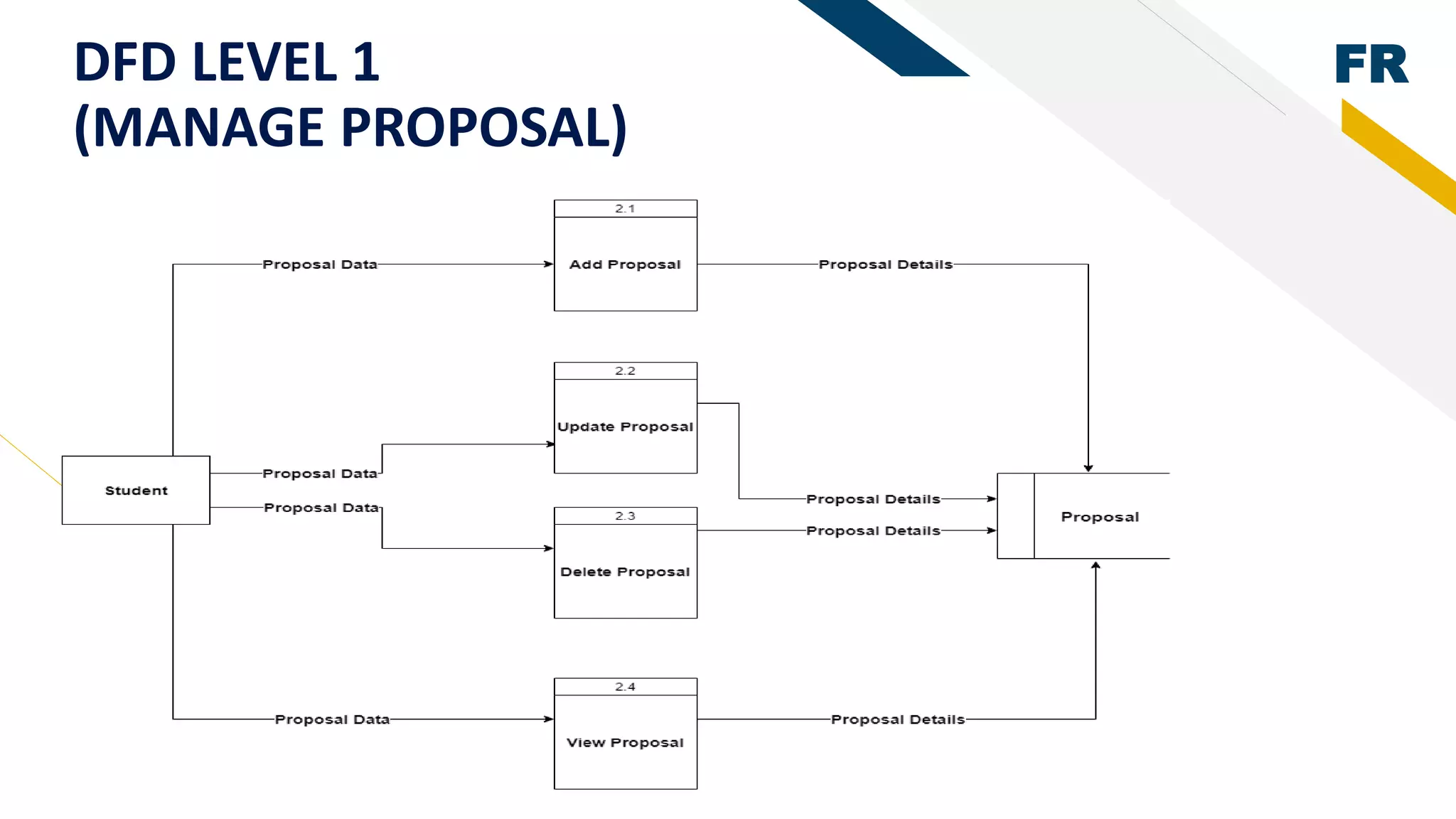
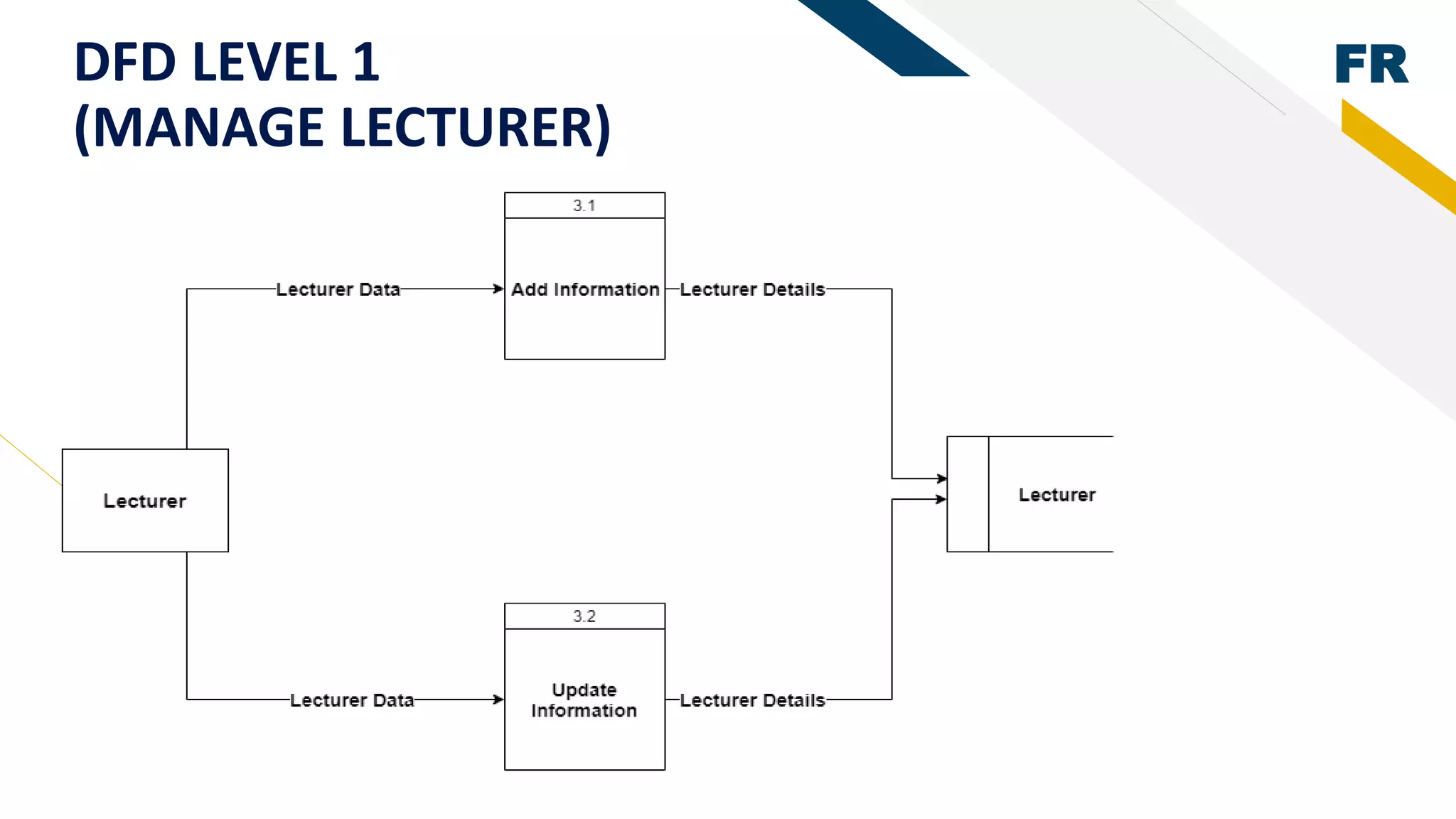
1. The document describes a student management system project that uses rapid prototyping and the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) technique.
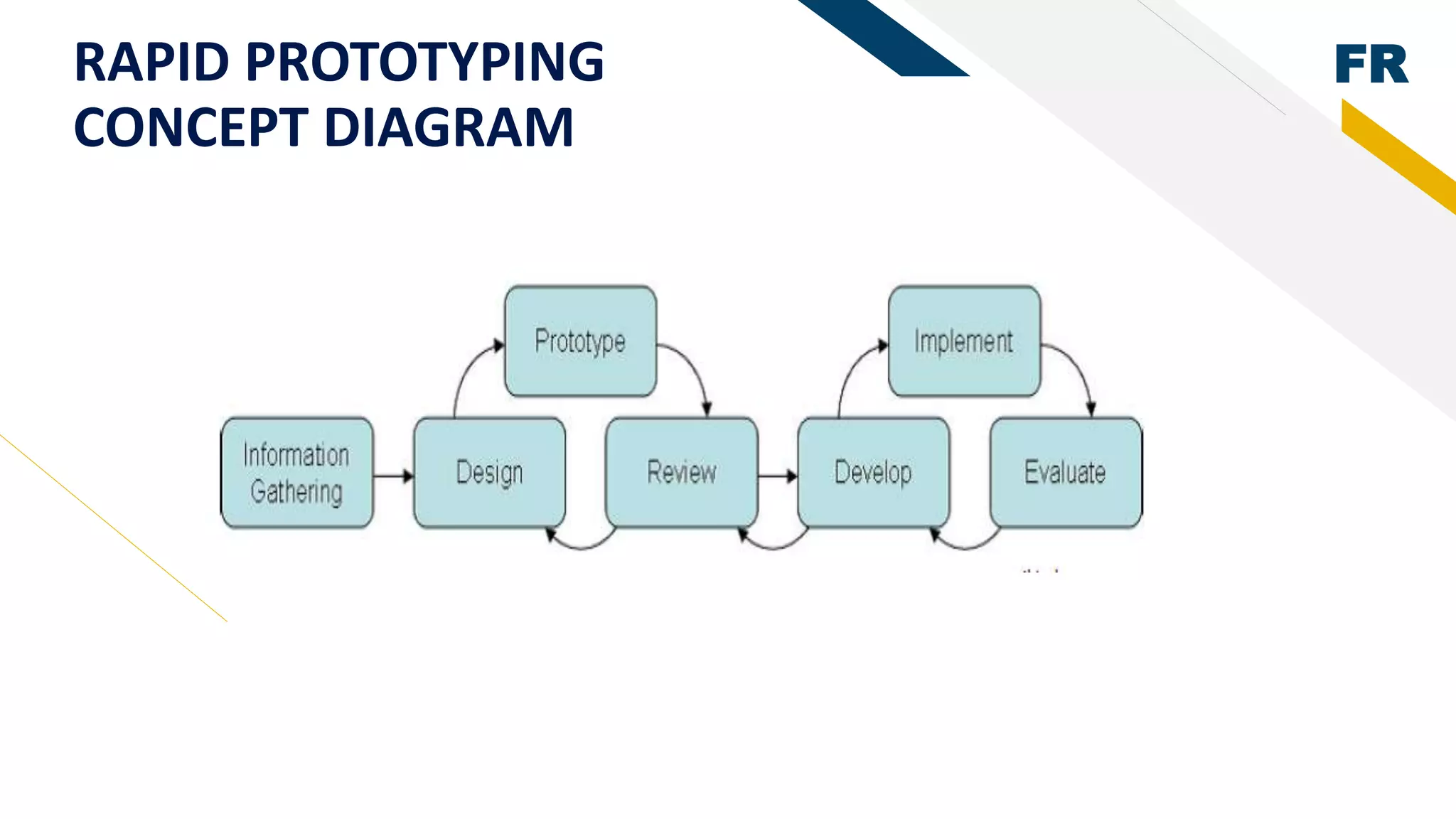
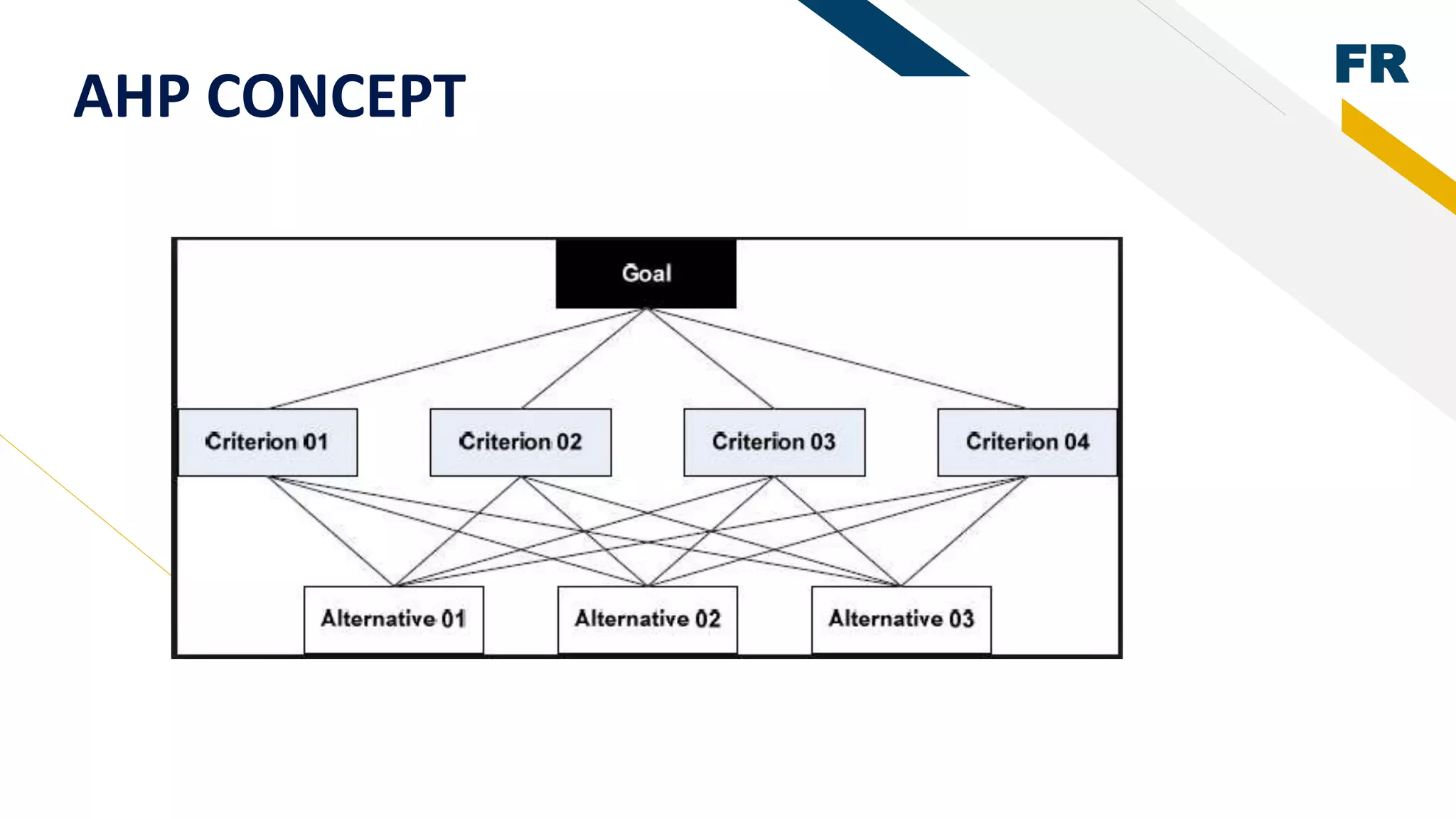
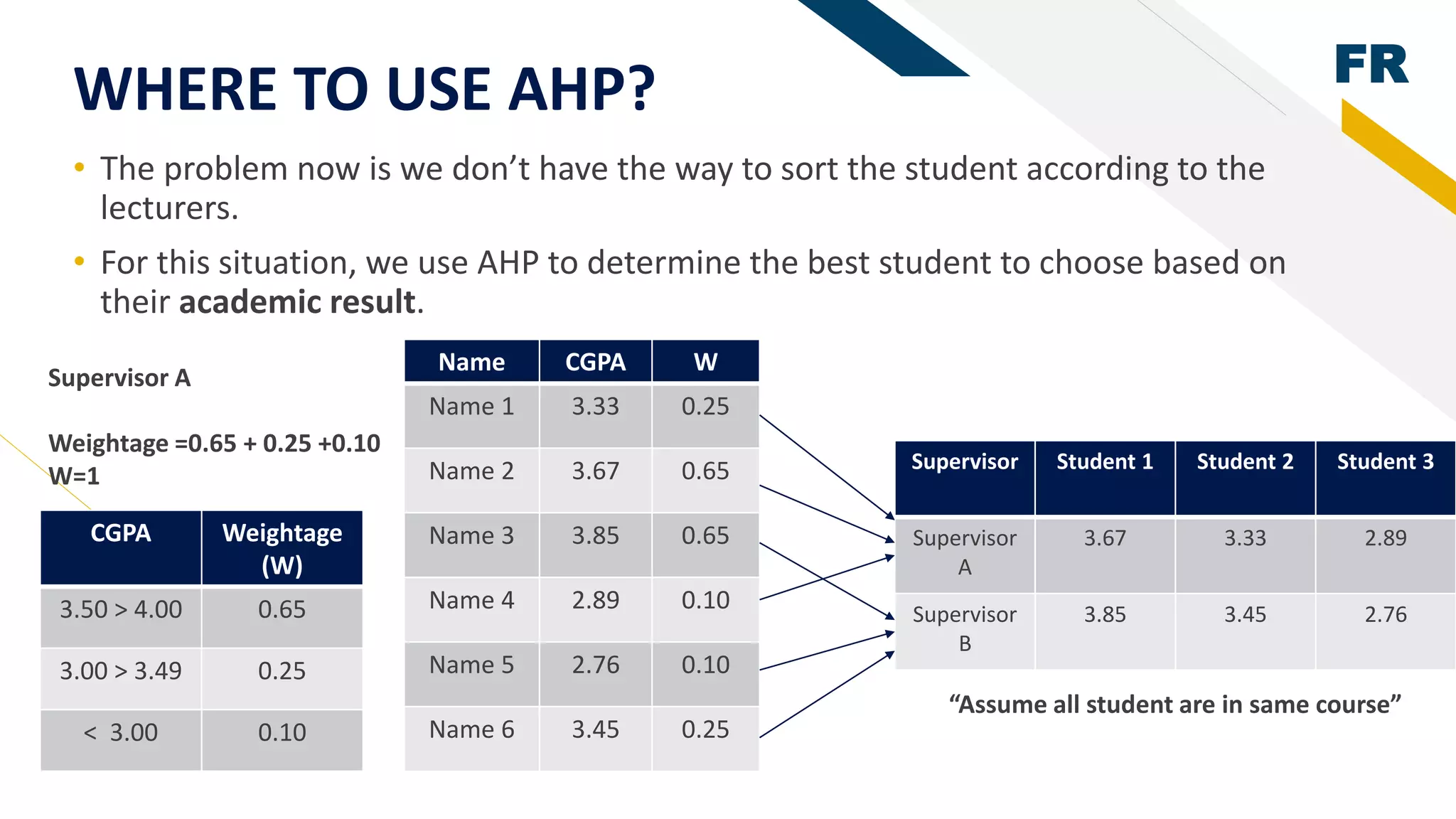
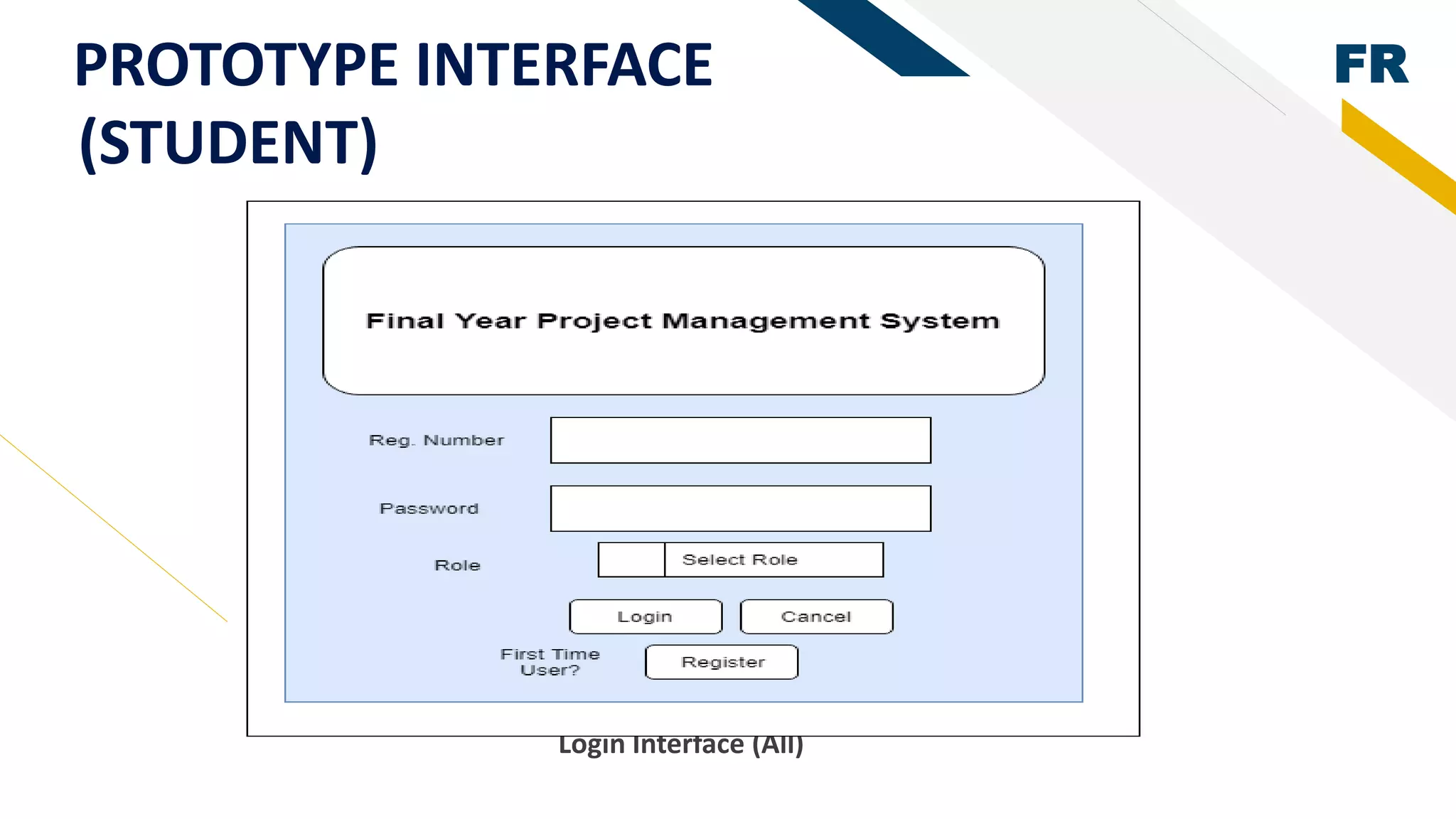
2. Rapid prototyping was used in the methodology to reduce risks and easily visualize the system. AHP was used to determine the best student based on their academic results by generating weights for evaluation criteria.
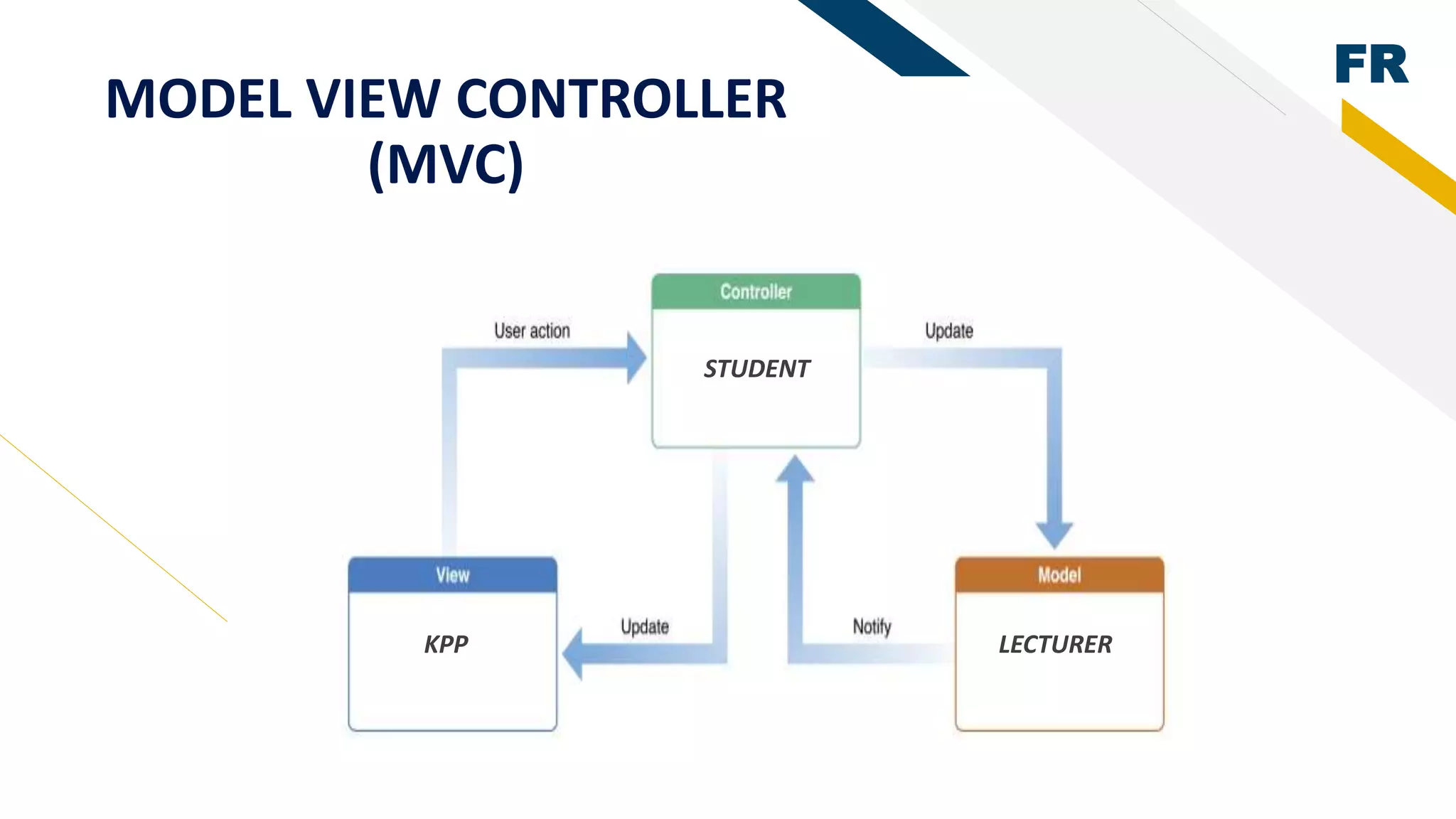
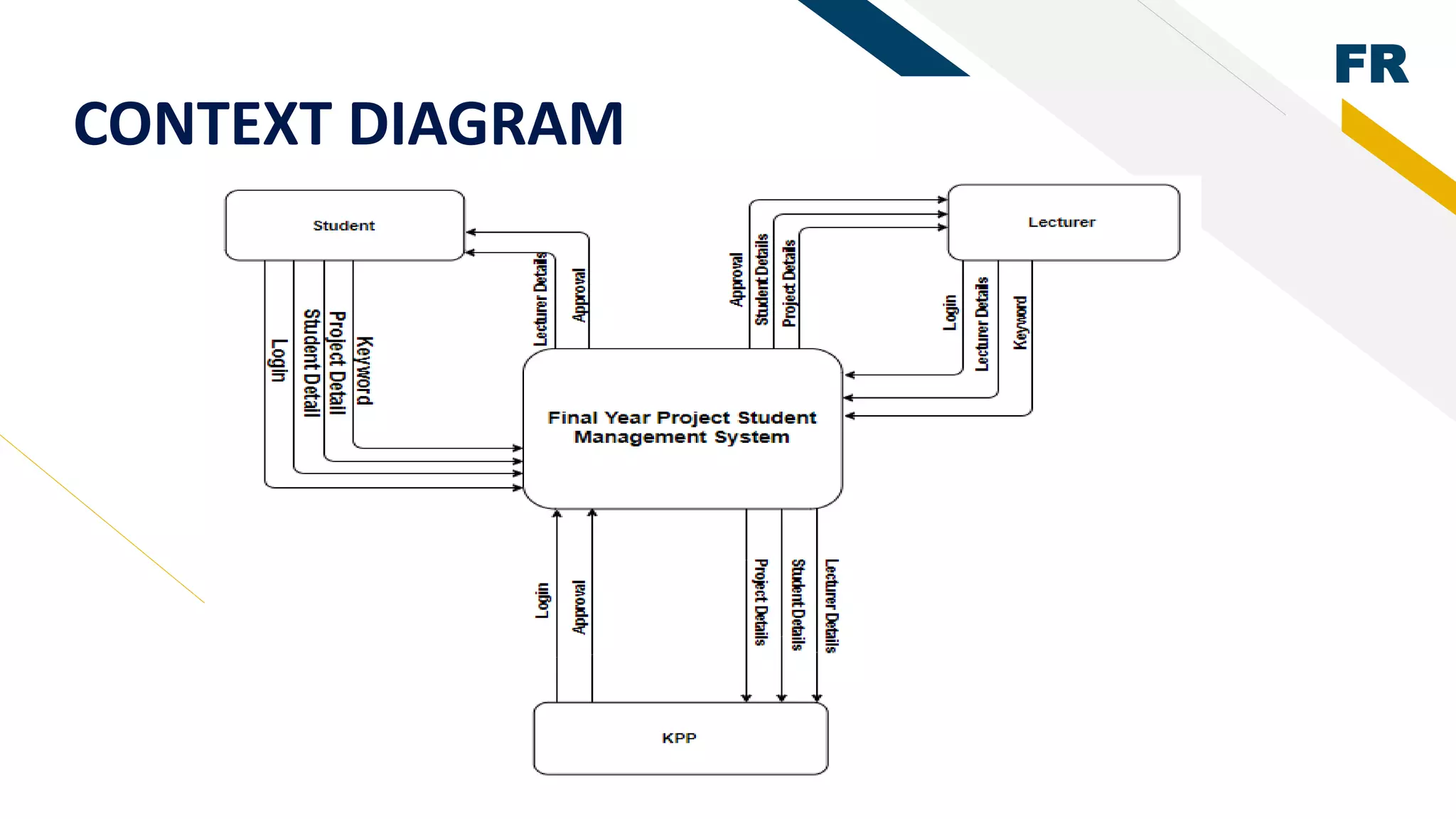
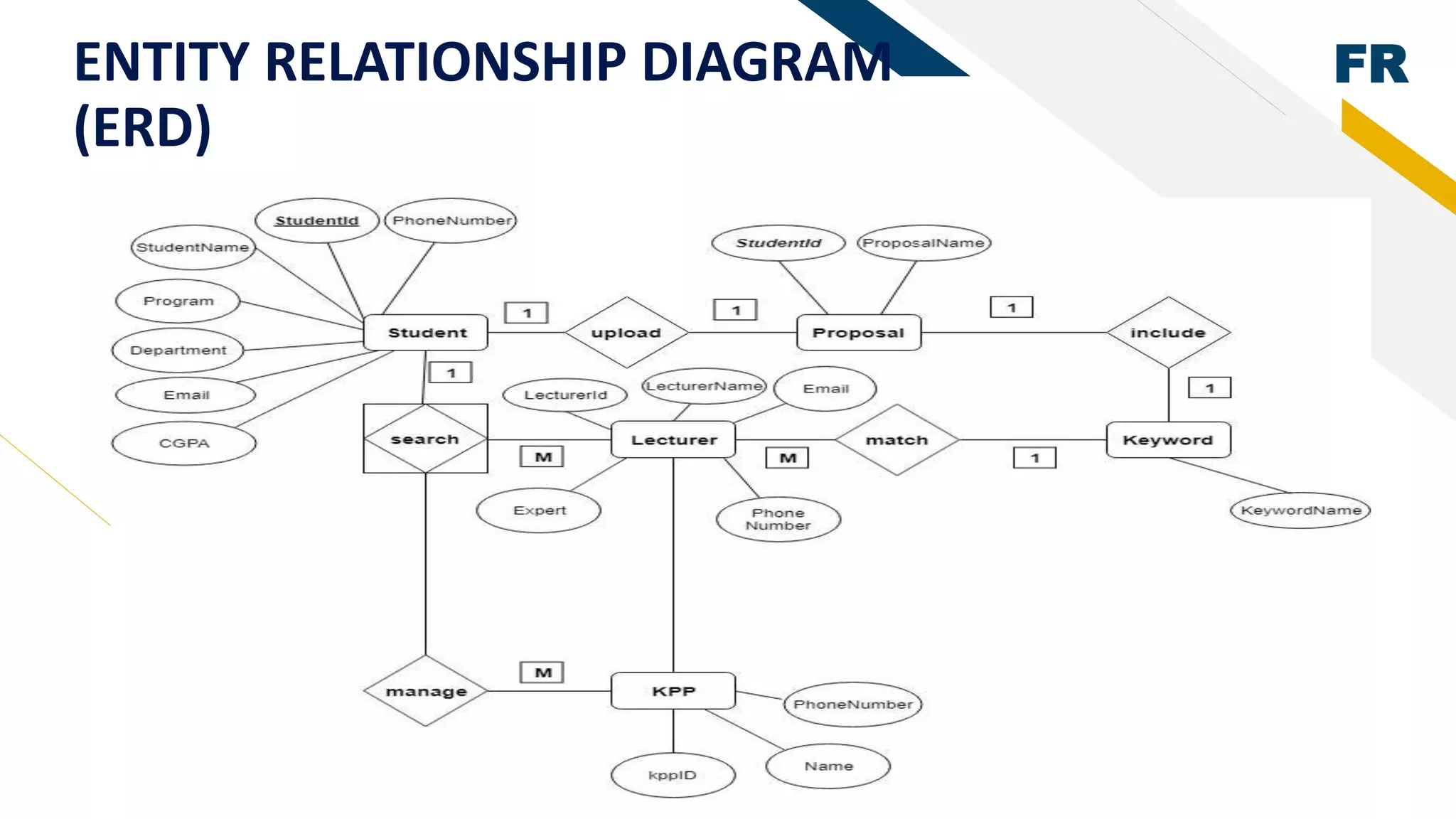
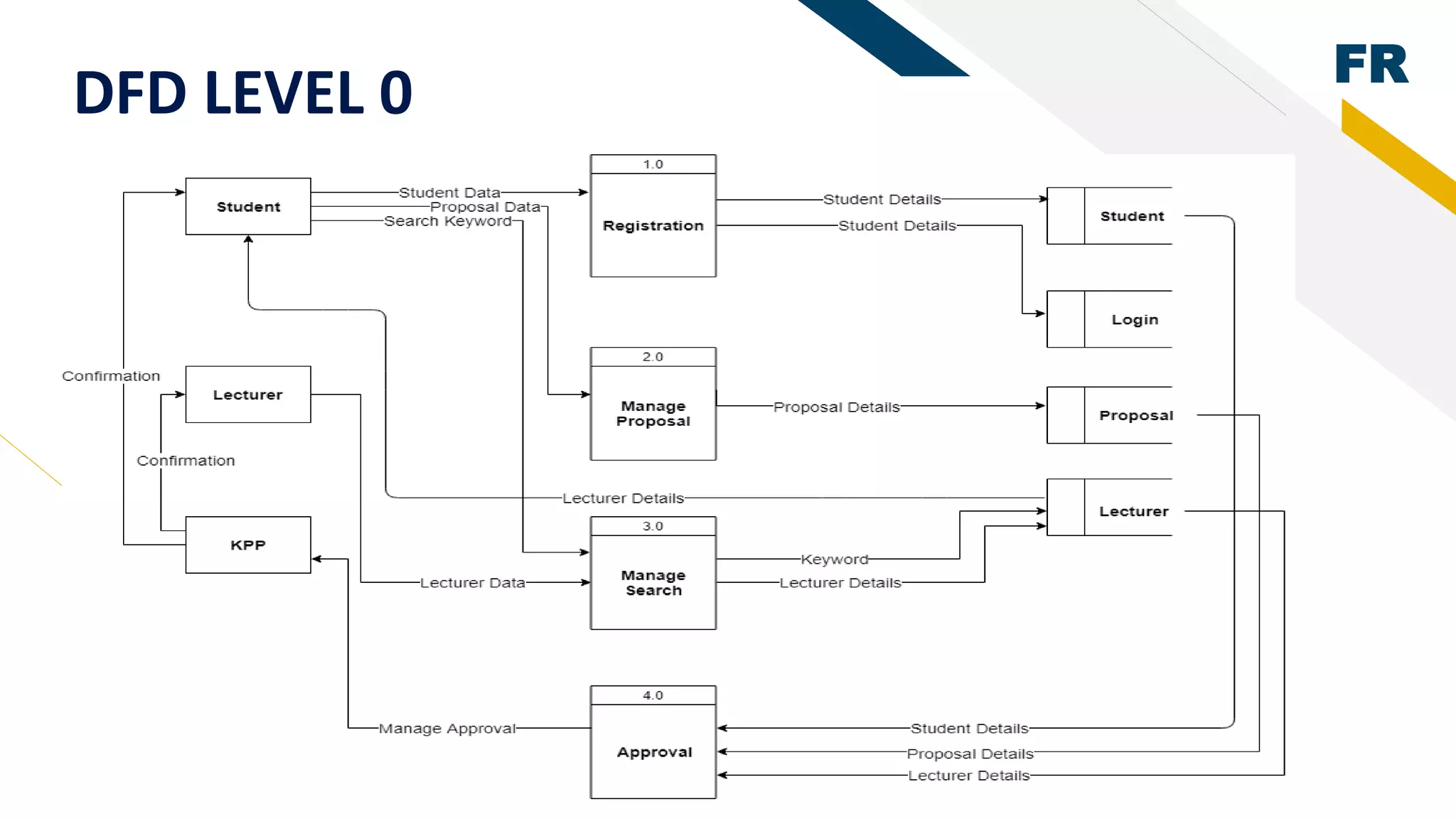
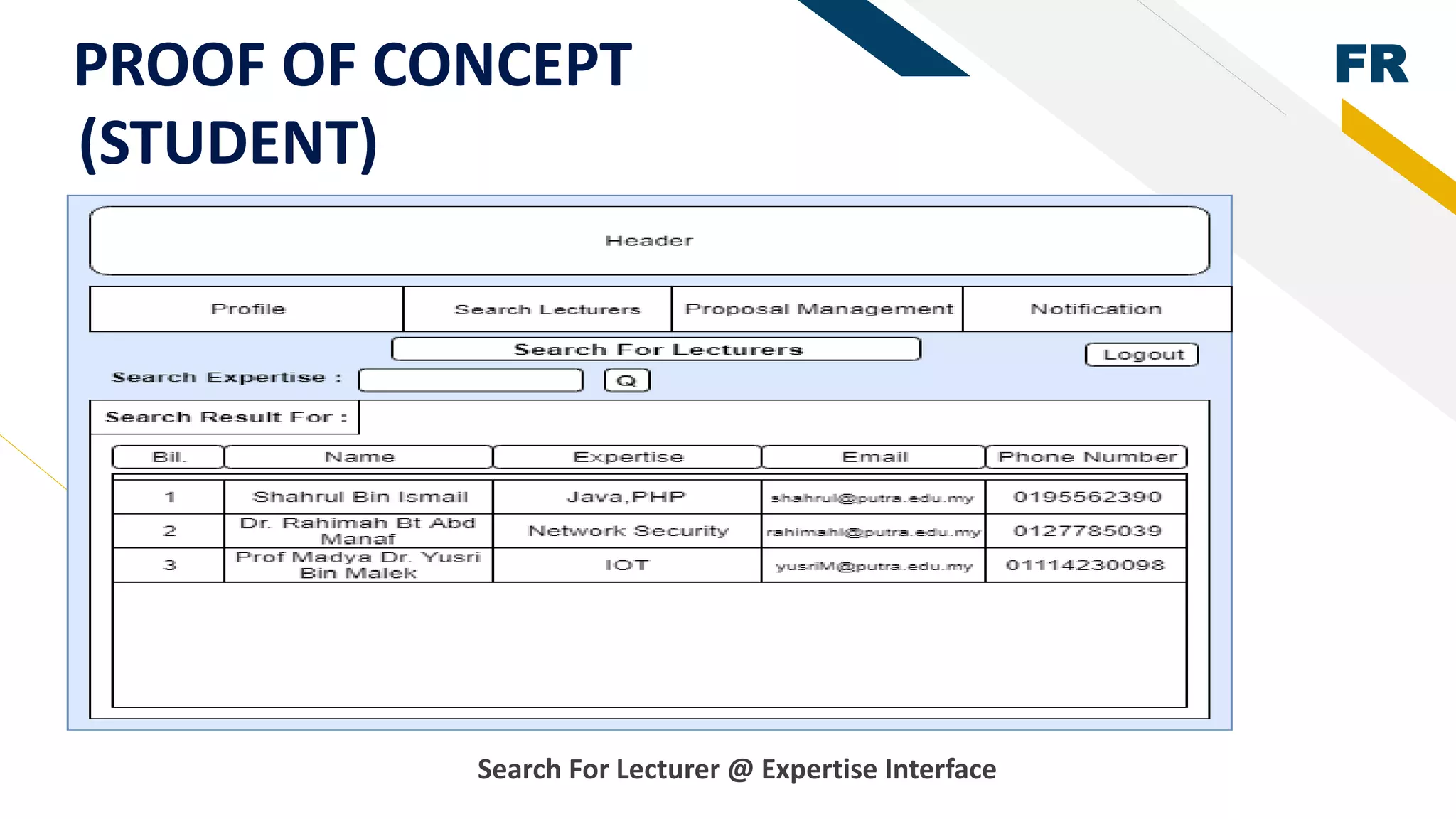
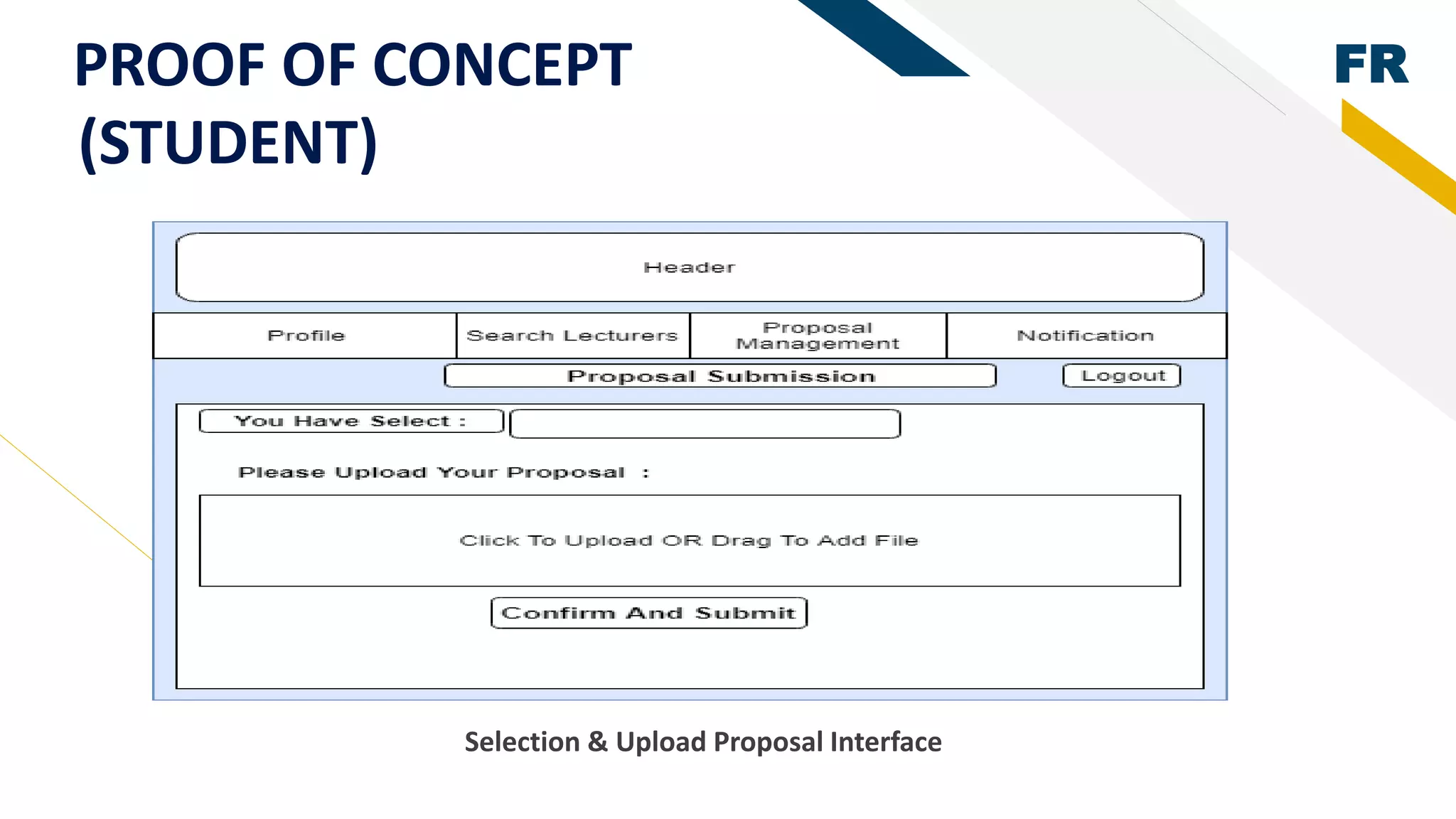
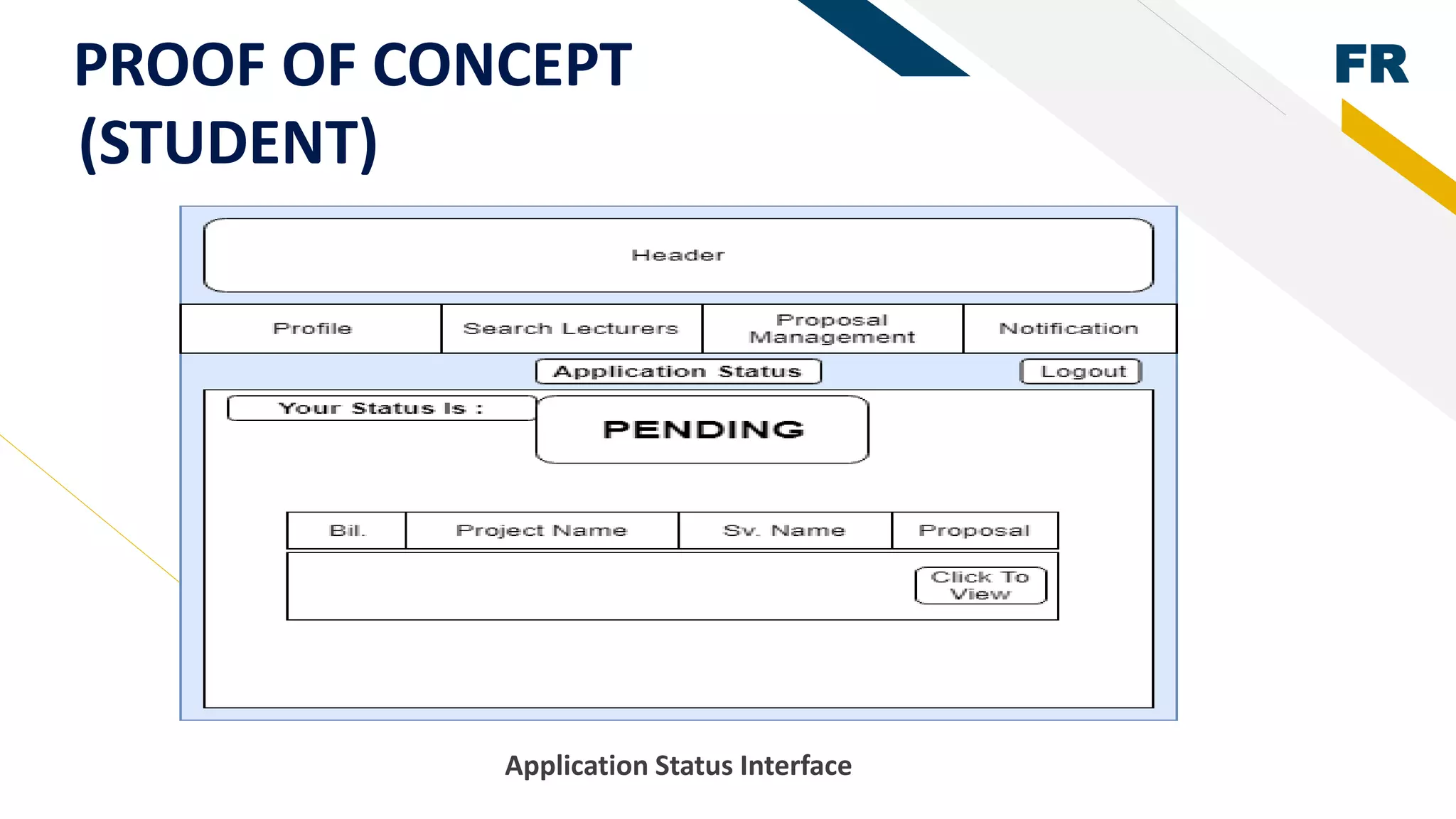
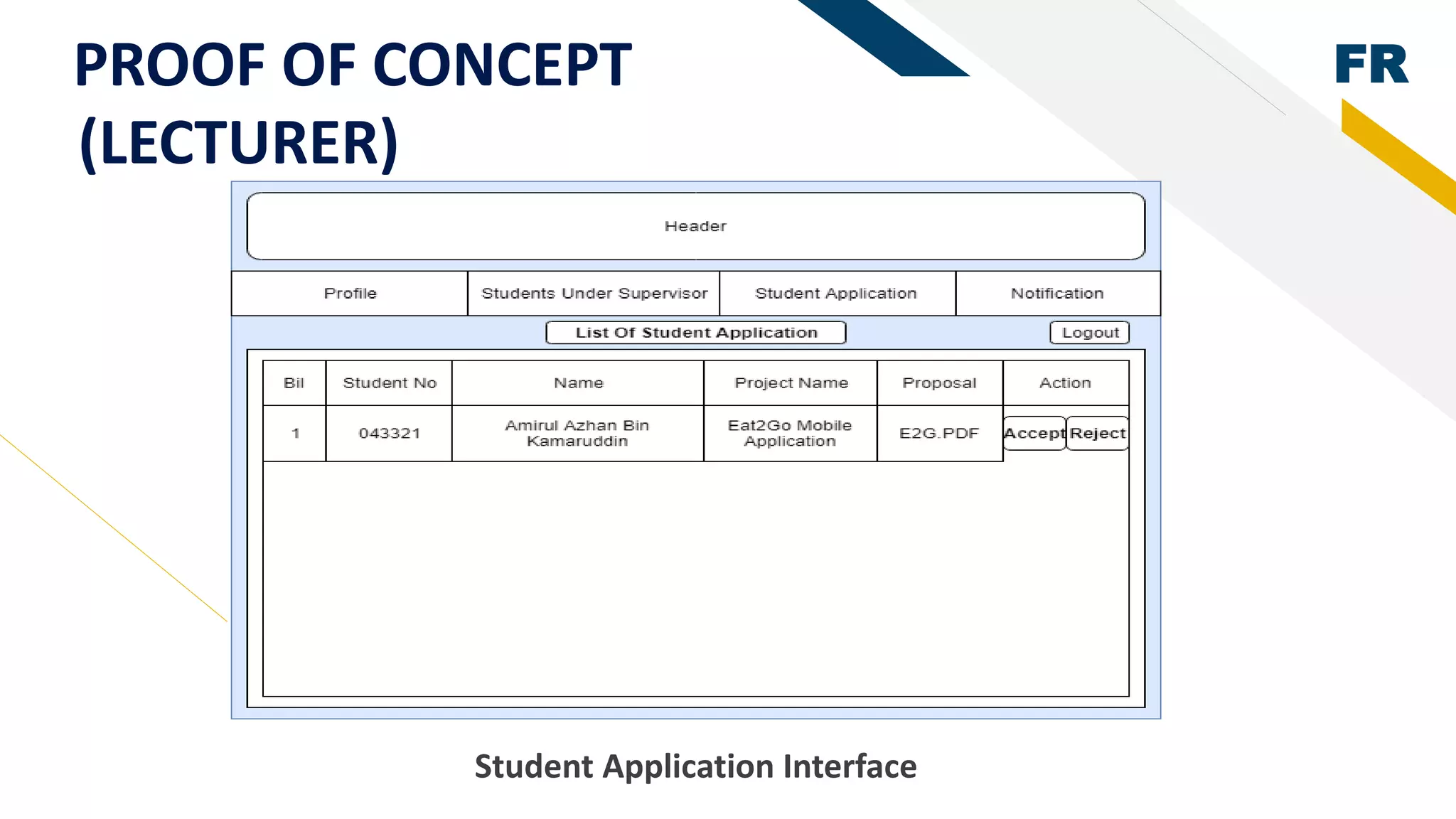
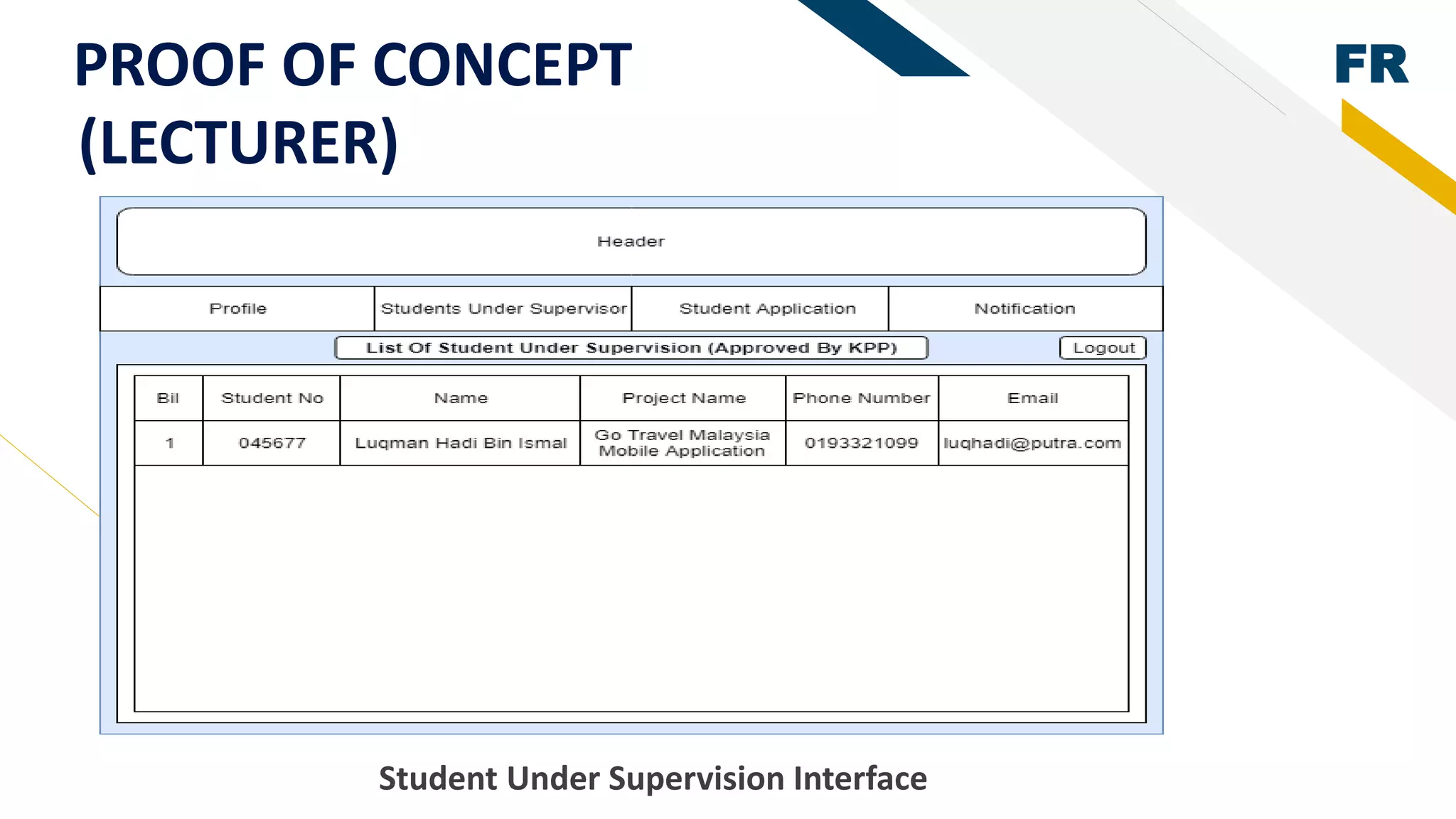
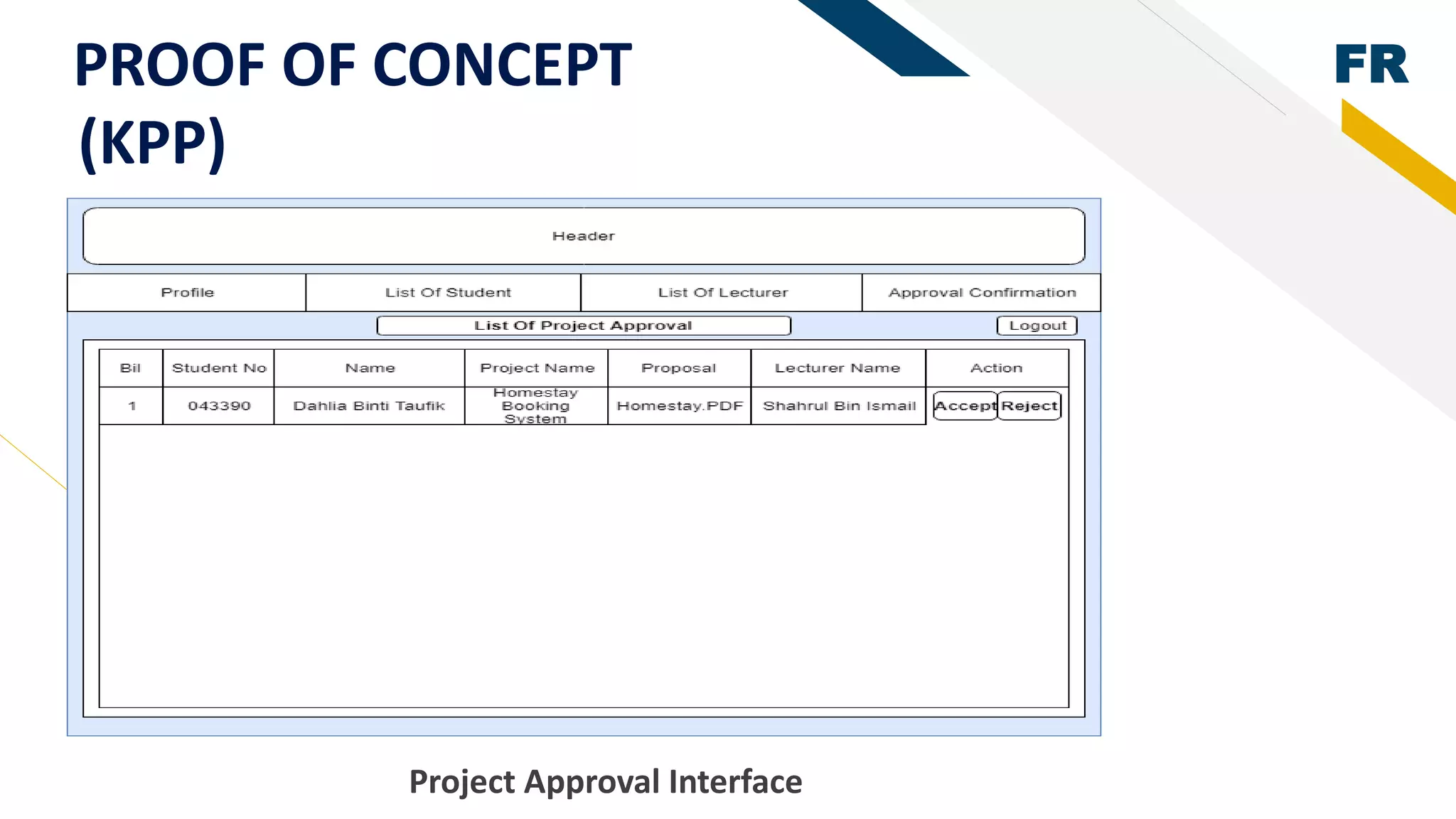
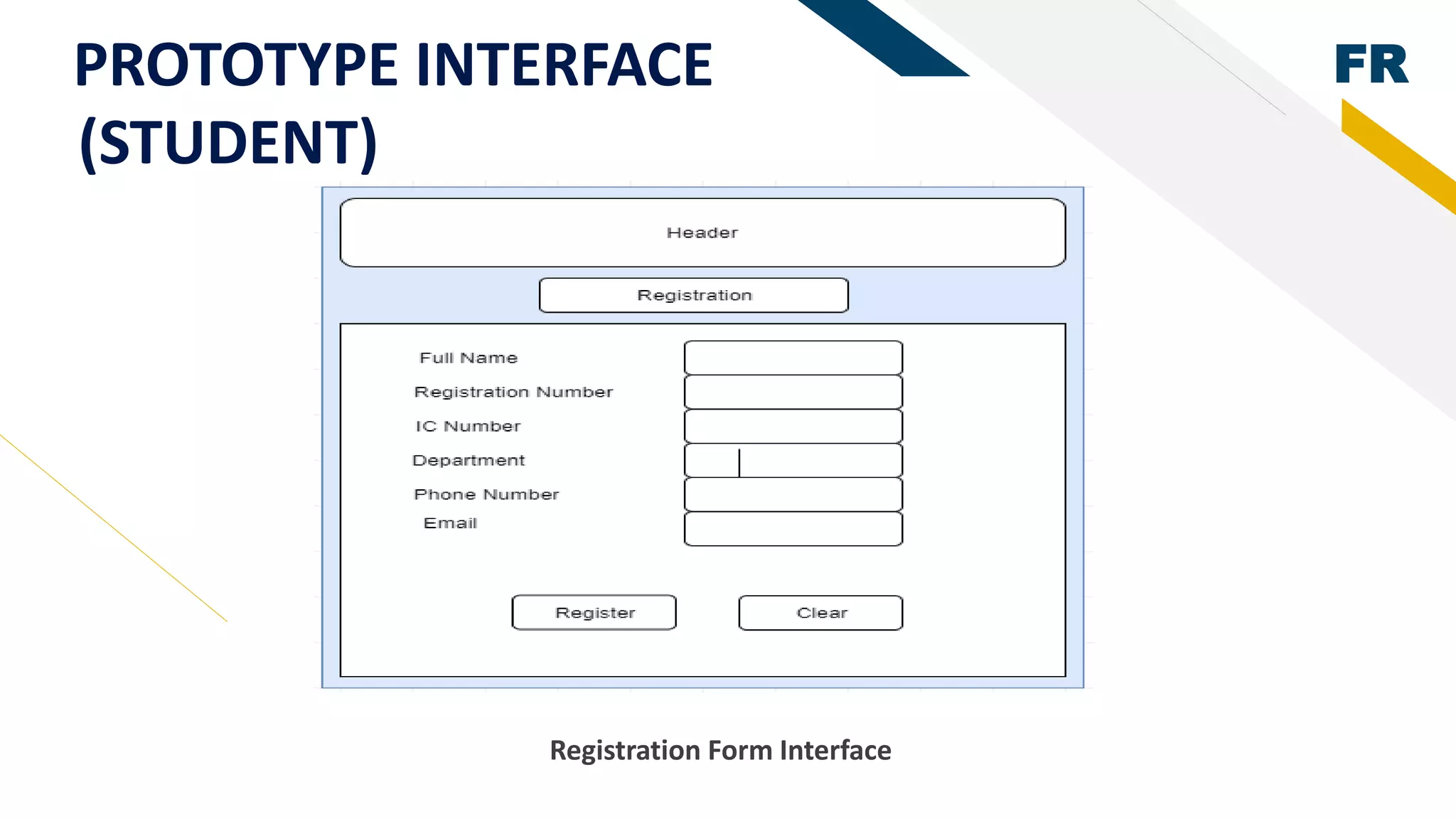
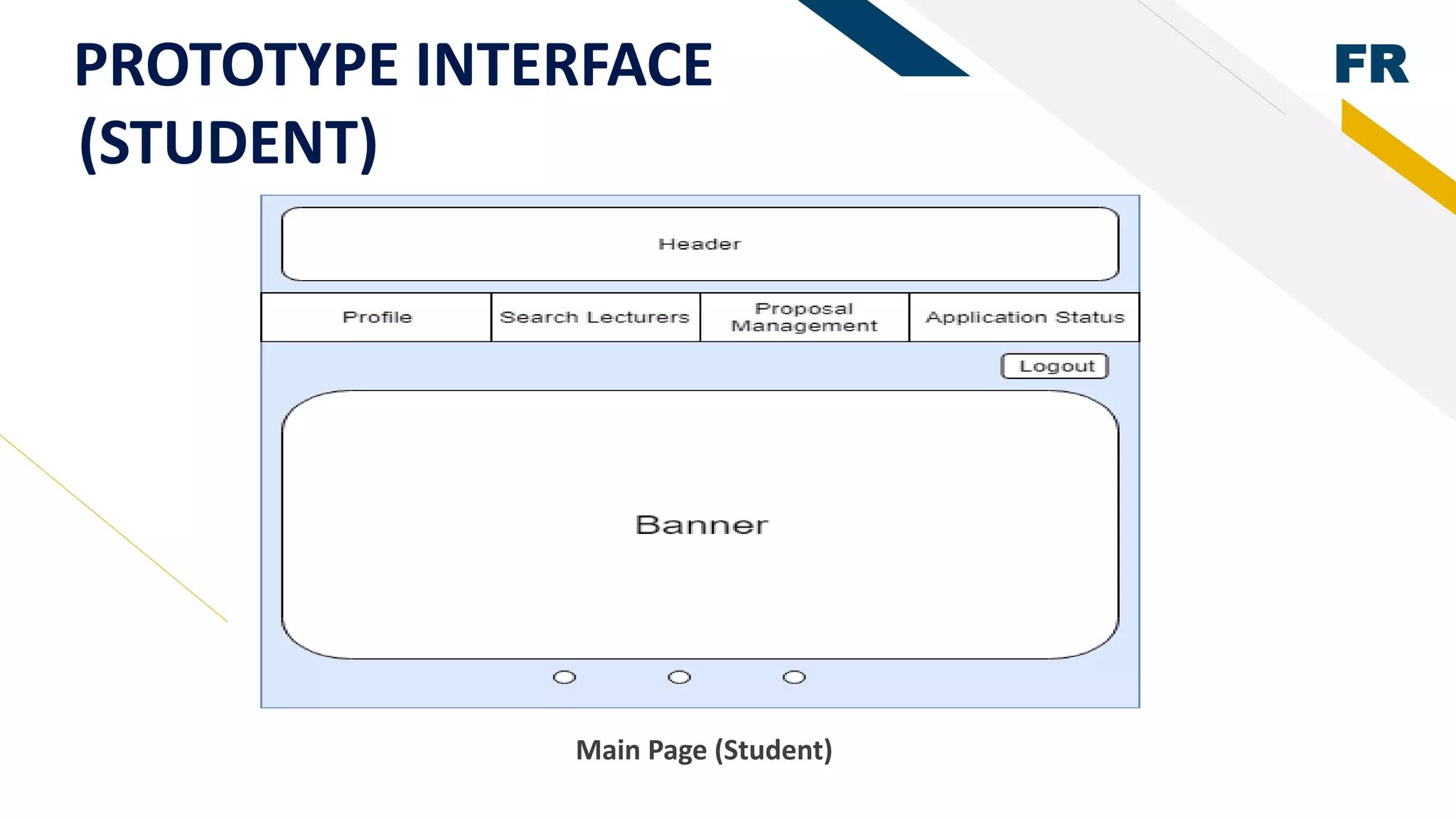
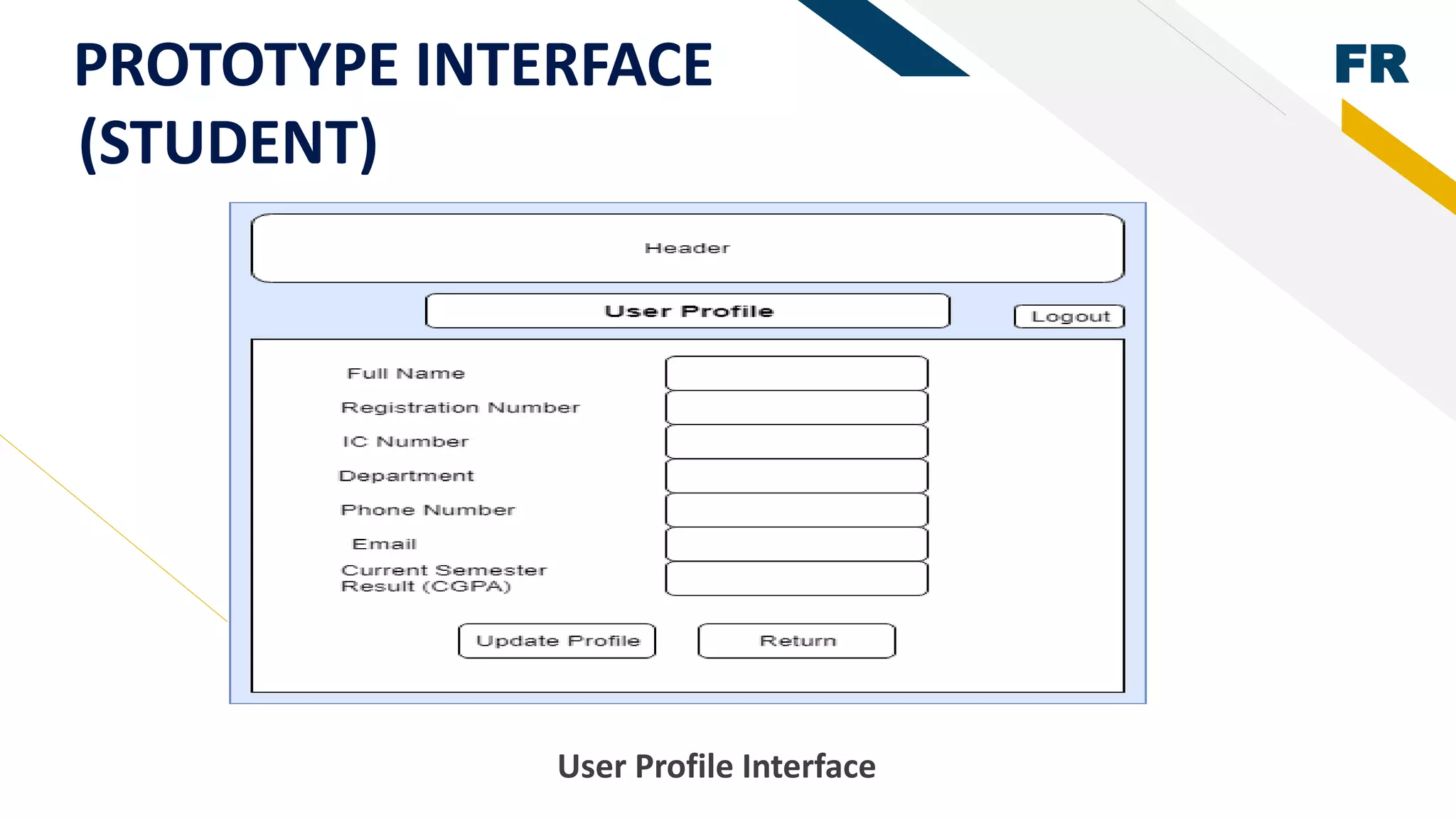
3. Proof of concept interfaces were created for students to search for lecturers, upload proposals, check application status, and view their profile. Lecturers can view student applications and those under their supervision.