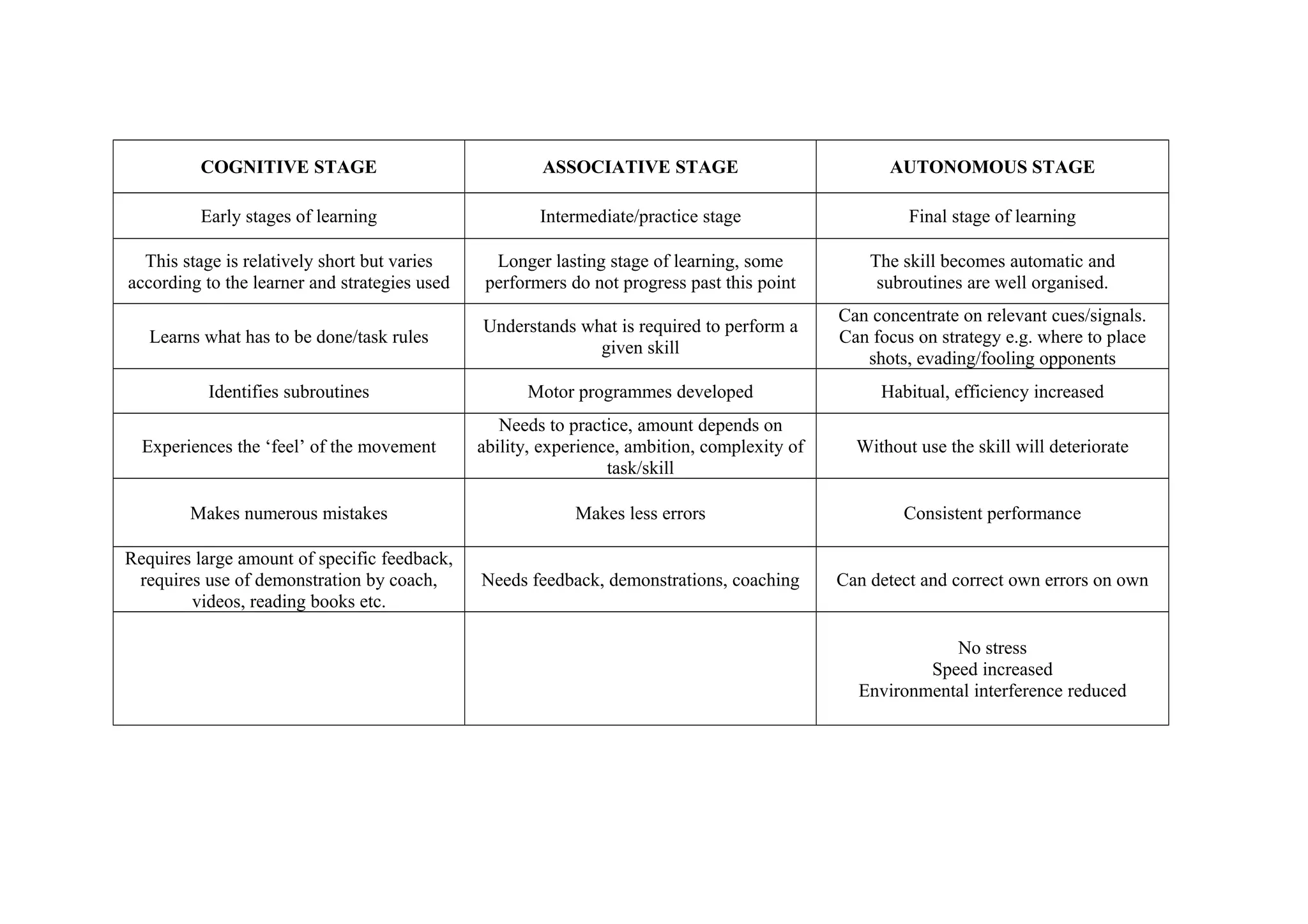
The document describes the three stages of learning a new skill: the cognitive stage where the learner understands the task and identifies subroutines, the associative stage where the learner develops motor programs through practice but still makes errors, and the autonomous stage where the skill becomes automatic and the learner can focus on strategy with consistent performance and reduced errors.