Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

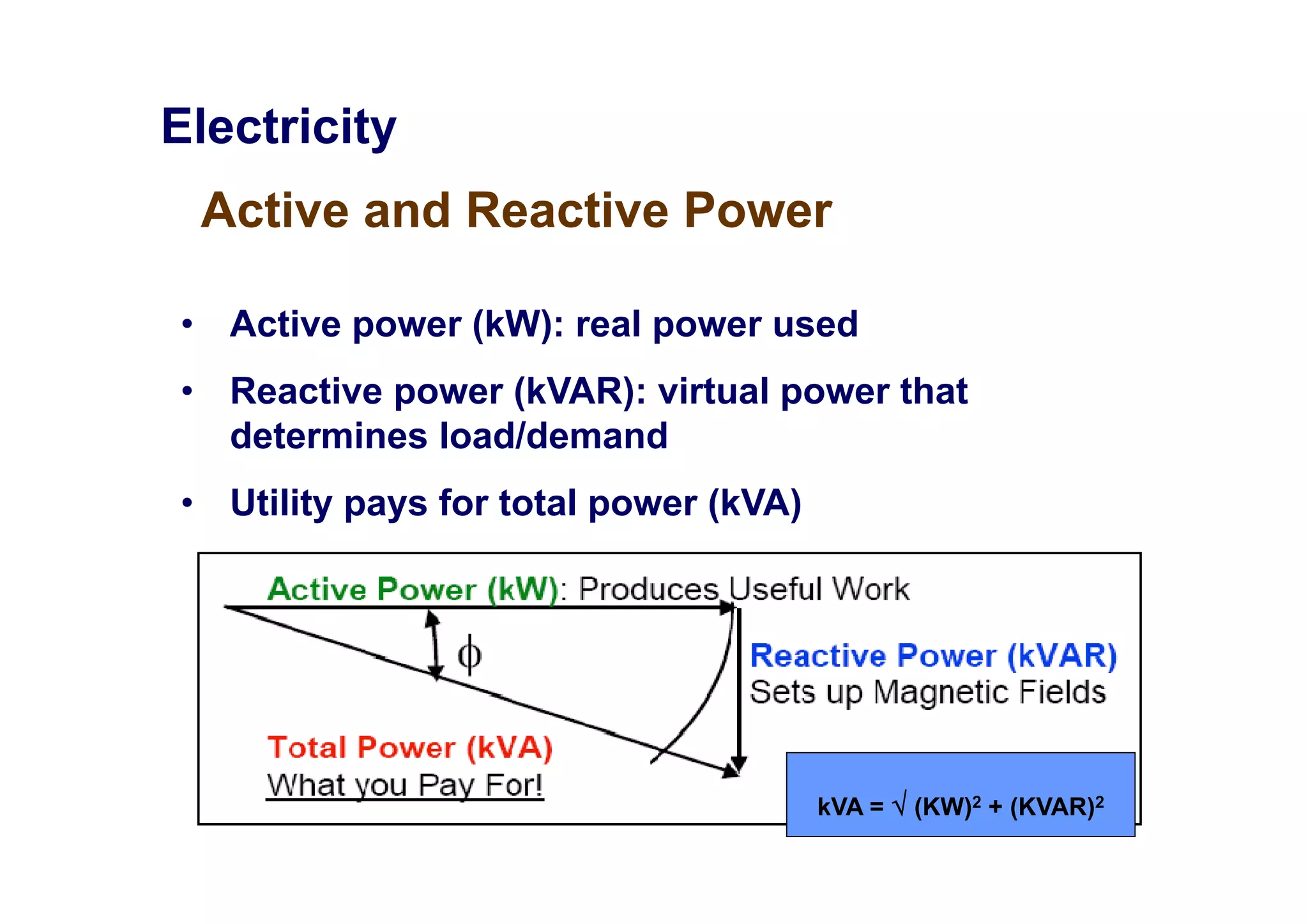
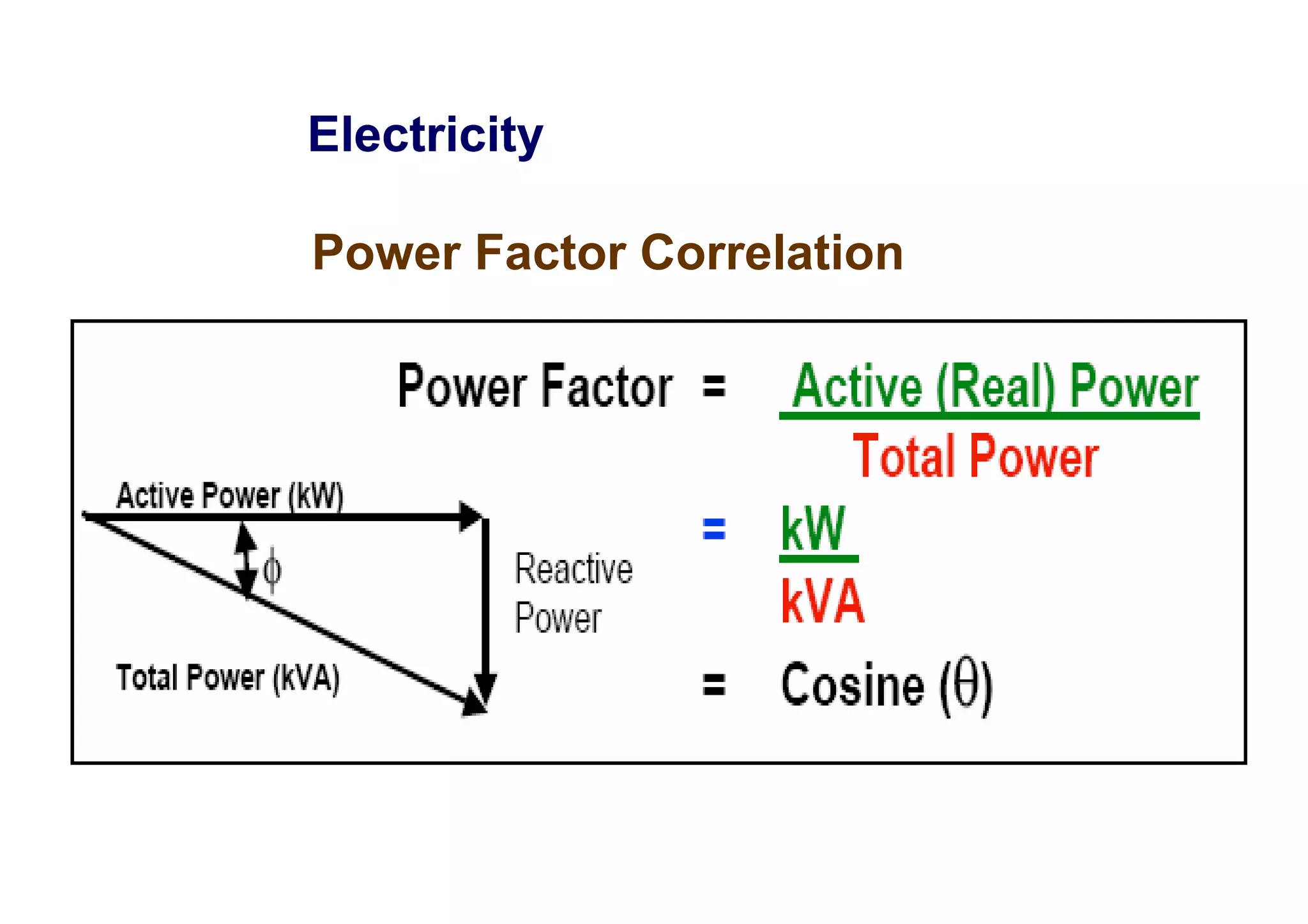
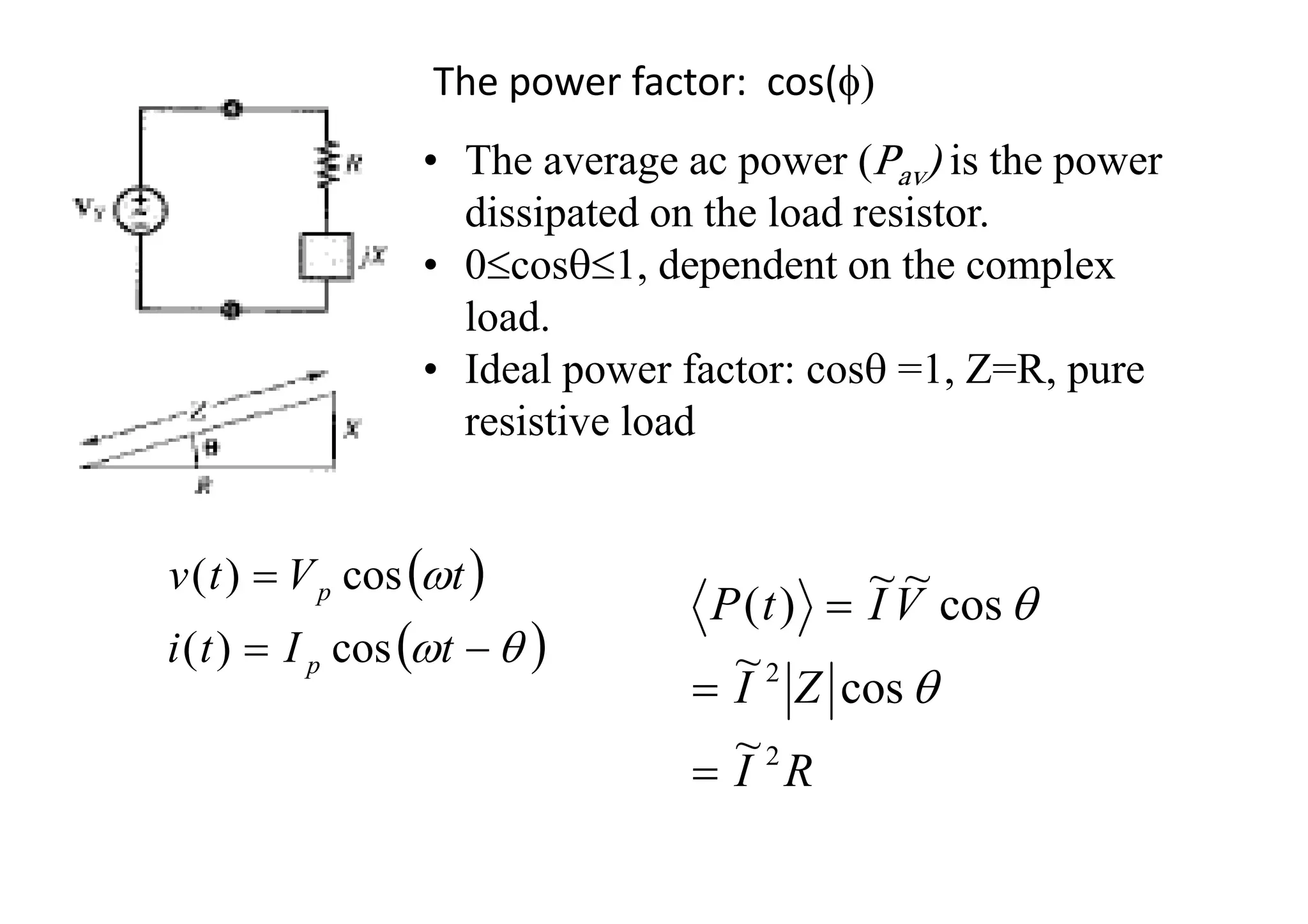
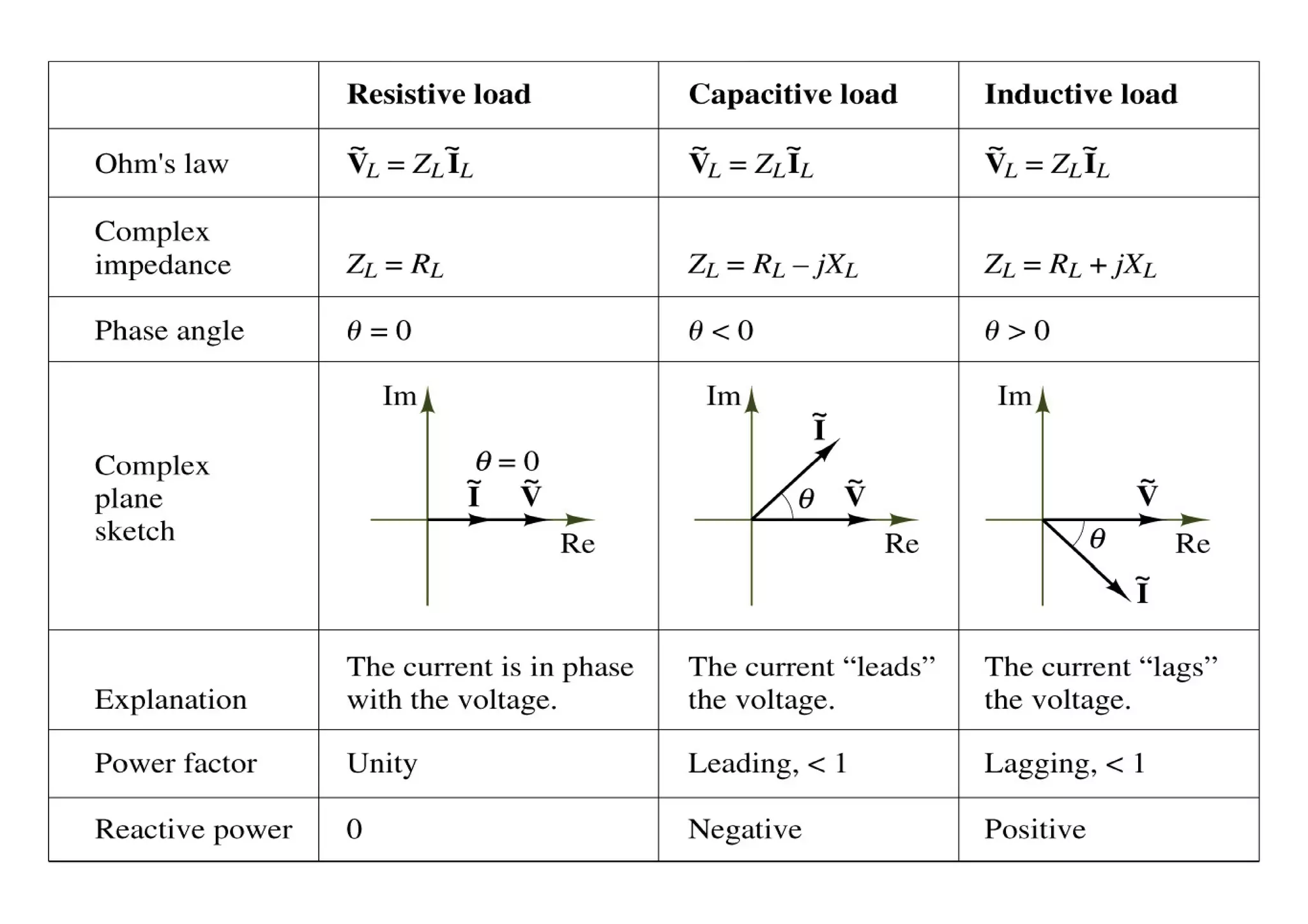


Power factor is a measurement of how efficiently an electrical power system is being used. It is the ratio of the real power consumed by a load to the apparent power flowing in a circuit. Reactive power does not perform work but contributes to energy loss. A power factor of 1 is ideal, with only real power being used. The utility charges for total power used based on apparent power, so consumers aim for a power factor close to 1 to reduce costs.





