Embed presentation
Download to read offline






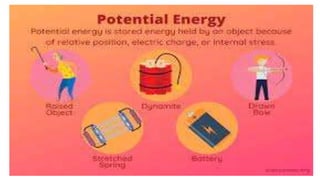


This document discusses potential, kinetic, and total energy. It defines potential energy as stored energy using the equation PE = (m) (g) (h), where m is mass, g is gravitational acceleration, and h is height. Kinetic energy is defined as the energy of motion using the equation KE = 1/2 mv^2, where m is mass and v is velocity. Sample problems are provided to calculate the potential energy of a book lifted 0.5 m and the kinetic energy of a 150 kg object moving at 15 m/s. Exercises at the end ask the reader to calculate the kinetic energy of 100 kg and 250 kg objects moving at 12 m/s and 15 m/s, respectively, using








