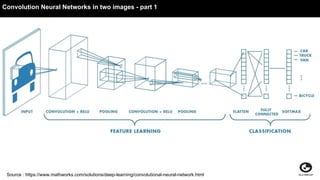
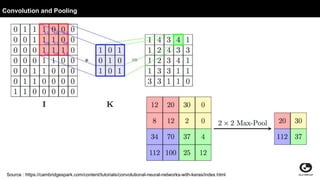
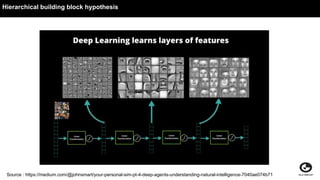
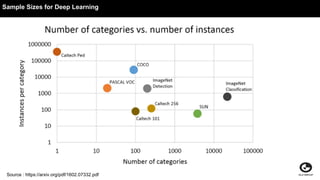
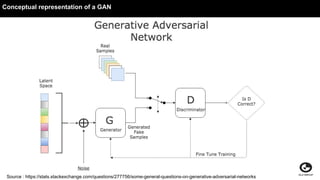
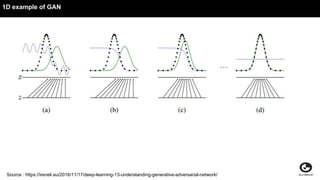
This document discusses using generative adversarial networks (GANs) for semi-supervised learning. It explains that GANs can help in a semi-supervised setup by creating a more diverse set of unlabeled data and improving generalization when training data is limited. The document provides an example of how a GAN can be used in the role of semi-supervised learning for a classifieds company to help identify spam, and discusses options for deploying these models on platforms like Amazon SageMaker and AWS Lambda.