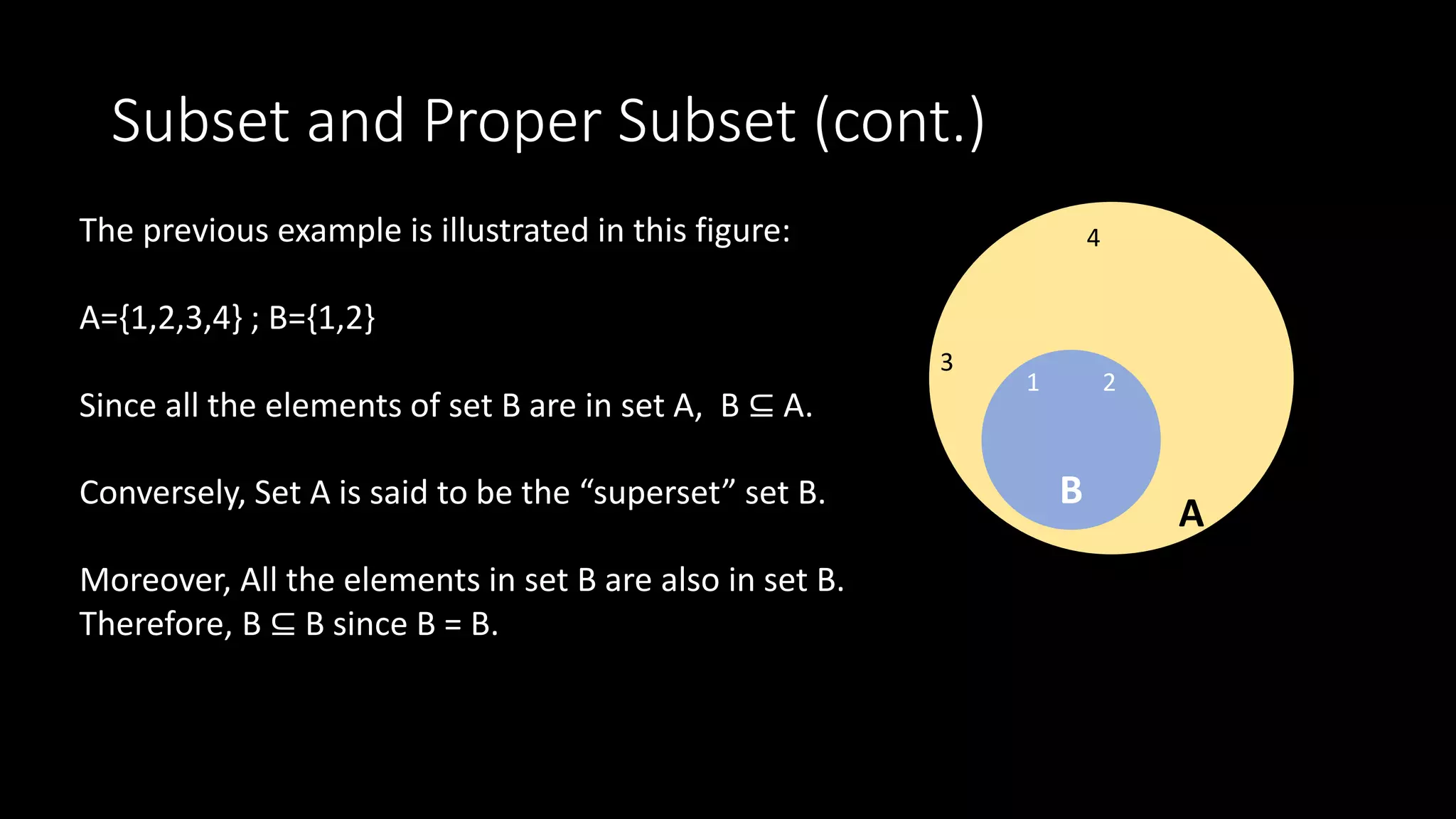
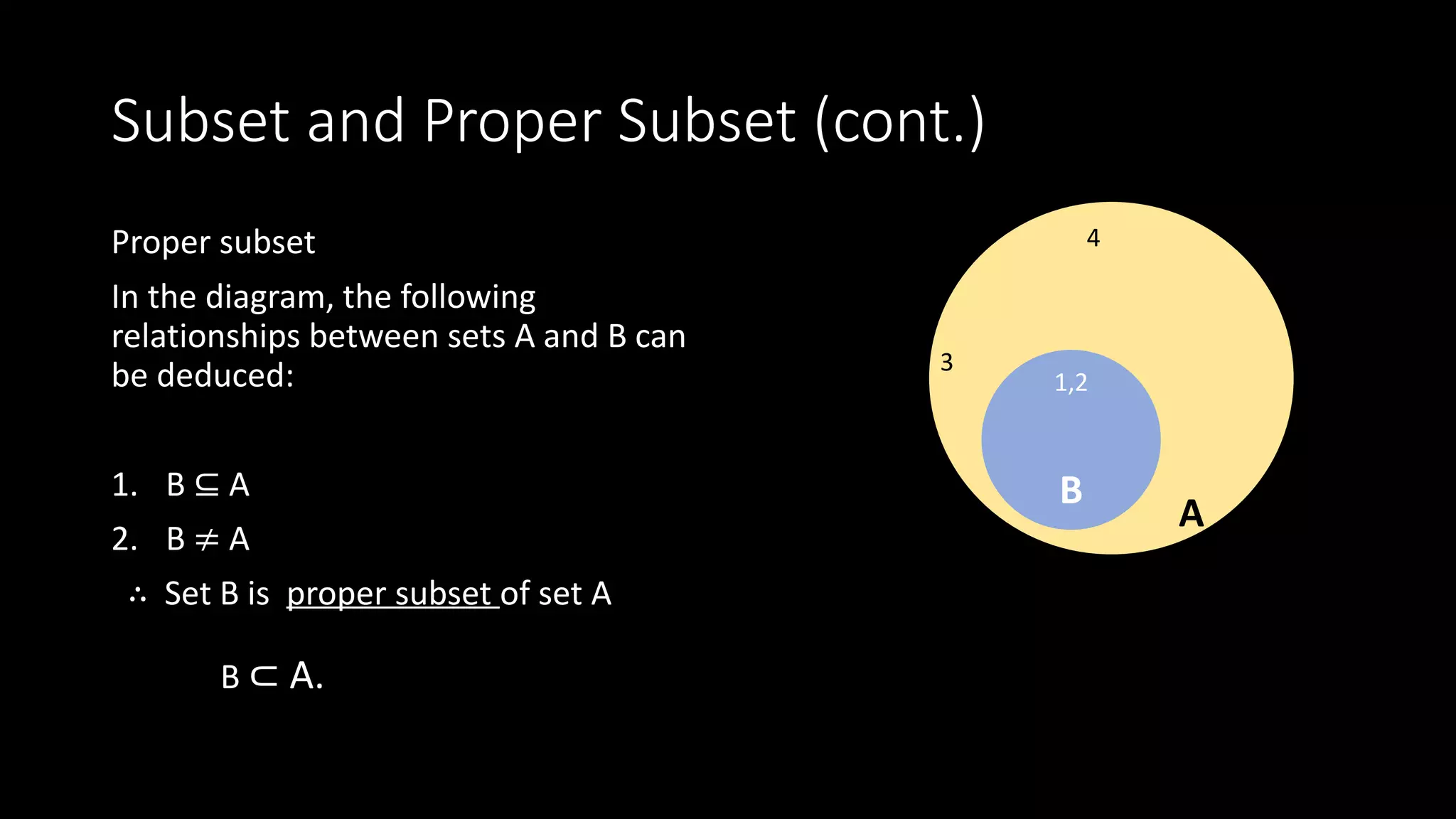
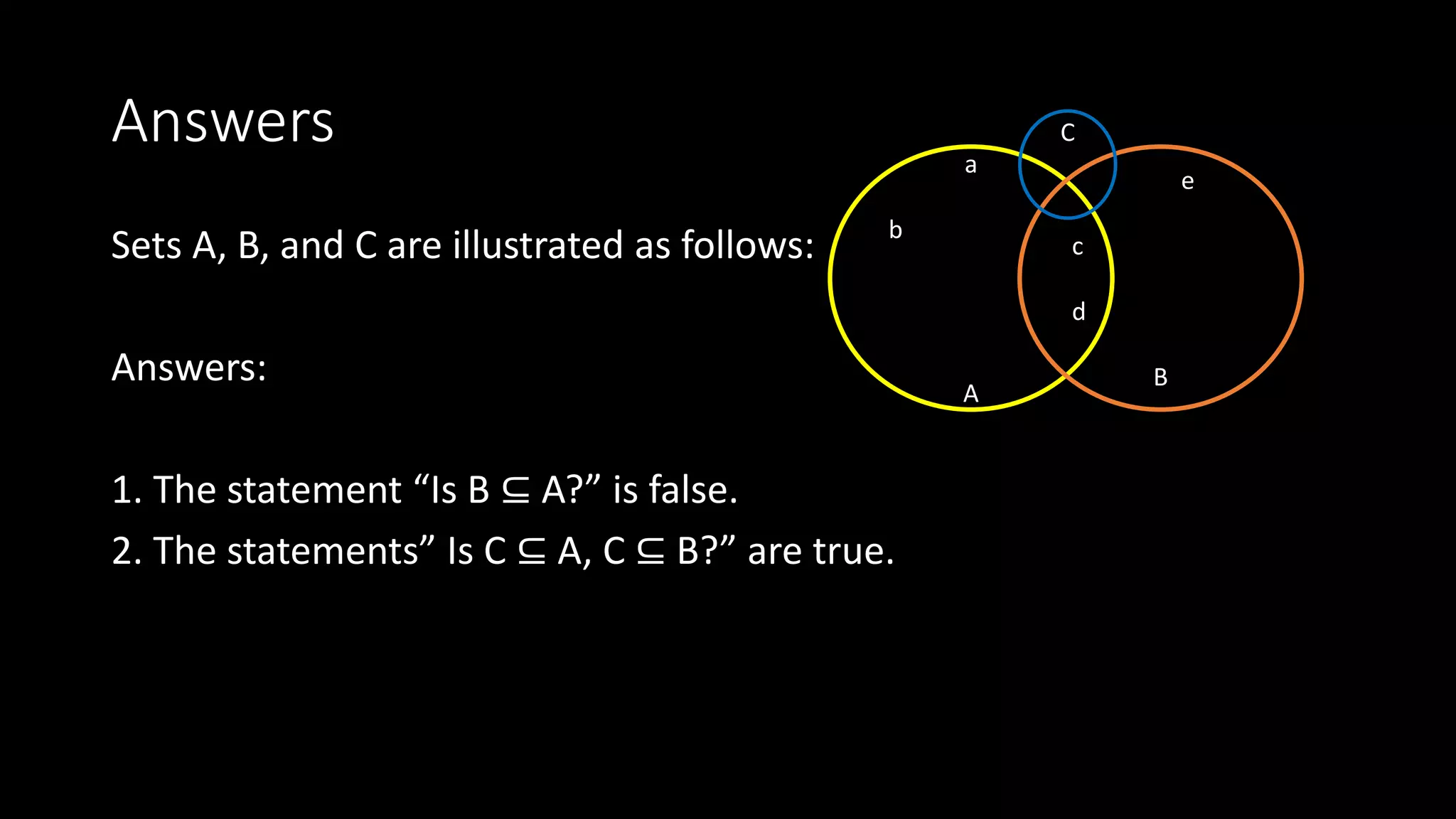
1. A subset is a set where all elements are contained within a larger set, called the superset. A proper subset is where the subset is not equal to the superset.
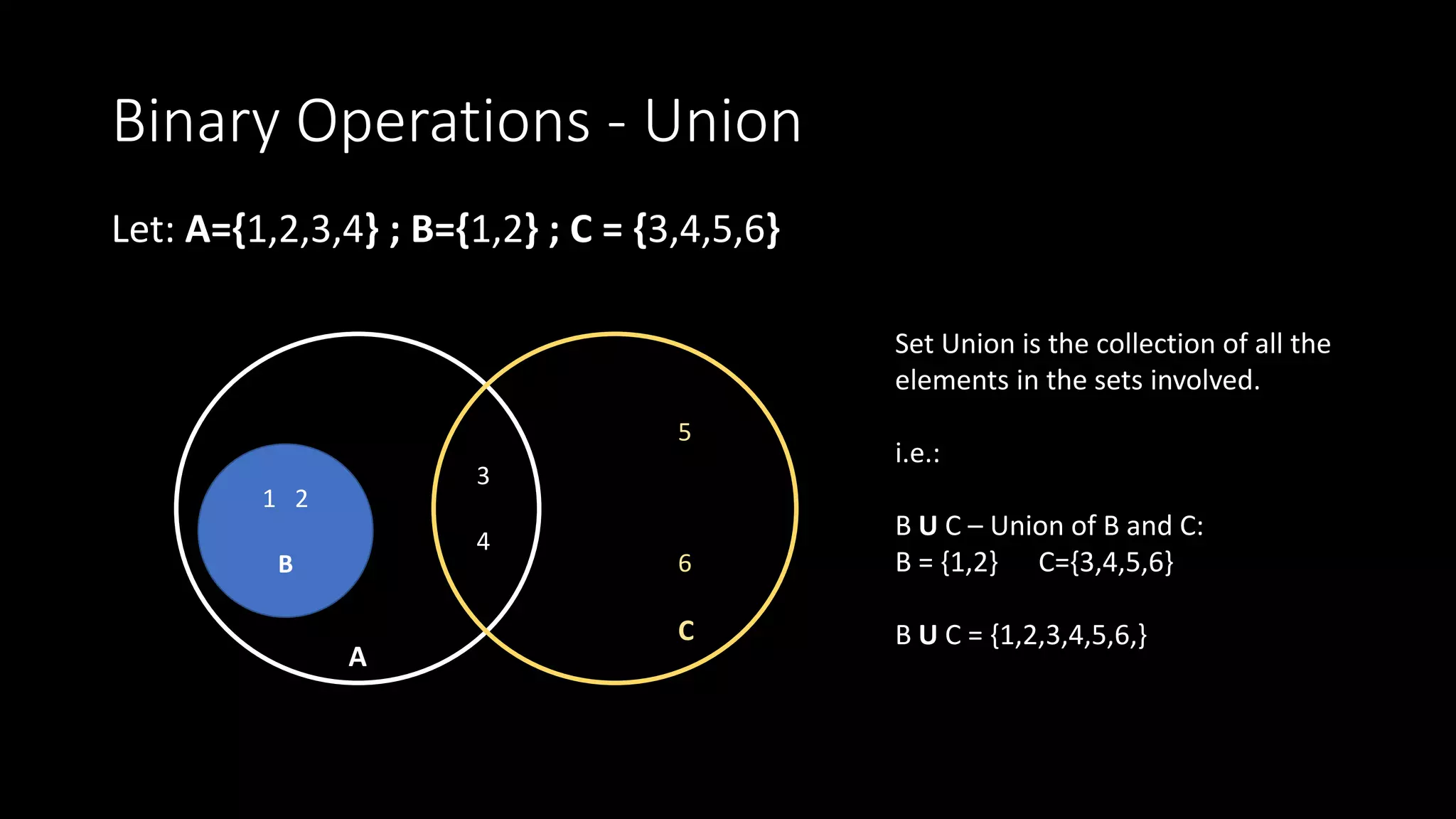
2. Set union combines all elements contained in both sets.
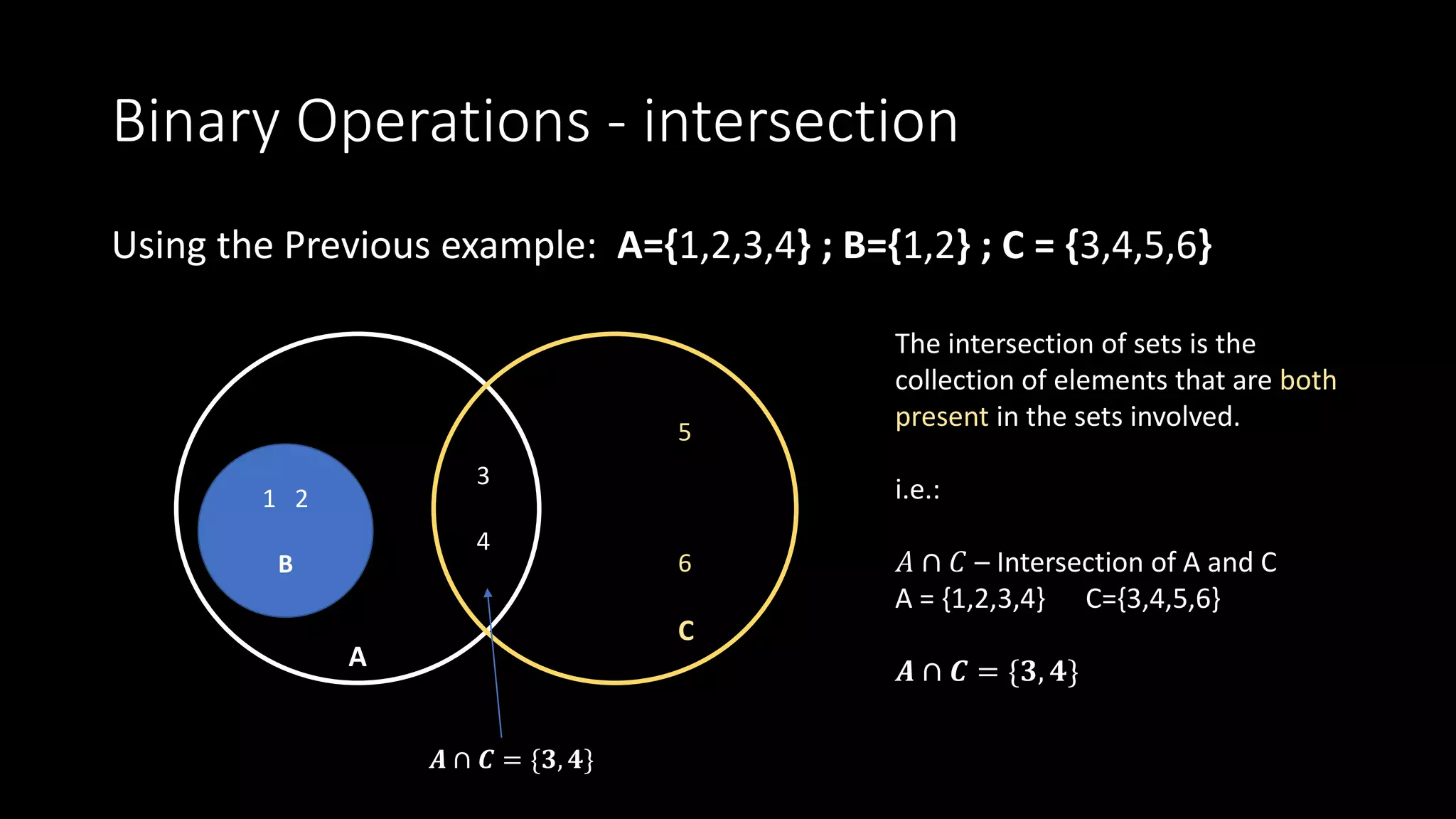
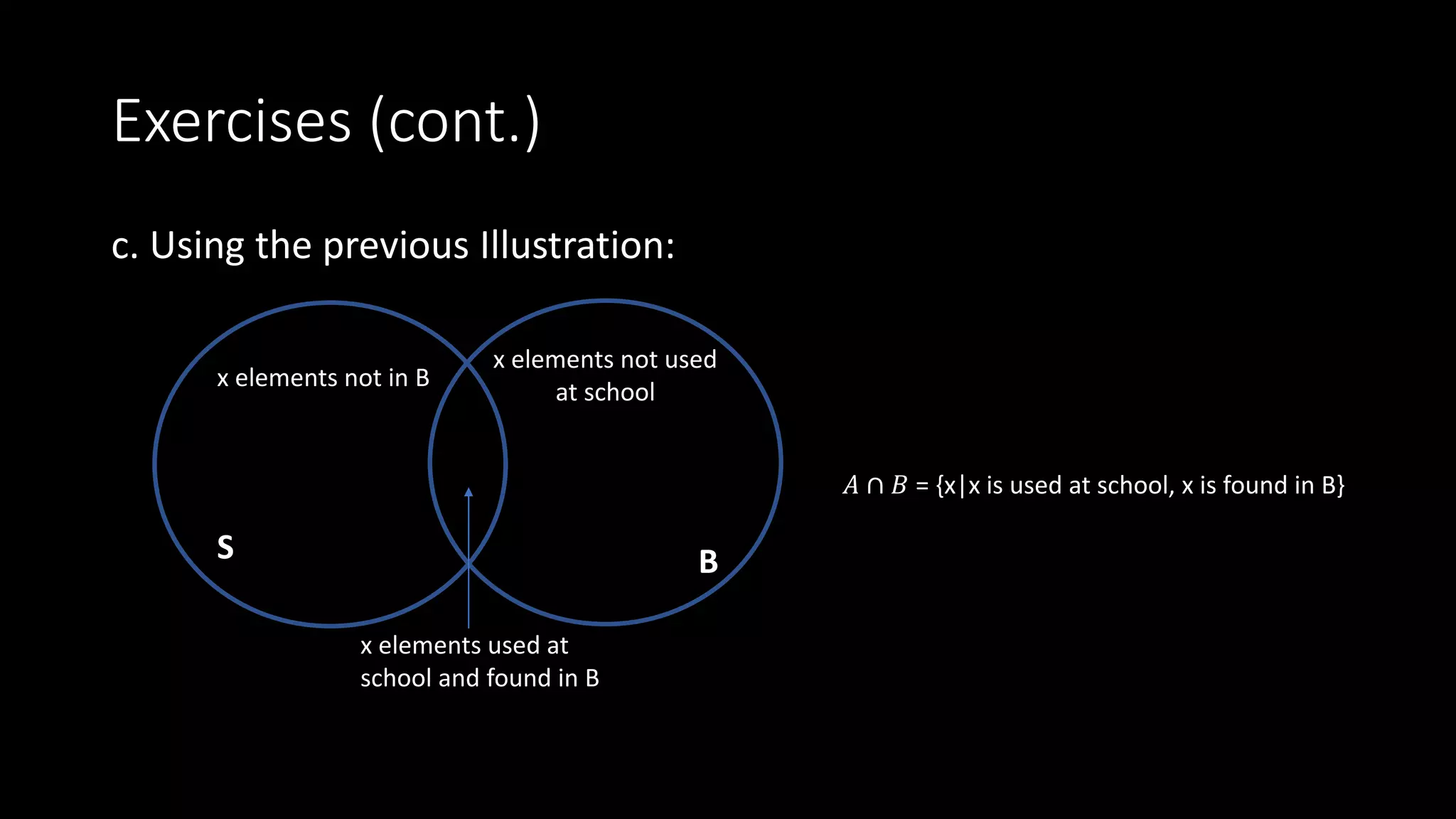
3. Set intersection filters elements to only those contained in both sets.