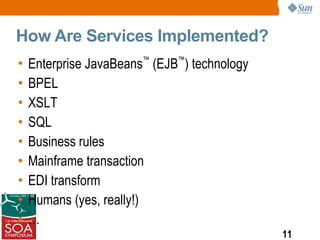
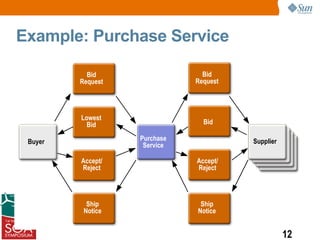
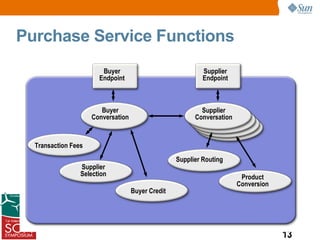
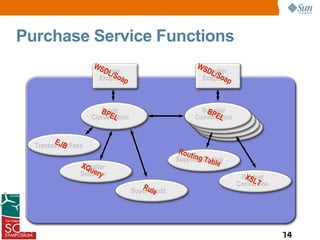
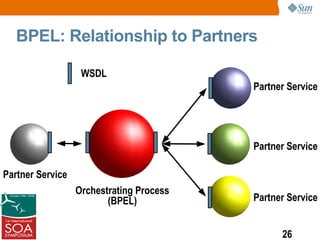
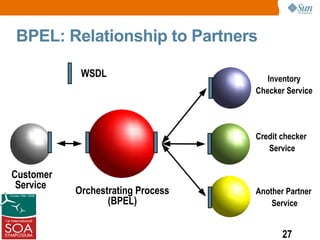
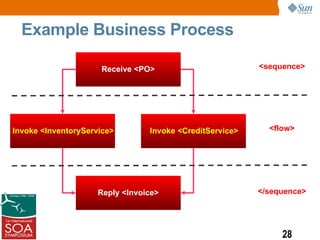
This presentation discussed how to develop composite applications using SOA principles and Java EE technologies like BPEL and EJB. It began by defining composite applications and services, then discussed how Java EE provides services and how BPEL can orchestrate them. It showed how NetBeans IDE allows designing BPEL processes to coordinate Java EE and external web services. Finally, it summarized how SOA enables flexible applications by reusing and composing services, and that BPEL is used to orchestrate services into composite applications. The presentation concluded with a demo and call to action.