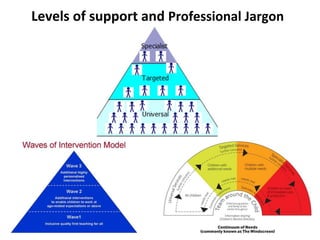
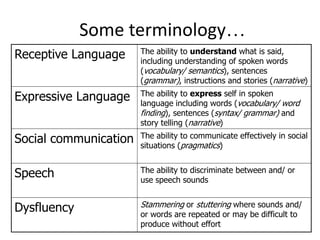
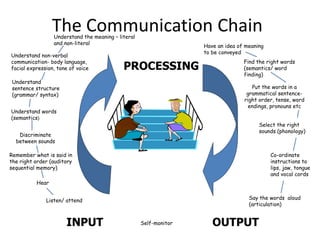
This document provides information about speech, language and communication needs (SLCN) and the roles of professionals who support students with SLCN. It defines terms like receptive language, expressive language, and social communication. Signs of different types of SLCN are outlined. The impact of unidentified SLCN on educational achievement, behavior, and future outcomes is described. Strategies teachers can use to support students with receptive, expressive, speech and social language needs are suggested. The importance of allowing mistakes and providing feedback is emphasized.