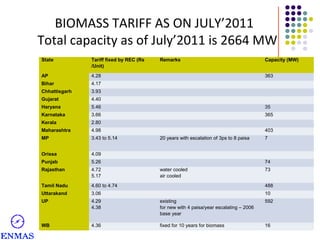
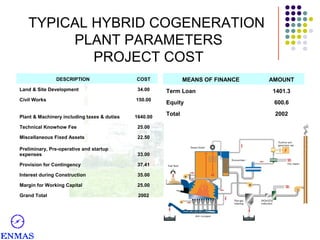
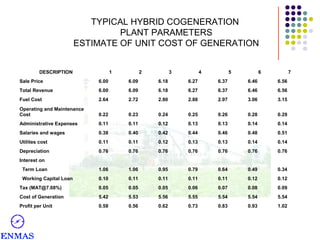
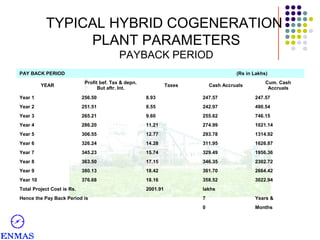
This presentation discusses hybrid cogeneration power plants. It begins by defining cogeneration as the simultaneous generation of electricity and steam. It then discusses the types of industries that can benefit from cogeneration and the advantages it provides in reducing costs compared to using diesel generators. The presentation provides details on typical cogeneration plant components, configurations, costs and financial metrics. It also discusses policy support in India for biomass projects and the viability of napier grass as a fuel. Overall, the presentation provides an overview of hybrid cogeneration plants and makes a proposal for a comprehensive solution to set up a 3 MW plant.