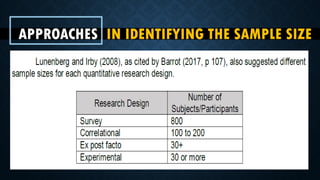
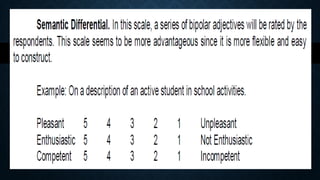
The document outlines the components of research methodology, specifically focusing on research design, environments, respondents, sampling procedures, instruments, data gathering, and analysis. It emphasizes the importance of selecting appropriate designs and instruments in quantitative research to enhance clarity and validity. Additionally, it provides guidance on how to write about each aspect of the research process.