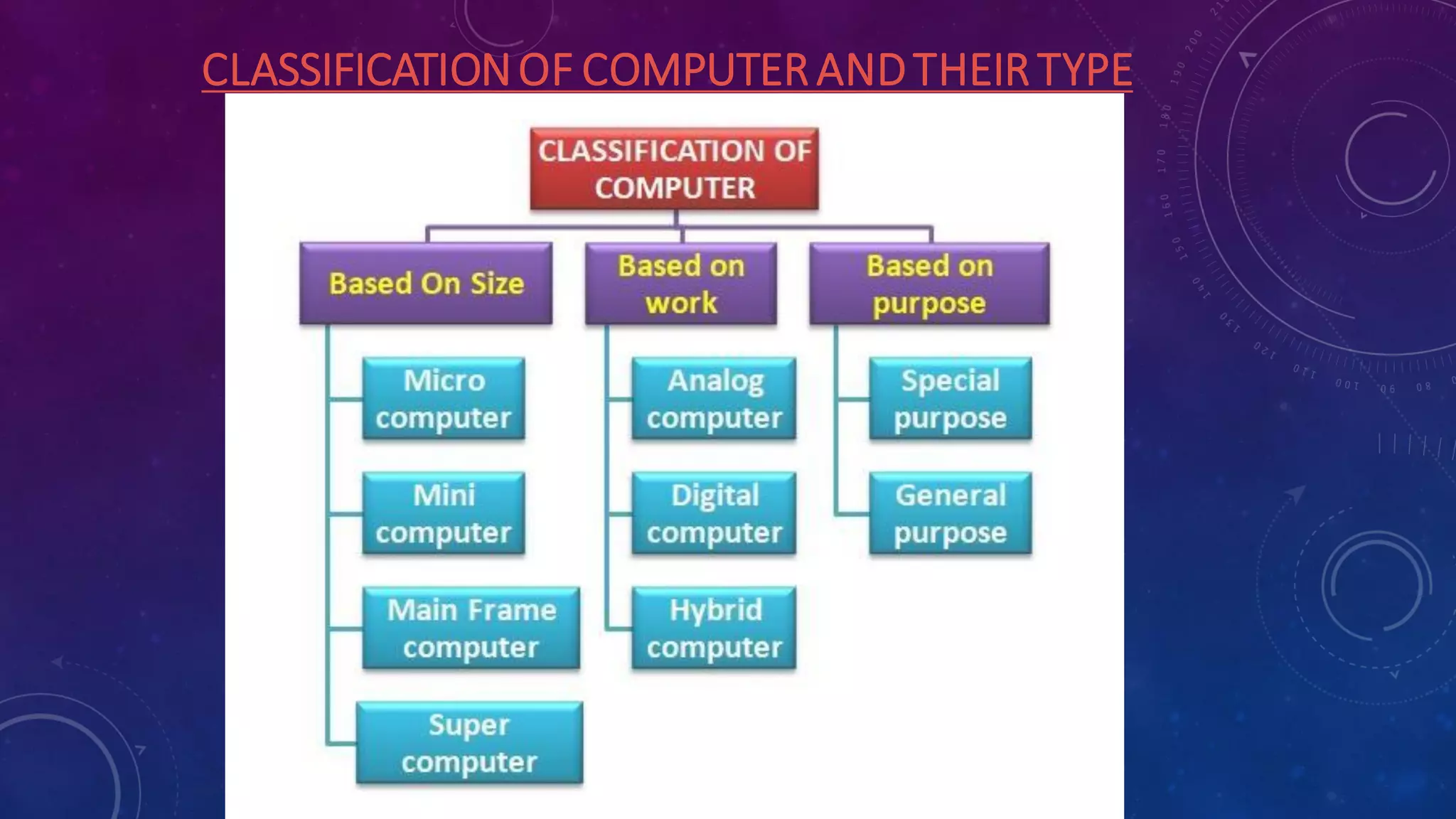
This document classifies computers into different types based on size, work, and purpose. It discusses microcomputers, minicomputers, mainframe computers, and supercomputers as classifications based on size. Based on work, it covers analog computers, digital computers, and hybrid computers. Finally, it describes general purpose computers that can solve a variety of problems by changing programs or instructions, and special purpose computers that are dedicated to solving a single type of problem.