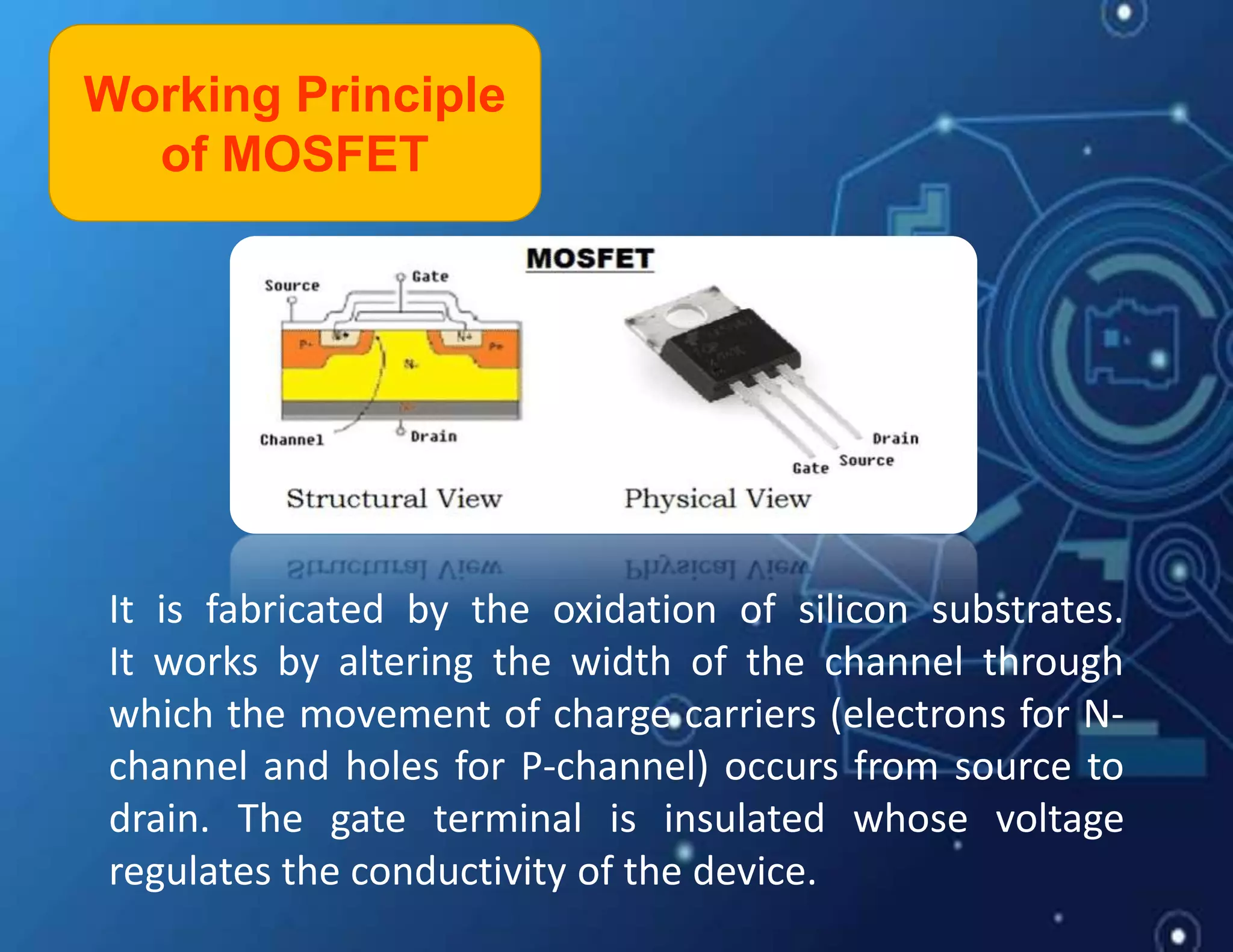
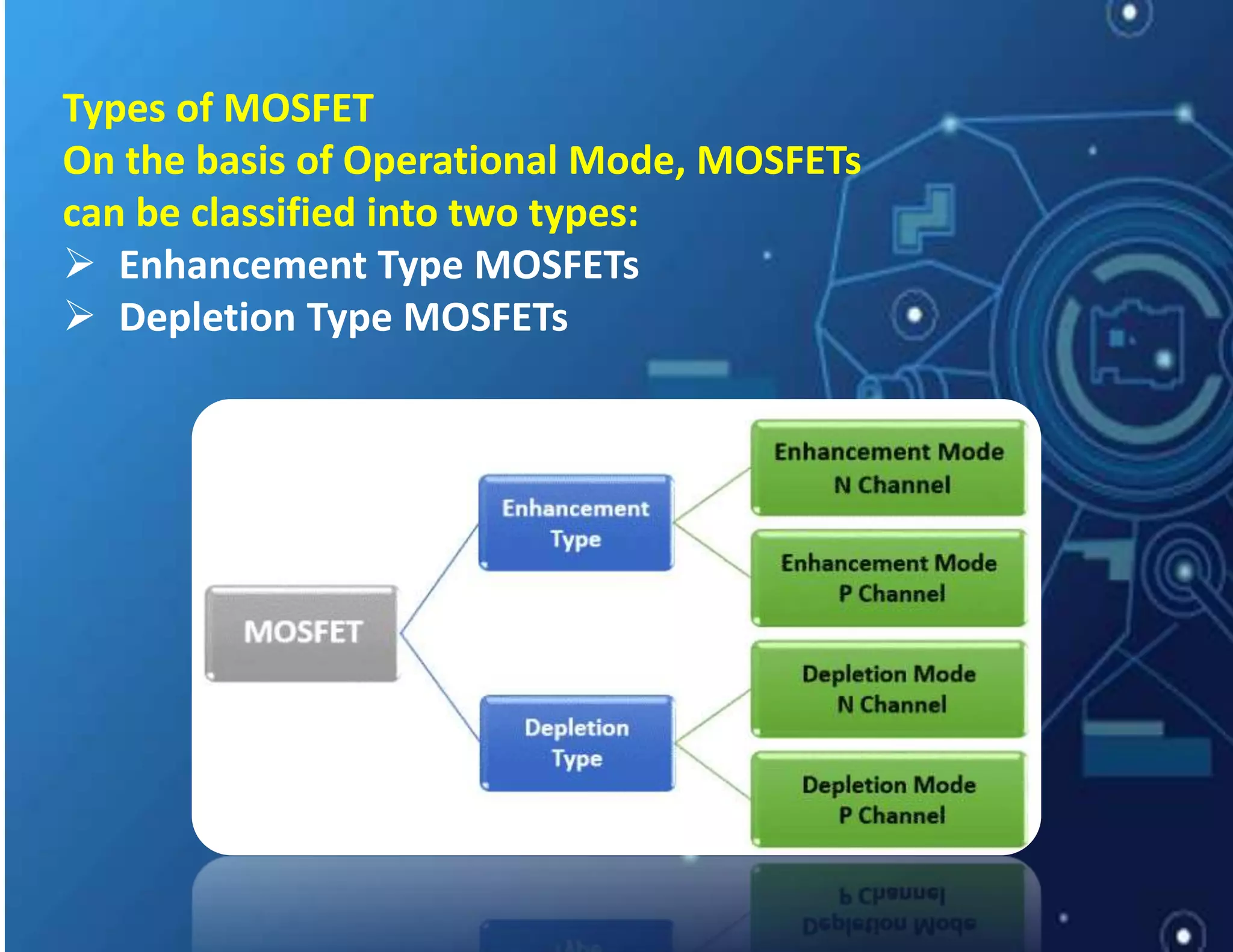
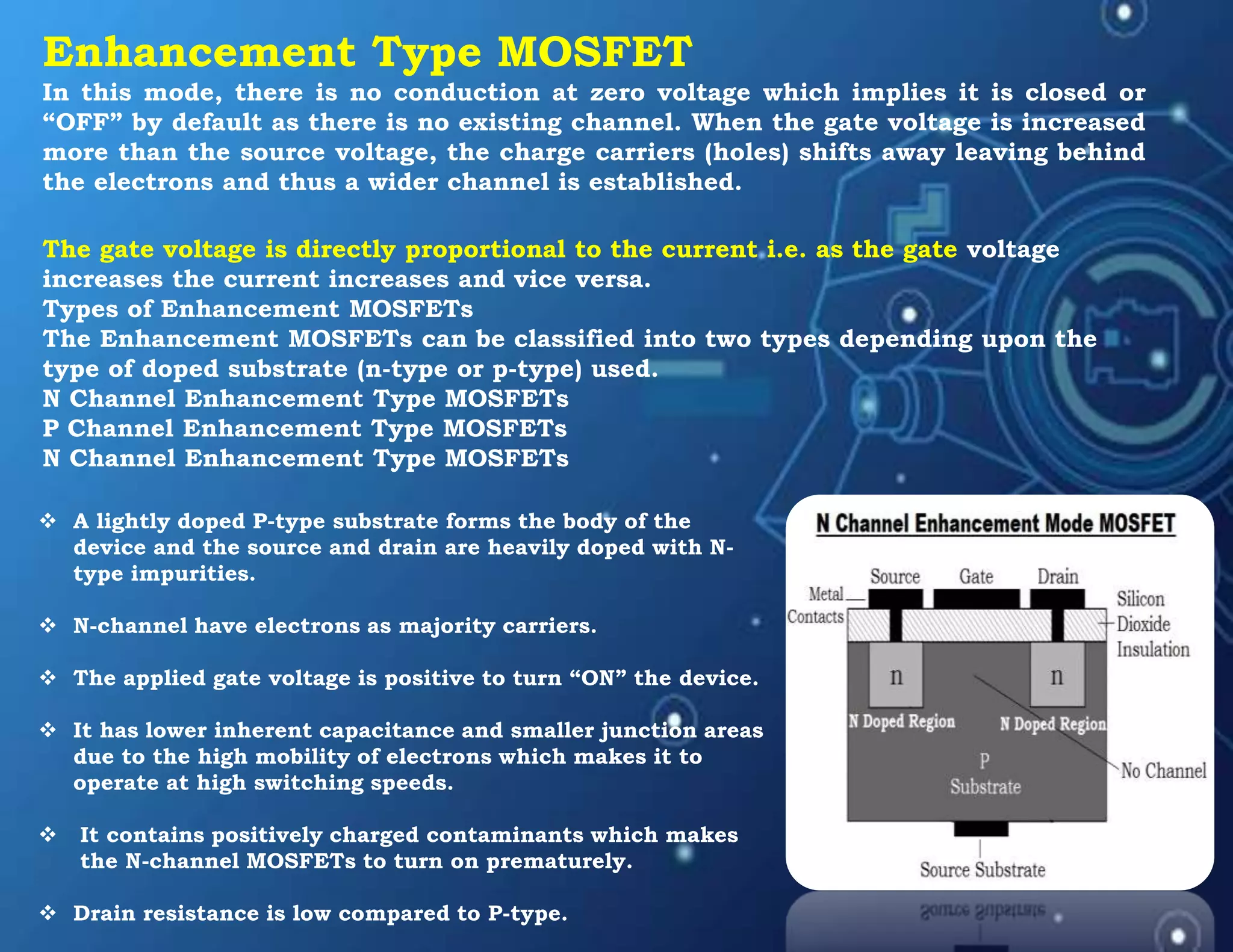
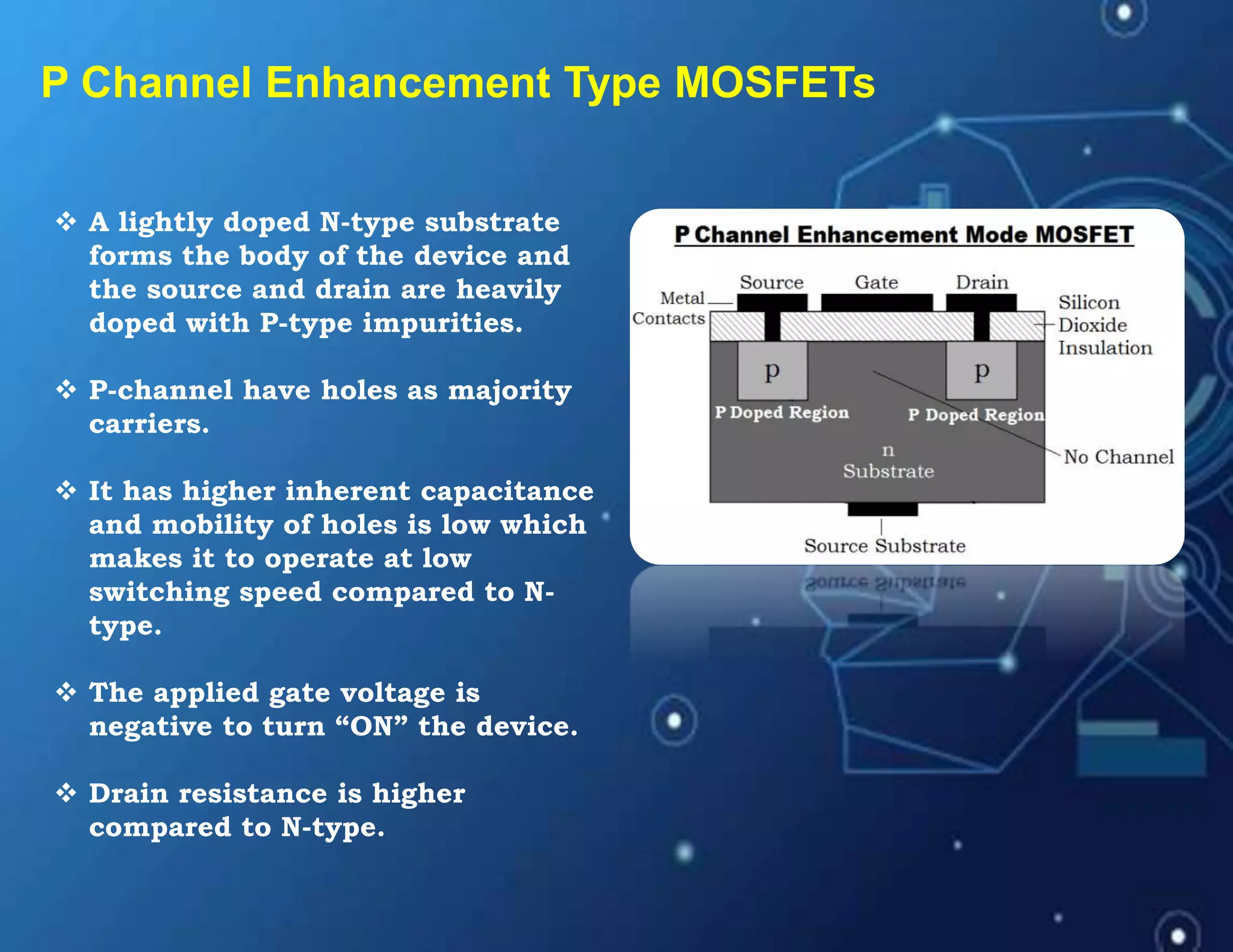
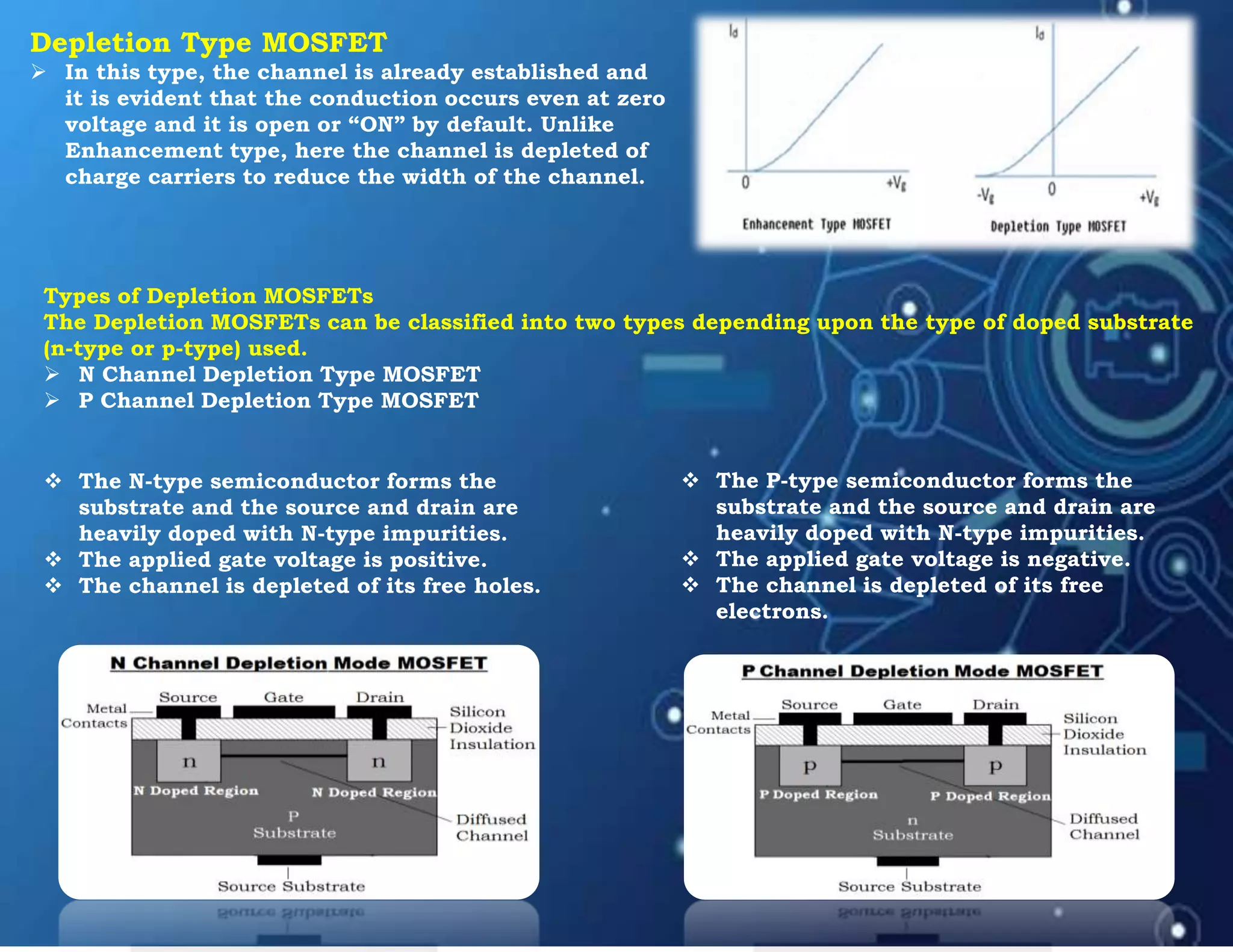
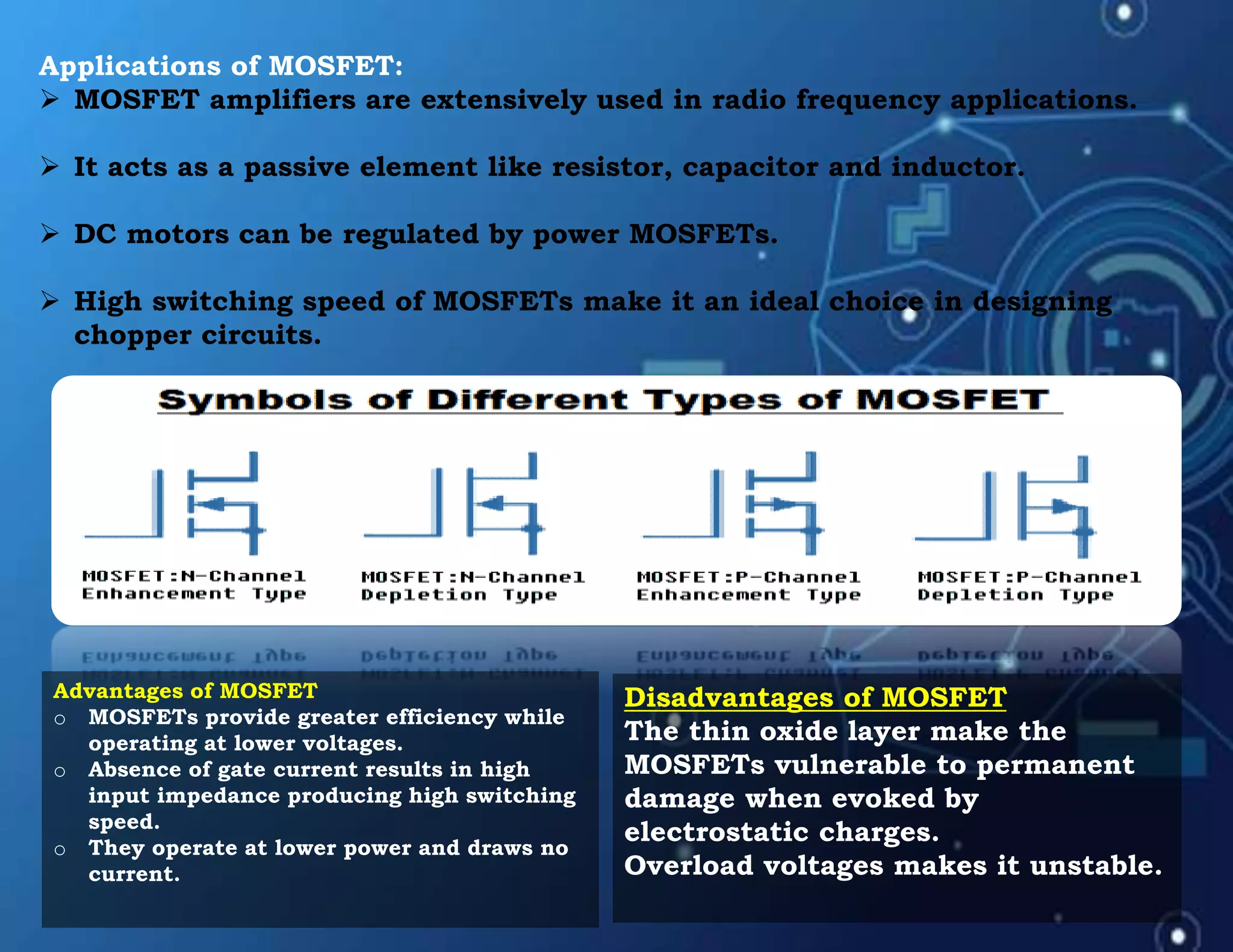
MOSFET stands for Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor. It is a three-terminal device used as an electronic switch or amplifier. MOSFETs work by controlling the width of a channel for charge carriers (electrons or holes) to flow between its source and drain terminals using an electric field established by its gate terminal. There are two main types - enhancement mode and depletion mode - which differ in whether the channel is open or closed with no gate voltage. MOSFETs are widely used in digital integrated circuits and applications like DC motor control due to their high switching speeds, low power consumption, and high input impedance.