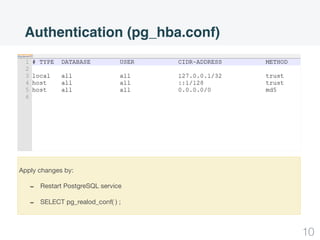
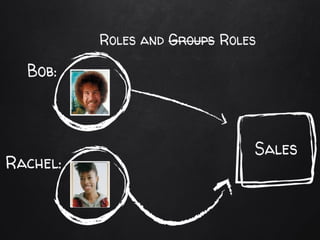
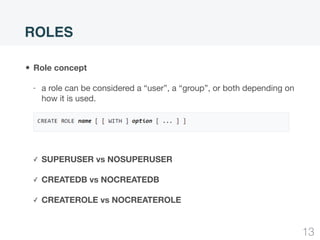
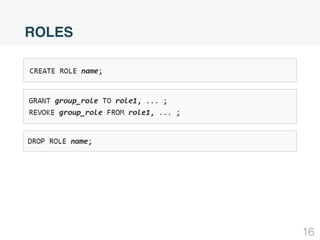
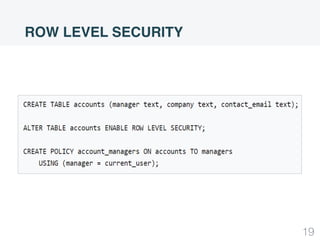
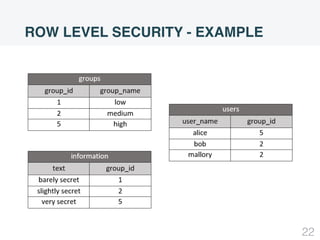
This document summarizes security concepts in PostgreSQL including authentication, roles, and row-level security. It begins with an introduction comparing PostgreSQL and MySQL. Authentication methods in PostgreSQL include password, peer, and LDAP authentication configured via pg_hba.conf. Roles in PostgreSQL define privileges and inheritance and include attributes like SUPERUSER, LOGIN, and INHERIT. Row-level security controls access at the row level and examples demonstrate how to configure policies and the default policy.