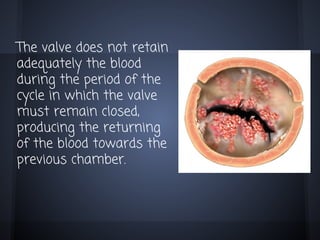
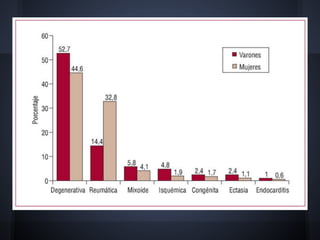
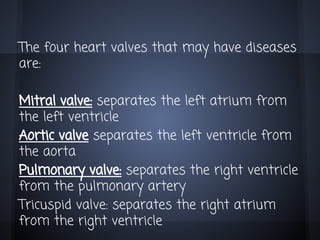
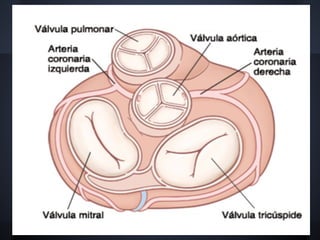
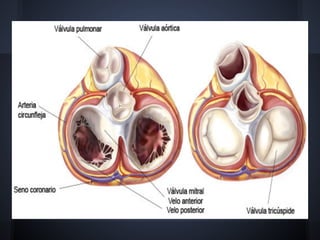
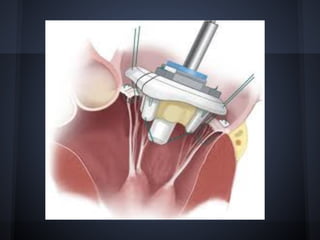
Cardiac valvulopathy is a condition where the heart valves become inflamed and stiff, preventing them from closing properly and allowing blood to flow backwards. The valves can be damaged by infections, injuries, aging, or previously by rheumatic fever. The most common type is degenerative valvulopathy in elderly patients as the valves harden and lose mobility over time. Valvulopathy is classified as light, moderate, or severe depending on the level of affection and whether treatment or surgery is needed. The main valves that can be affected are the mitral, aortic, pulmonary, and tricuspid valves. Symptoms depend on increased pressure in the heart chambers and the heart's ability to pump blood effectively.