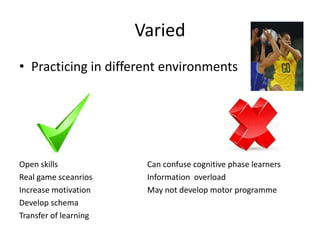
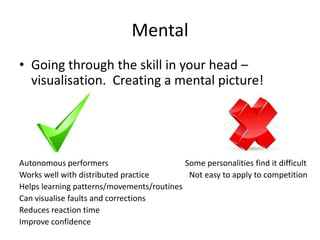
Practice should incorporate perfect practice principles like distributed practice with rest breaks, variation in environment and conditions, and mental rehearsal. Only perfect practice with these elements will lead to optimal skill development and performance, while massed or continuous practice risks injury, boredom, and inefficient learning.