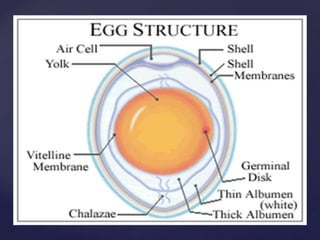
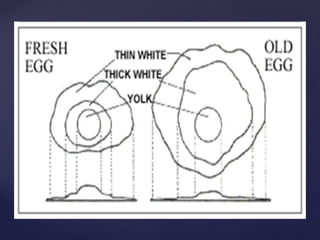
This document discusses tools and equipment for cooking eggs, the nutritional value and components of eggs, and characteristics of quality fresh eggs. It lists various utensils for serving, boiling, scrambling, frying, separating, and cracking eggs. Eggs provide high-quality protein and many vitamins and minerals. As eggs age, the air cell gets larger, the yolk flattens and breaks more easily, and the thick white becomes thin and watery. Eggs are graded A, B, or C based on qualities like yolk shape, air cell size, and shell condition.