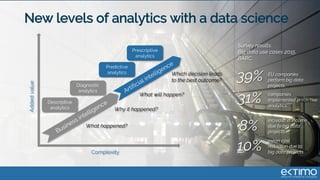
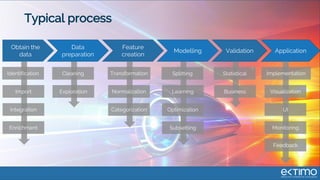
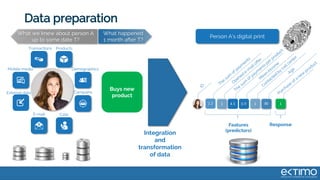
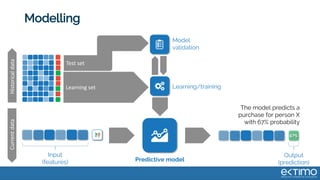
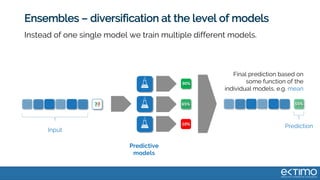
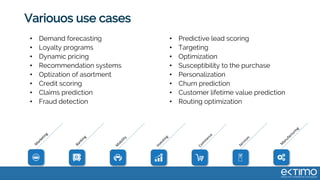
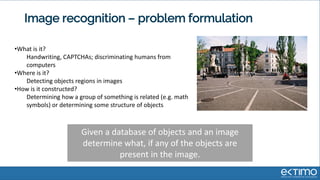
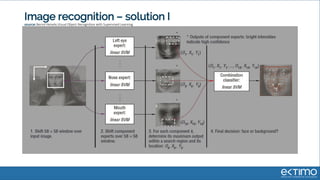
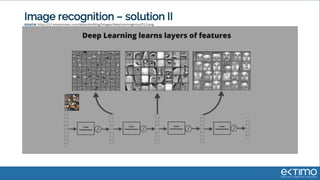
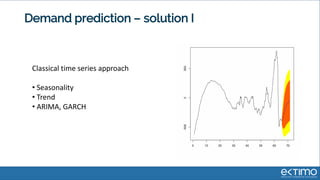
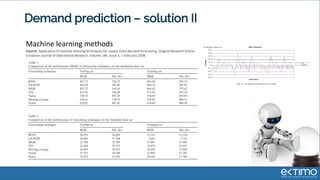
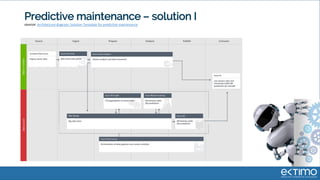
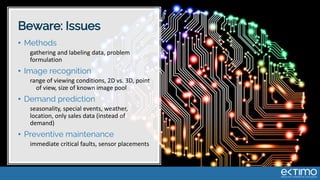
Predictive analytics uses data science techniques like machine learning algorithms to analyze historical and current data to forecast future events and outcomes. It has various applications like demand forecasting, predictive maintenance, image recognition, and personalized recommendations. For mobility, predictive analytics can help with tasks like obstacle detection, demand prediction, fault detection, and dynamic pricing optimization. Key challenges include properly formulating problems, gathering and labeling enough representative data, and accounting for external factors like weather.