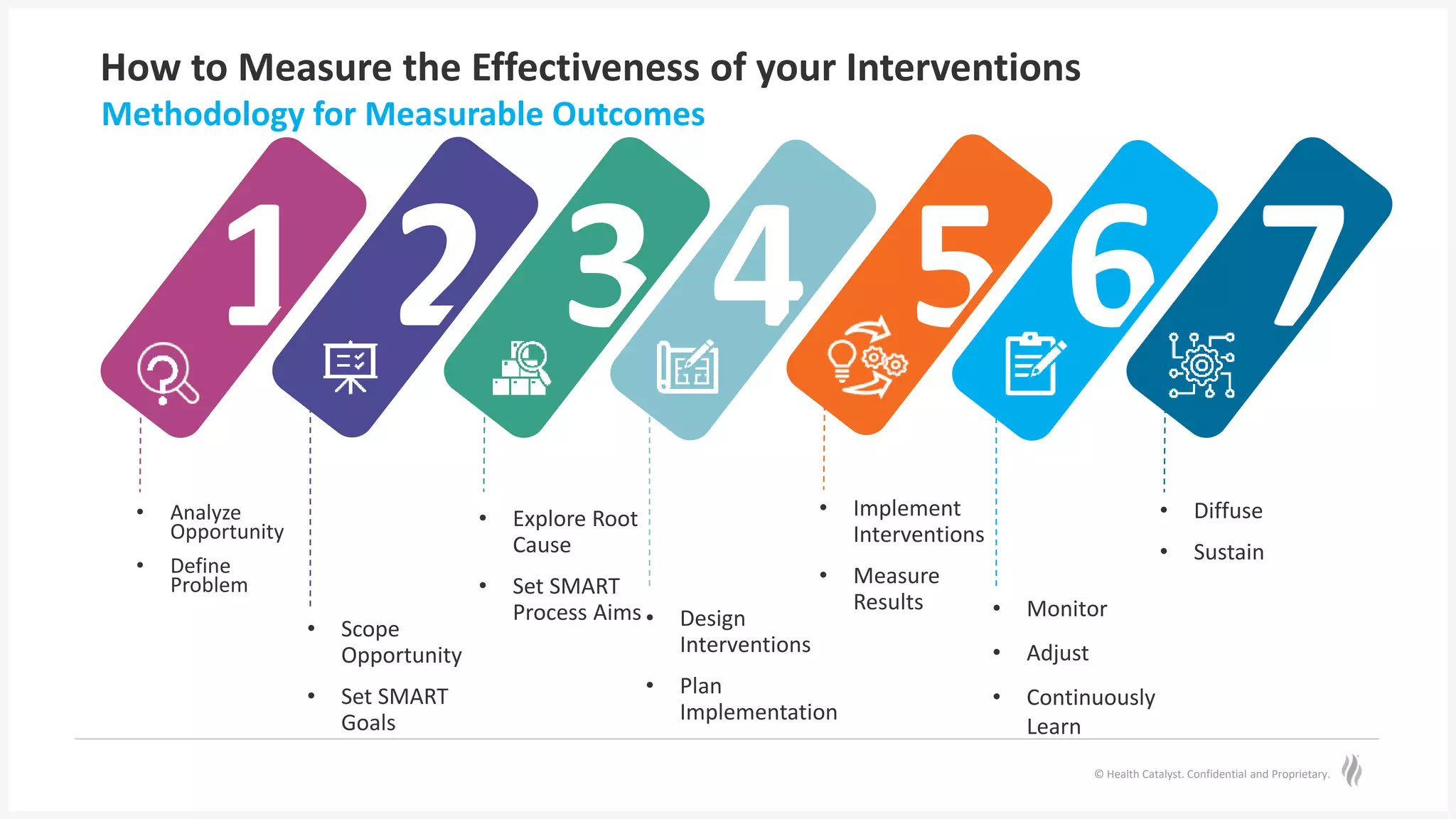
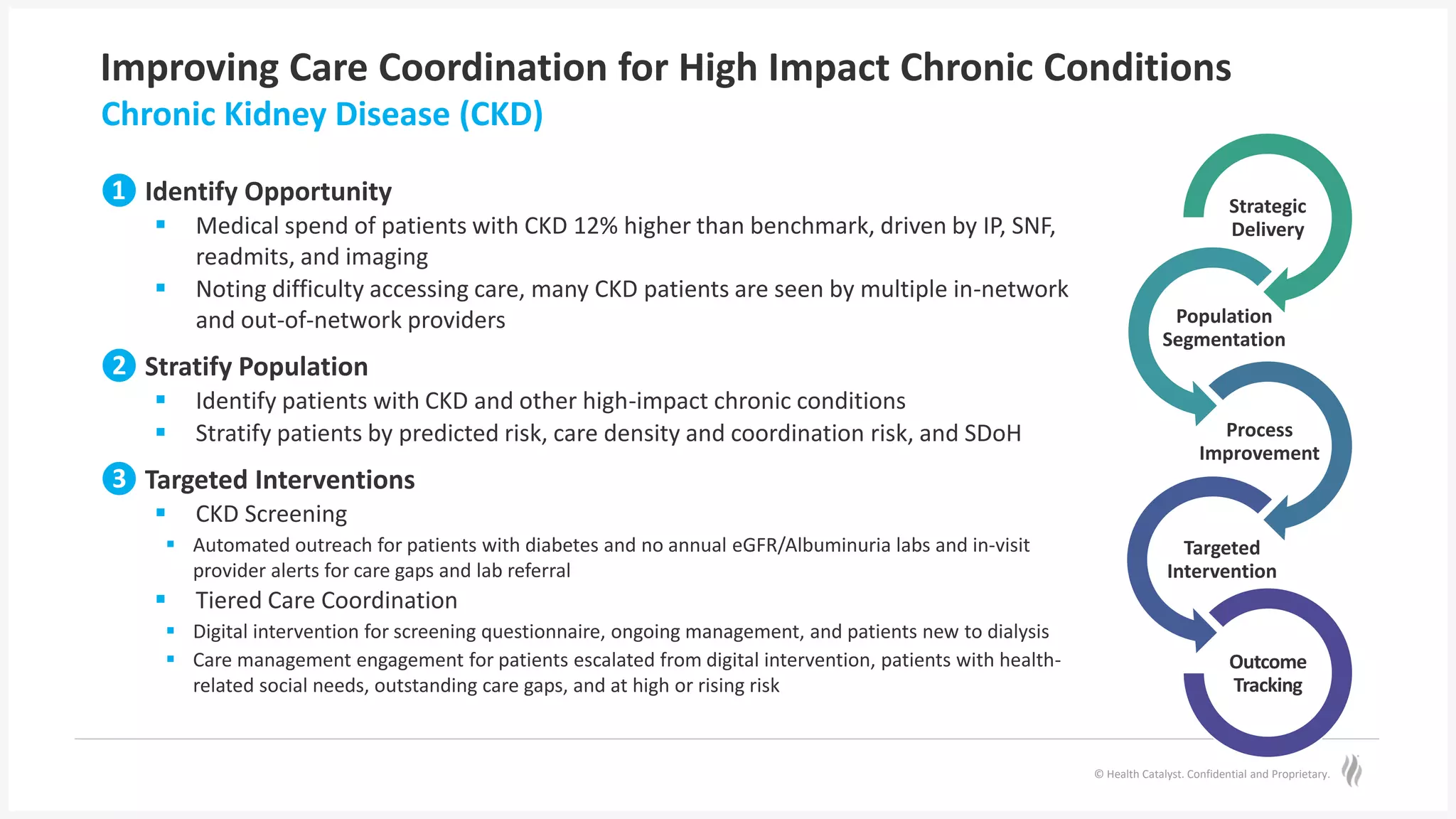
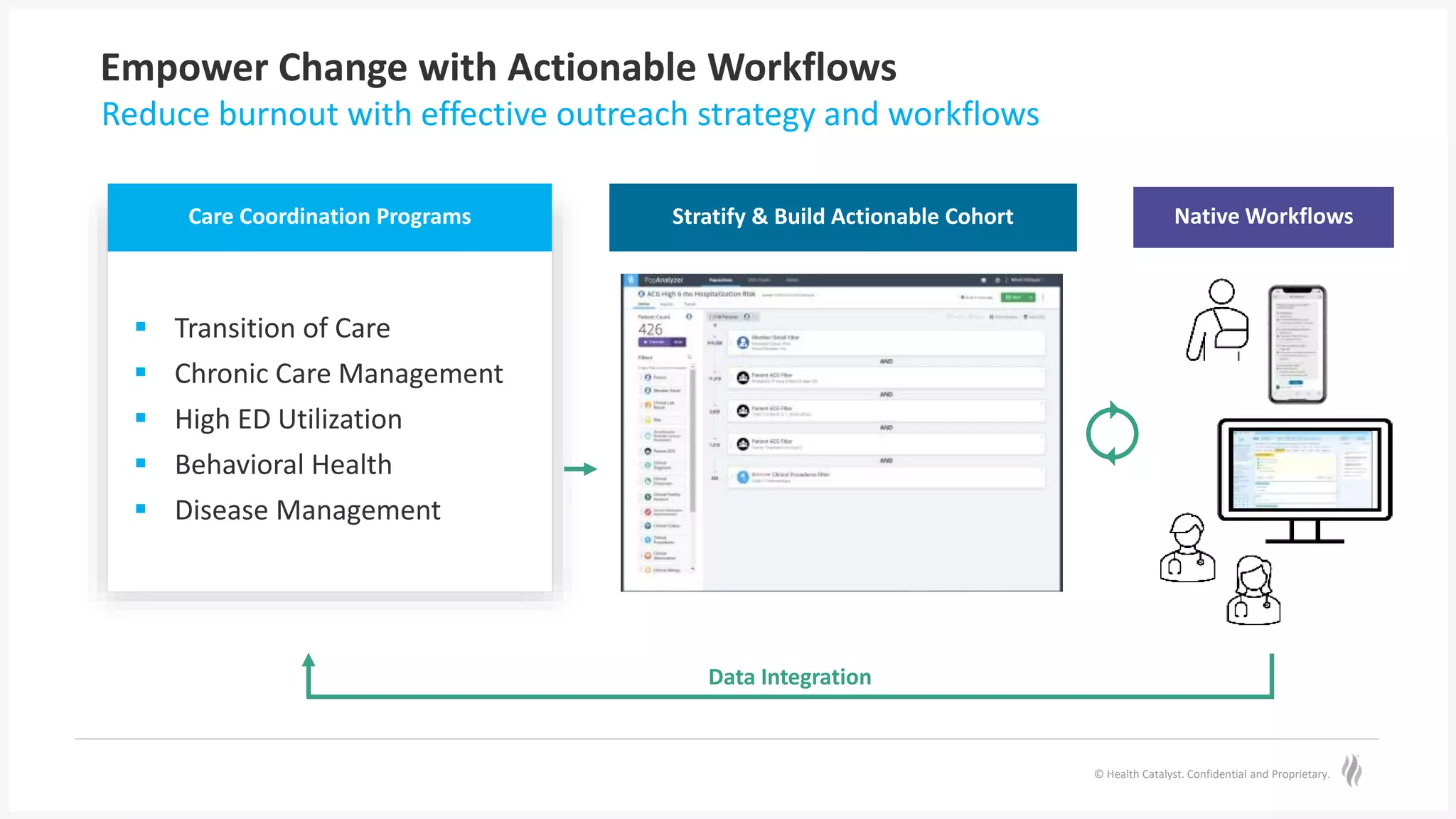
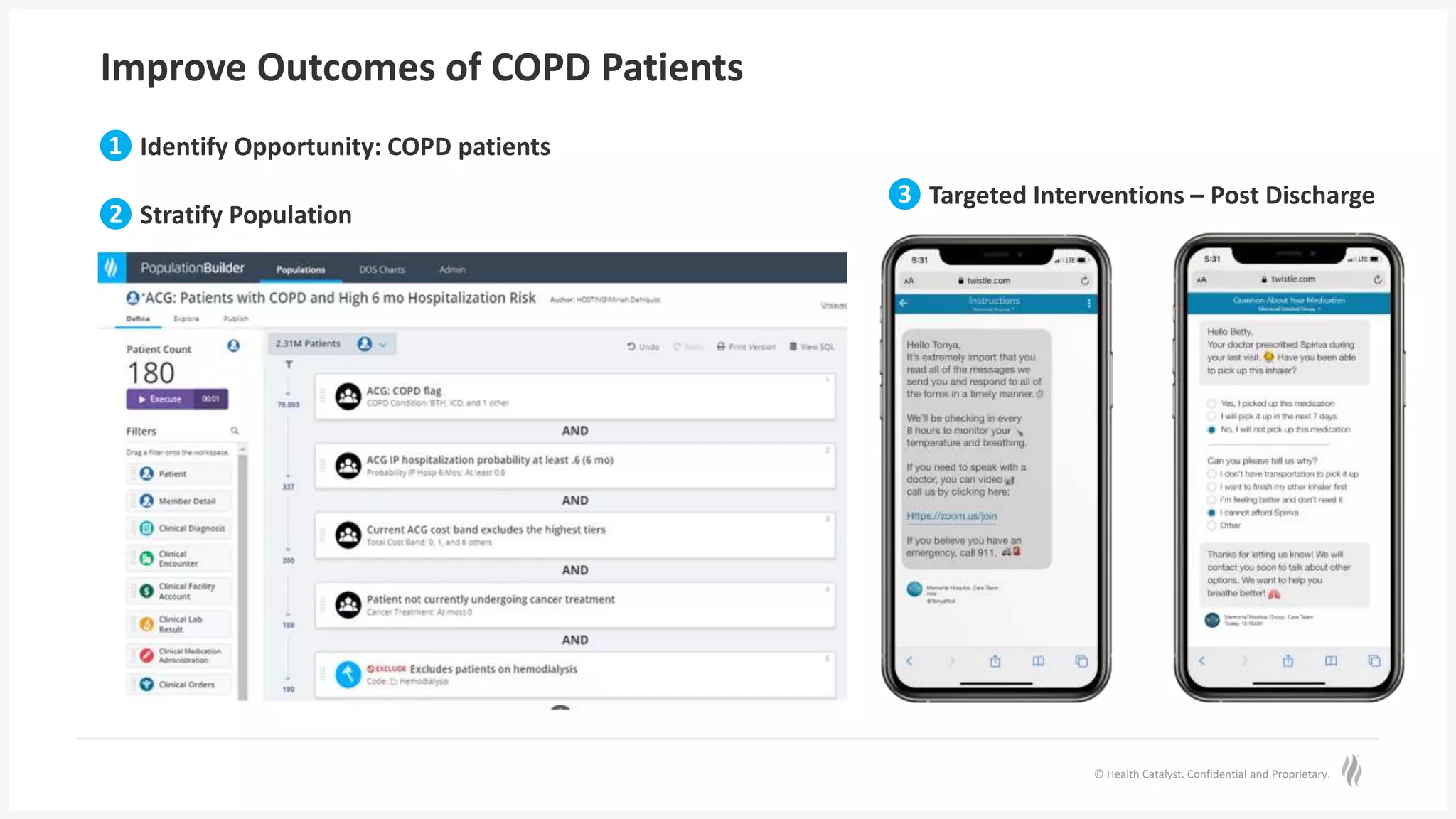
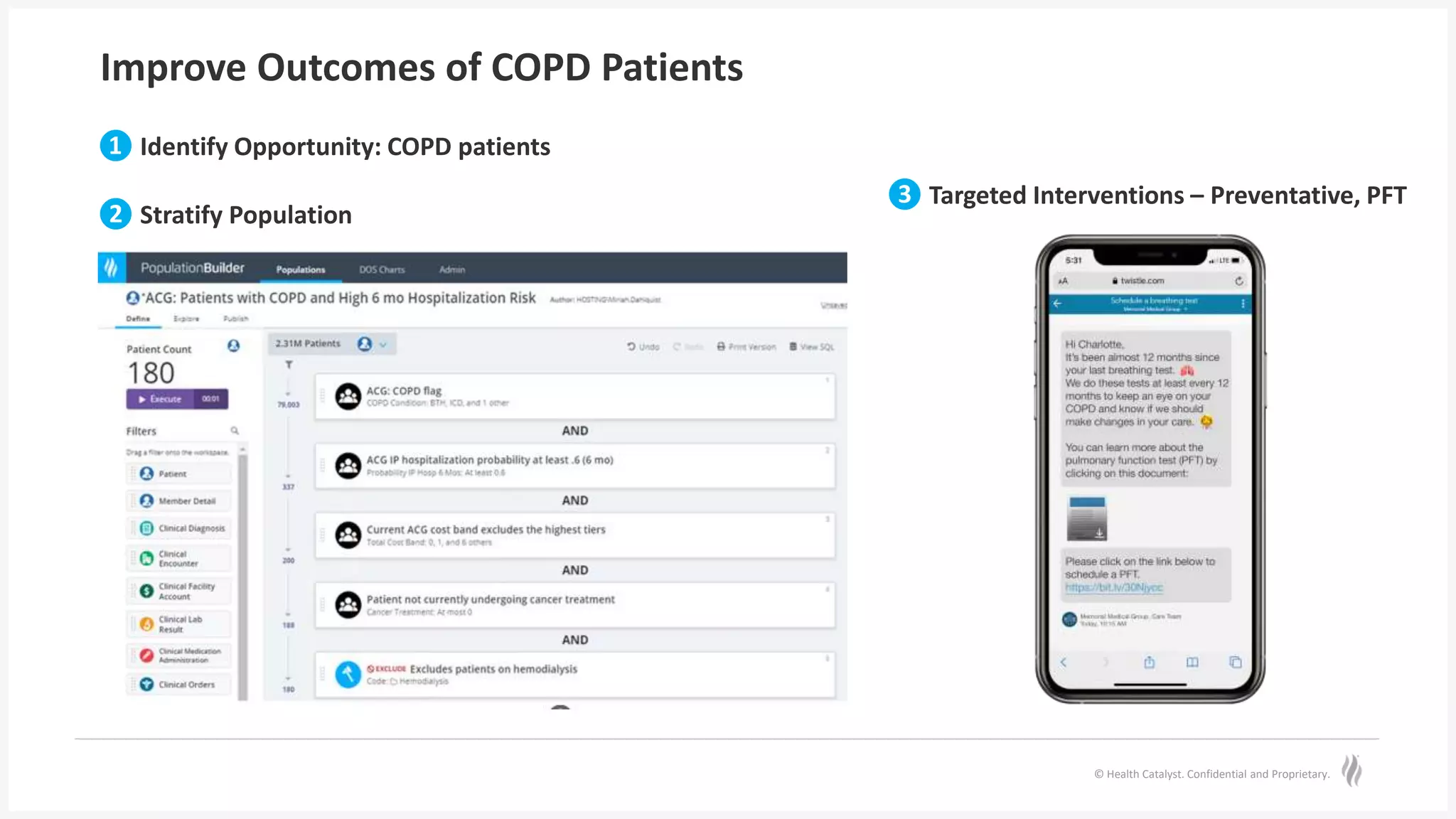
The document discusses predictive risk stratification in healthcare, highlighting its potential to identify high-risk patients and improve care management while addressing the challenges of clinician burnout and healthcare costs. Melissa Welch, MD, emphasizes the importance of data integration for effective risk stratification and targeted interventions, which can lead to significant financial and clinical improvements. Case examples illustrate successful implementations that enhanced outcomes for patients with chronic conditions and increased screening compliance for diseases like type 2 diabetes.











![© Health Catalyst. Confidential and Proprietary.
Improve Postpartum Detection of Type 2 Diabetes
The text-based messaging program
[Twistle] increased screening
compliance by 92%, which improved
our diabetes detection rates and
alleviates radical disparities in
healthcare.
– Helen Gomez, MD
Resident, ChristianaCare
”
92% increase in diabetes screenings
213% increase in detection rates for Type 2
Diabetes
211% increase in screening among Black
women
577% increase in detection of Type 2
Diabetes among Black women
Results
Preconfigured communication pathways delivered time-based, HIPAA-compliant
education reminders, reducing clinical workload.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/healthcatalystpredictiveriskstrat-221005213342-8c549d21/75/Predictive-Risk-Stratification-Using-Analytics-to-Empower-Change-with-Actionable-Workflows-Webinar-21-2048.jpg)

