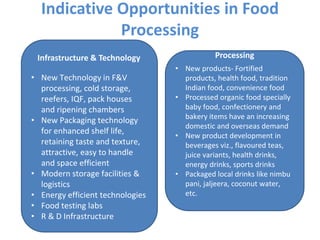
The document discusses opportunities in the Indian food processing industry. It notes that food production in India is likely to double in the next 10 years, with the food and grocery market projected to grow to $482 billion by 2020. However, it also reports that post-harvest losses of major agricultural produces in India are estimated at $13.6 billion annually due to lack of modern practices and infrastructure for storage, logistics, transportation, processing and distribution. The document outlines opportunities for investment and growth in the food processing sector to reduce losses and add value through cold chain infrastructure, packaging, new technologies and processing of fruits, vegetables, dairy and poultry. Fiscal incentives are provided by the government to encourage investment in this sector.