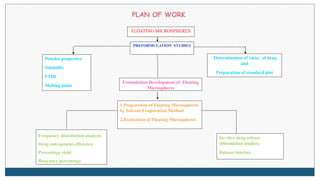
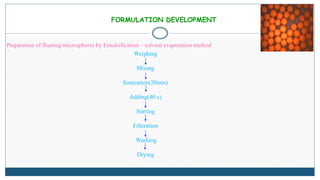
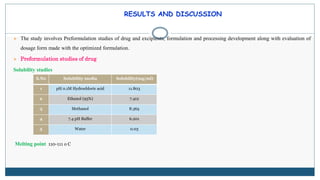
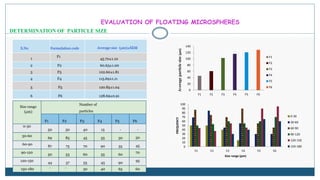
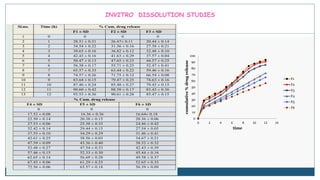
This document describes the formulation and evaluation of flurbiprofen floating microspheres. It discusses the drug profile of flurbiprofen and the various excipients used in the study such as ethyl cellulose and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose. Six formulations of flurbiprofen floating microspheres were prepared by solvent evaporation method and evaluated for particle size, drug entrapment efficiency, in vitro drug release and release kinetics. Formulation F6 showed the highest drug entrapment efficiency of 89.60% and floated for the longest duration of 91.83 hours. The drug release from the microspheres followed non-Fickian diffusion mediated release indicating that the release is governed by both diffusion and erosion