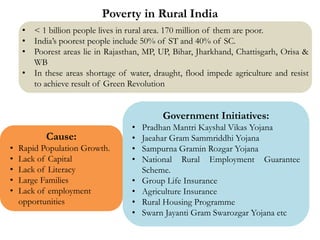
Poverty remains a significant problem in India, with over 27.5% of the population living below the poverty line. Poverty is most prevalent in rural areas, where nearly 75% of poor Indians live on $1 or less per day. The causes of poverty include rapid population growth, lack of education and employment opportunities, and dependence on agriculture. While the Indian government has implemented various initiatives to reduce poverty, such as employment guarantee schemes and rural development programs, poverty continues to disproportionately impact disadvantaged groups like Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes. Achieving truly inclusive growth and eliminating poverty will require expanded access to resources, education, and entrepreneurship opportunities across India.