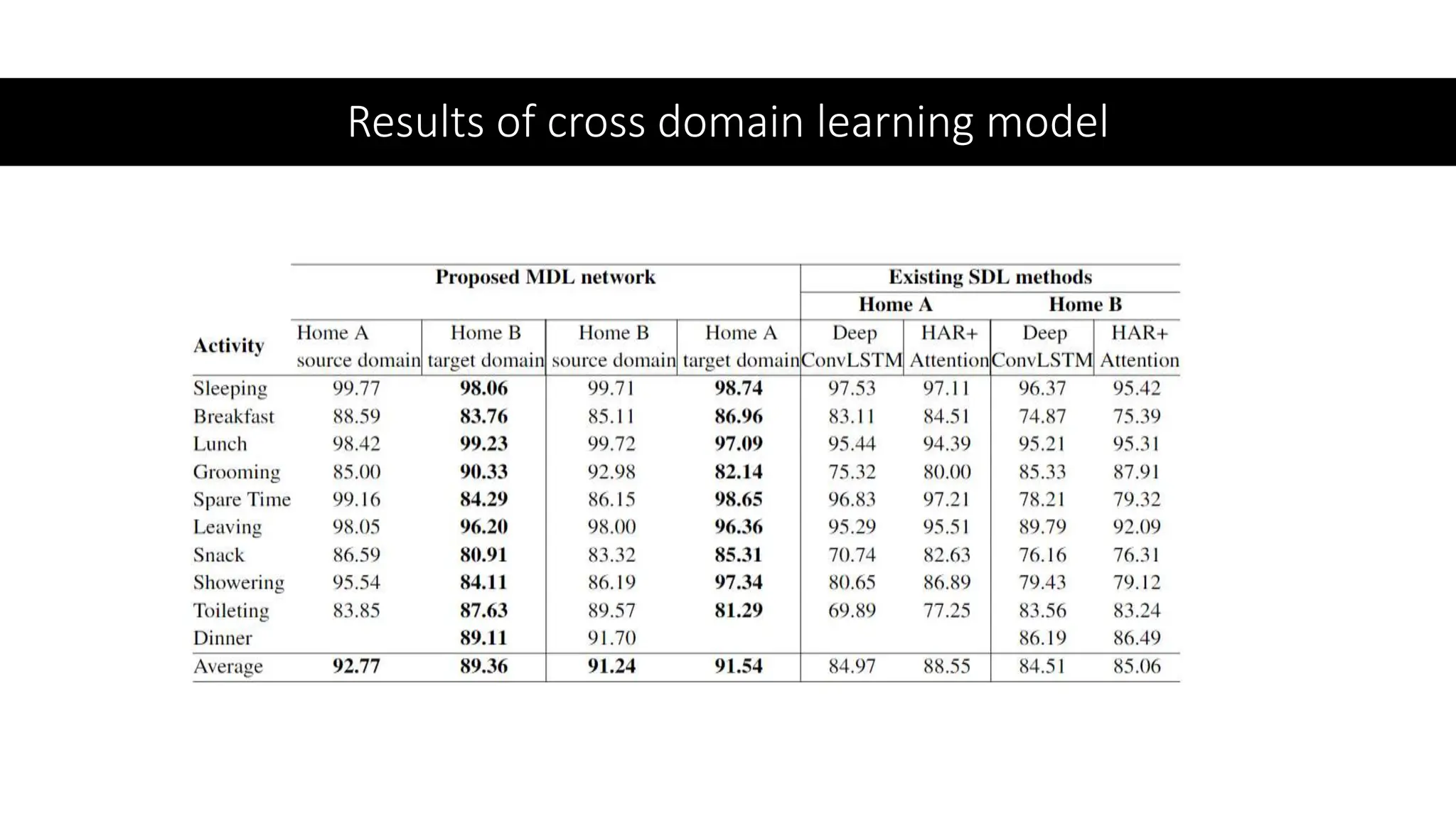
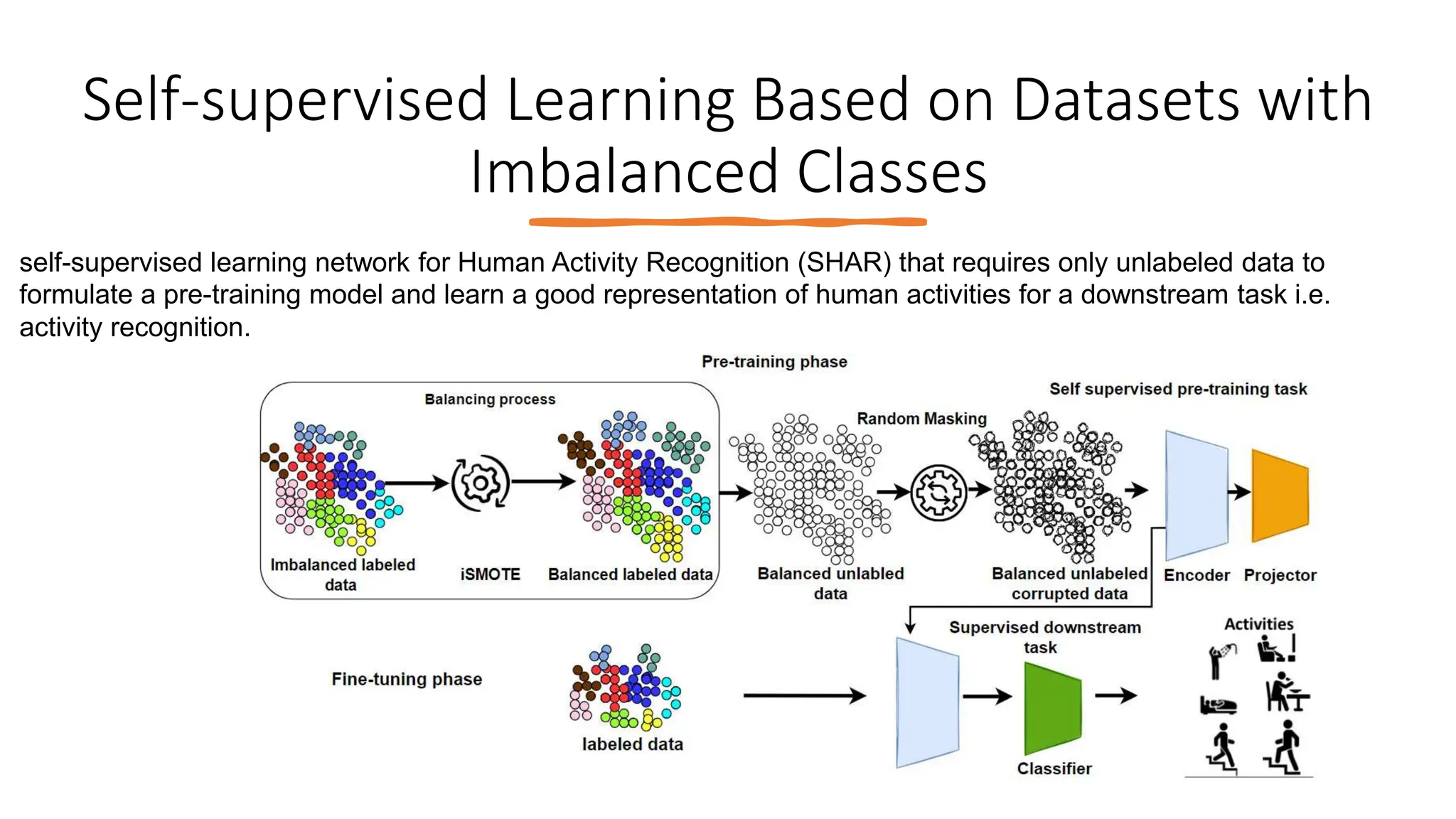
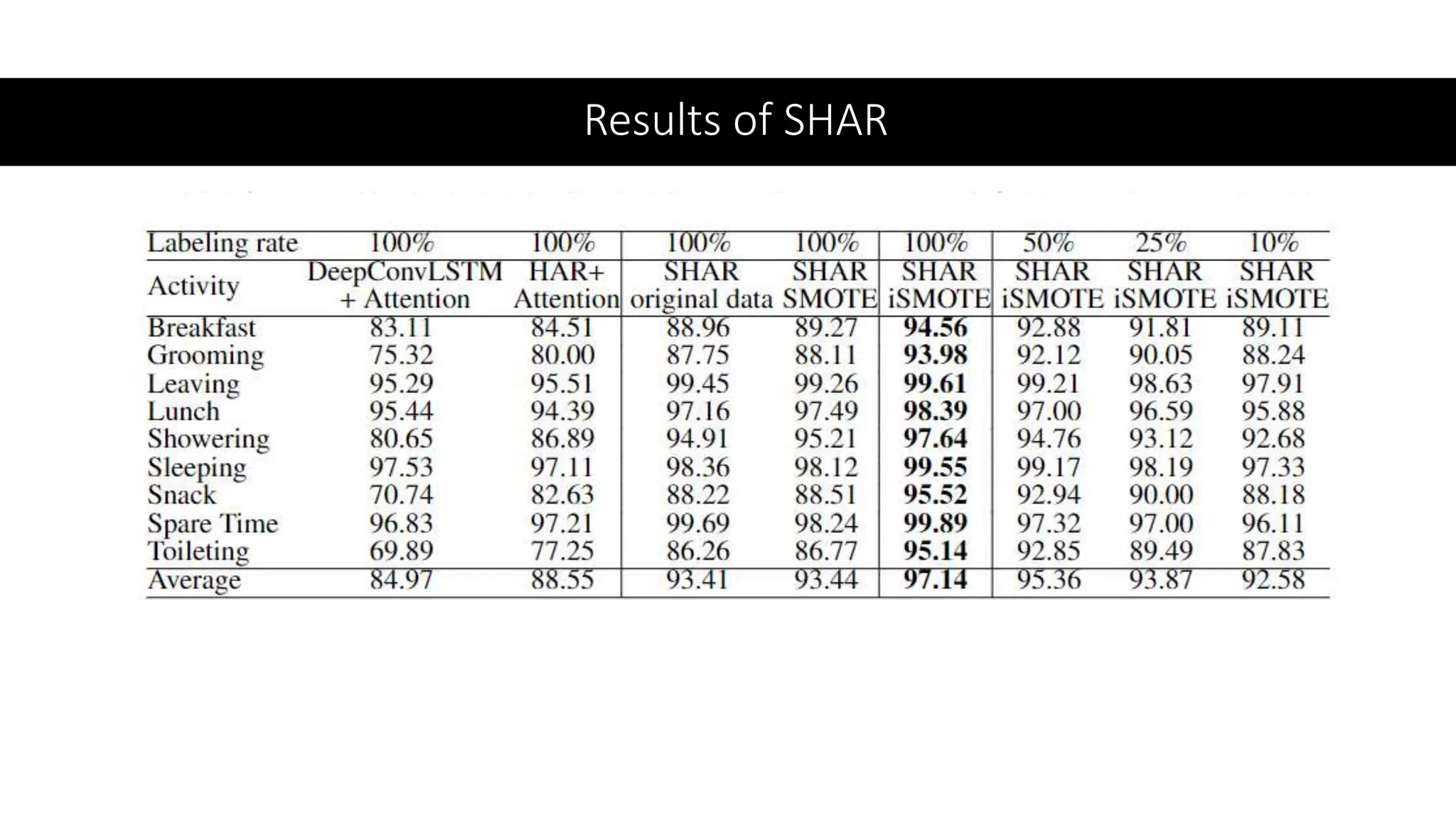
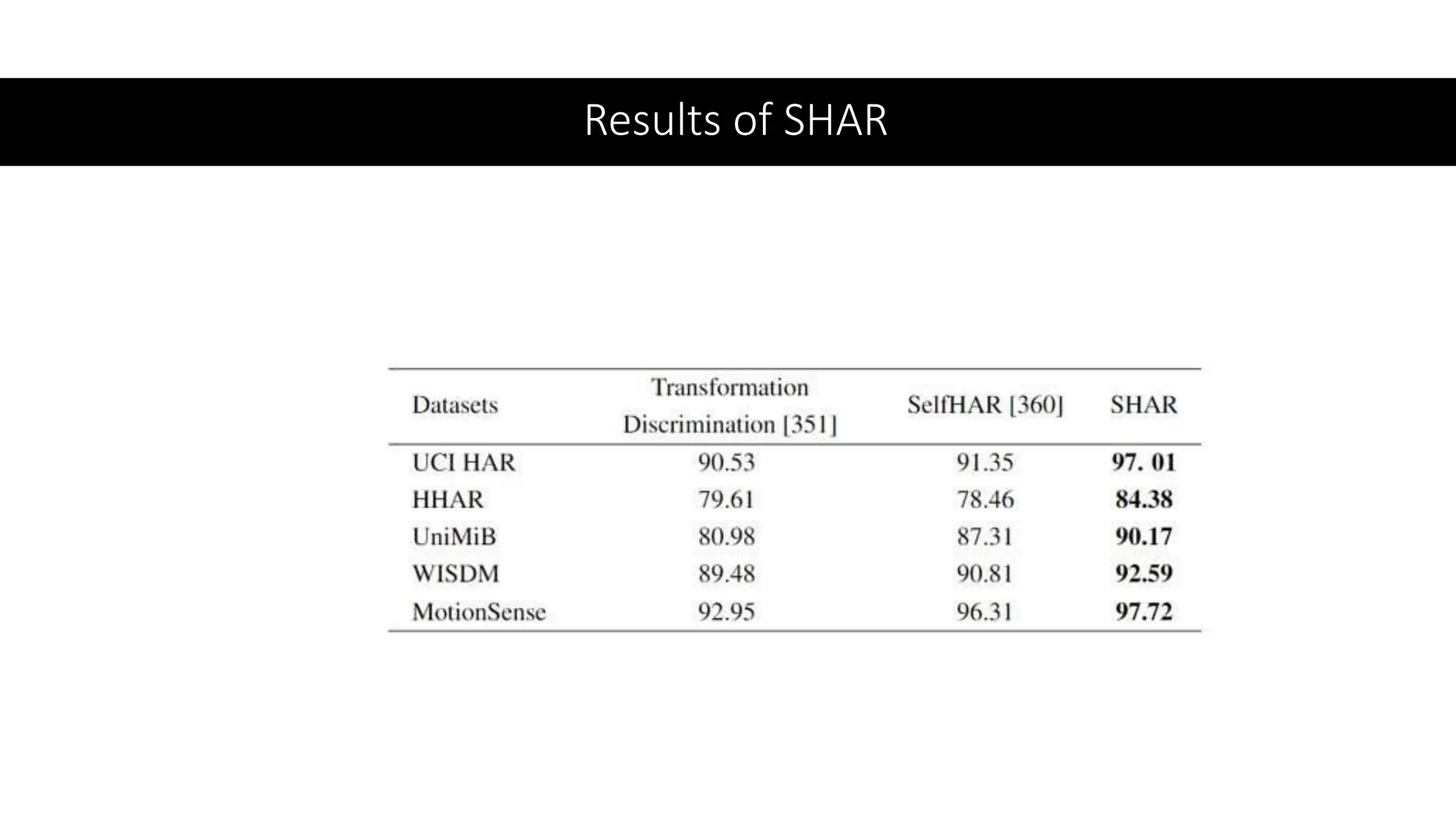
The thesis focuses on enhancing human activity recognition (HAR) through robust deep sequential neural networks, addressing challenges such as accuracy, imbalanced data, and the need for less annotated data. It proposes methods including dilated causal convolution with multi-head self-attention and joint learning for cross-domain activity recognition to improve performance. Future work includes developing hybrid models and better attention mechanisms to recognize complex, multi-user activities.