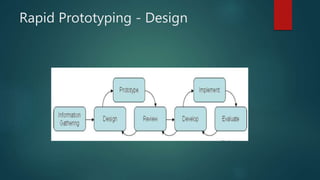
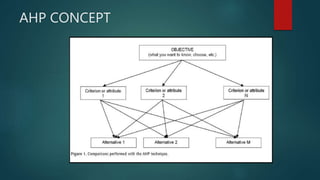
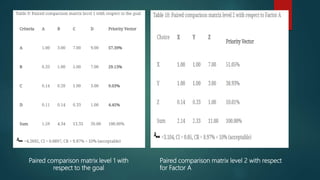
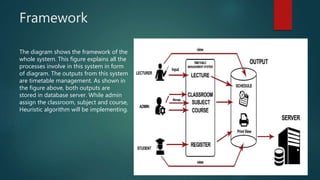
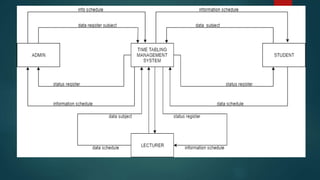
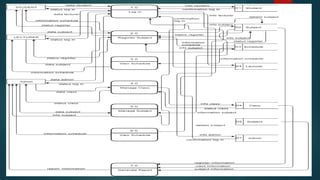
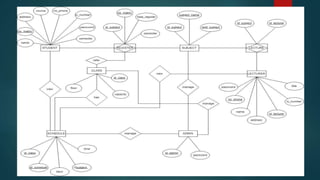
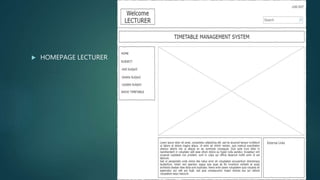
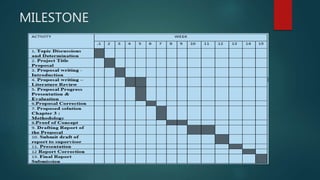
This document describes a project to develop a timetable management system using the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) technique. It provides background on the course timetabling problem for universities, which is time-consuming and complex due to various constraints. The objectives are to design and implement a system that processes course requirements using AHP to analyze alternatives and generate timetables. The methodology involves rapid prototyping and using AHP to structure criteria in a hierarchy and calculate weights to determine the best timetable. Diagrams show the framework, data flow, and entity relationships of the proposed system. A prototype interface is presented for administrators, lecturers and students.