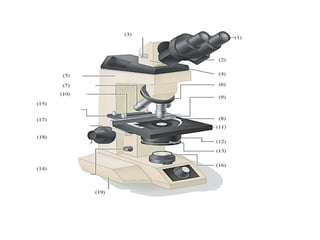
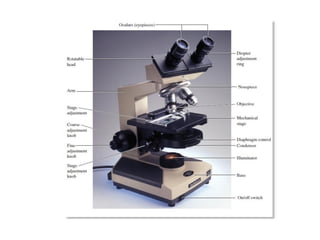
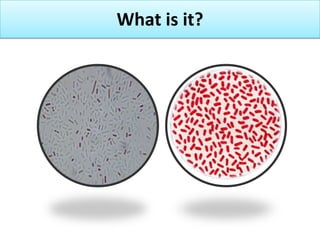
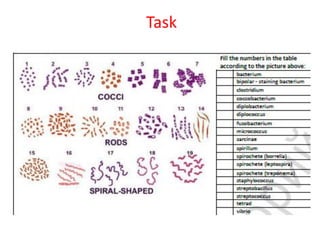
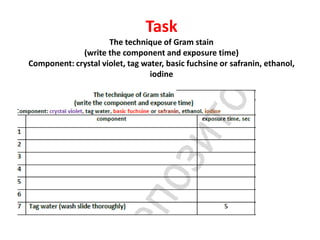
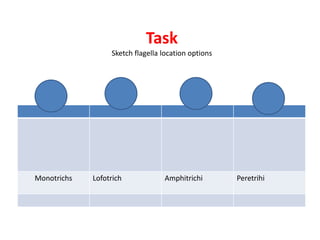
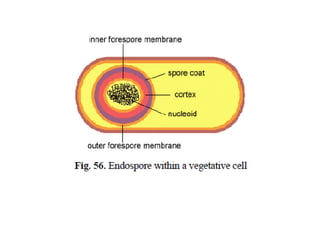
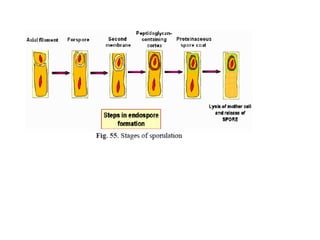
The document outlines the practical aspects of studying microorganisms, focusing on medical bacteriology, laboratory safety, and microbiological research methods. It emphasizes the importance of cleanliness and safety in the laboratory, including personal protective equipment and proper disposal of materials. Additionally, it covers various microscopy techniques and practical tasks for preparing and observing bacterial cultures.