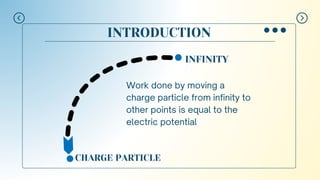
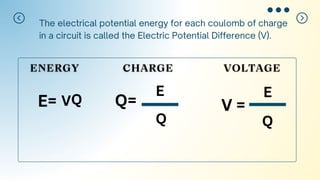
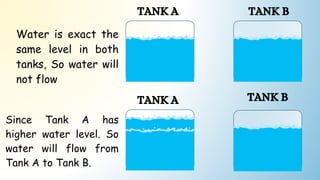
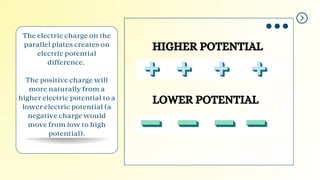
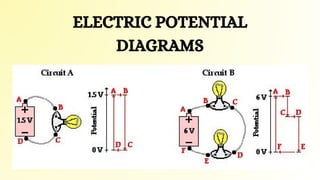
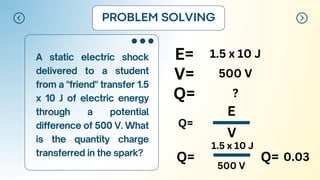
This document introduces the concept of electric potential difference. It states that the work done to move an electric charge from infinity to another point is equal to the electric potential. An electric charge has electric potential energy due to the electric field from a power supply. As the charge flows through a load, its energy decreases. The electric potential energy for each coulomb of charge in a circuit is called the electric potential difference. The document then provides an example of how electric potential difference is calculated using the equation V=E/Q, where V is potential difference, E is energy, and Q is charge.