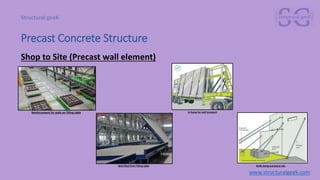
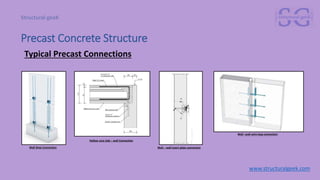
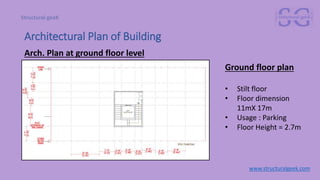
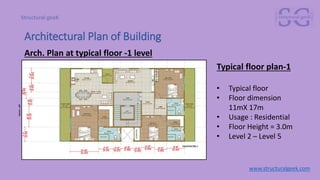
The document outlines an introduction to precast concrete structures, covering the course objectives, challenges, design principles, and applications in the industry. It details the construction process of precast elements, their structural design, and relevant architectural plans, along with essential structural codes and analysis software used for design. The focus is on enhancing product quality and reducing construction time through controlled production environments.