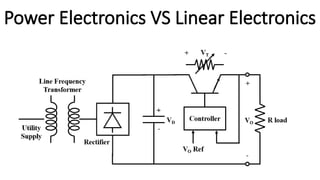
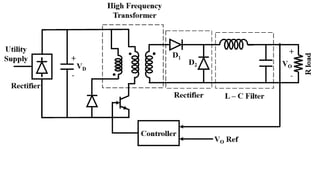
Power electronics is a field that applies electronics principles to control and convert electrical energy at high power levels, contrasting with electronics engineering which focuses on low power signals and data. It encompasses power engineering and involves the processing of significant electrical energy, with devices operating in switching modes for improved efficiency. Key differences with linear electronics include power handling, efficiency, size, and thermal management, highlighting the advantages of power electronics in various applications.