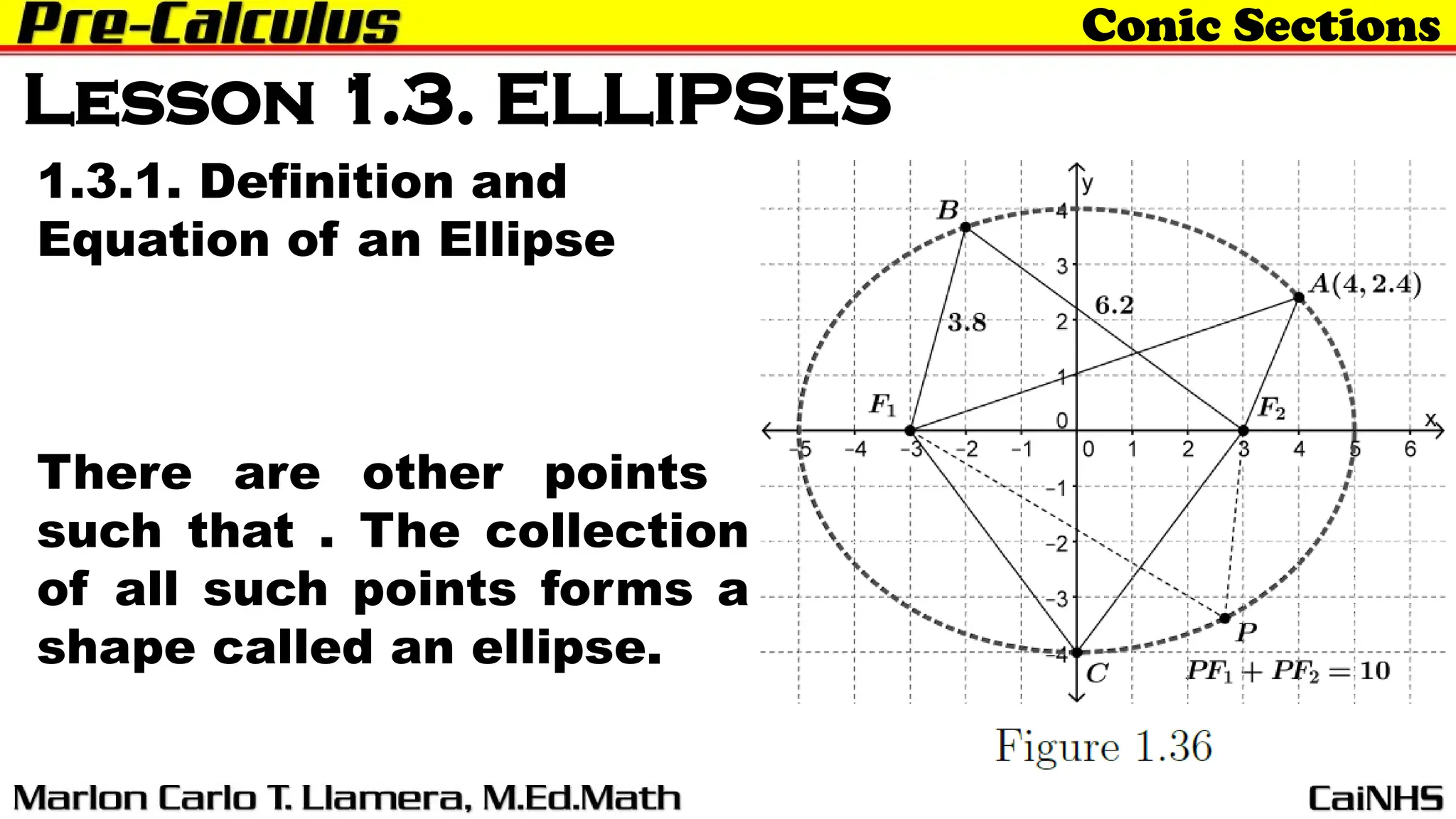
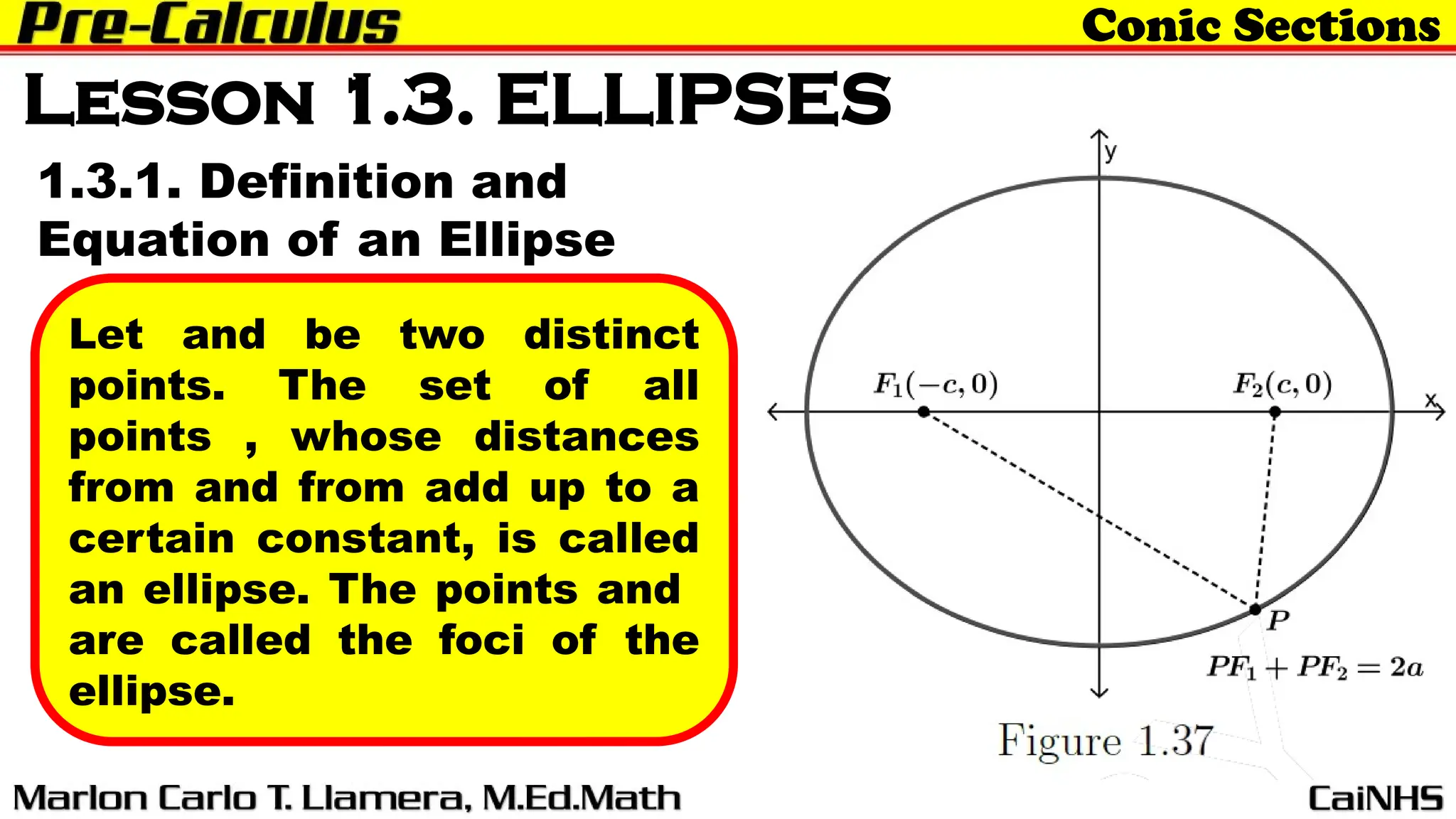
The document outlines a lesson on ellipses as part of conic sections, detailing learning outcomes such as defining an ellipse, determining its standard equation, graphing, and solving problems related to ellipses. It introduces the definition and properties of ellipses, including their geometric characteristics and applications, such as planetary orbits. The lesson aims to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of ellipses in a mathematical context.