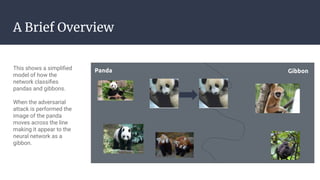
This document discusses adversarial image attacks against machine learning models. It explains that adversarial attacks involve purposefully manipulating input data to cause machine learning models to make incorrect predictions. One example shown is adding imperceptible noise to an image of a panda to cause the model to misclassify it as a gibbon. The document also discusses Nightshade, a defensive technique that adds noise to training data to make models more robust against adversarial attacks. Real-world security issues from adversarial attacks are noted.


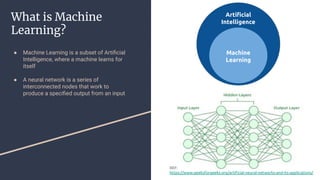
![How Machine
Learning Works
REF: Confidence-Guided-Open-World [Li et al]
● A neural network is trained on
labelled data and can practice
classifying the image with feedback
● It is then tested against images it
hasn’t seen before
● If the neural network is trained on the
training data too much it will start to
overfit, and when given test data will
not necessarily give accurate results](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adversarialimageattacks-240405100419-3c83dce4/85/Presentation-about-adversarial-image-attacks-4-320.jpg)
![What is an Adversarial
Image Attack?
● Purposefully causing a ML model to produce mispredictions
when identifying data
● There are 3 main fields:
○ Image recognition
○ Natural language
○ Auditory processing
● As a field it is relatively new as it has only been around since
2013
REF:
Making an Invisibility Cloak: Real World Adversarial Attacks on Object
Detectors [Wu et al]
https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6199](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adversarialimageattacks-240405100419-3c83dce4/85/Presentation-about-adversarial-image-attacks-5-320.jpg)




![Real World Example: Stop Sign
REF: Robust Physical-World Attacks on
Deep Learning Models [Ekyholt et al]
Researchers in Michigan placed
small pieces of tape on this stop
sign which caused the model to
misclassify it as a 45 mph speed
limit sign.
When this technology is used in the
real world it has the potential to go
wrong very drastically.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adversarialimageattacks-240405100419-3c83dce4/85/Presentation-about-adversarial-image-attacks-11-320.jpg)
![Adversarial Examples
REF: Making an Invisibility Cloak: Real World Adversarial Attacks on Object Detectors [Wu et al]
The adversarial attack varies in
effectiveness, due to a variety of
factors, a small rotation or slight
illumination. Can cause the attack to
stop working.
The man is wearing an adversarial
patch as a jumper. This stops him
being recognised by the image
recognition network. However in a
slightly different environment, his is
recognised and identified.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adversarialimageattacks-240405100419-3c83dce4/85/Presentation-about-adversarial-image-attacks-12-320.jpg)




