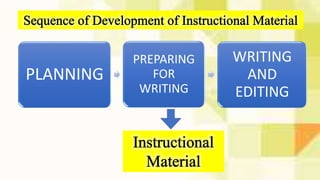
The document outlines the process for developing instructional materials which includes 5 key stages:
1) Planning - which involves mapping content, agreeing on structure and format, and developing a plan for materials.
2) Preparing for writing - including profiling learners, identifying objectives, and gathering resources.
3) Writing and editing - where the materials are written in drafts, reviewed by others, and edited.
4) Requirements in preparation - such as using multiple resources, determining how to explain ideas in different forms, and evaluating resources.
5) Expertise needed - including subject field knowledge, methods, acquisition and presentation of knowledge, critical thinking, and use of literature.