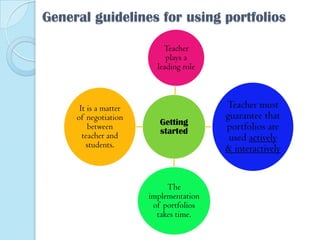
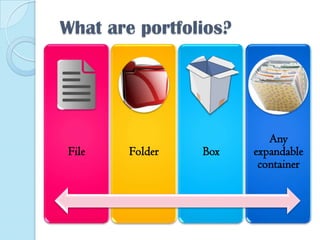
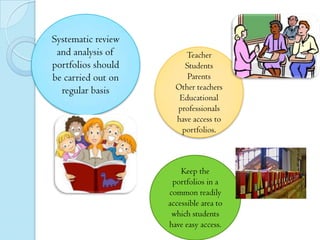
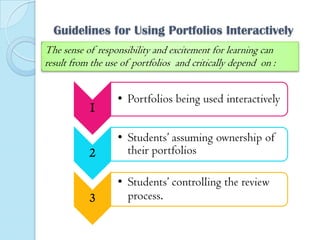
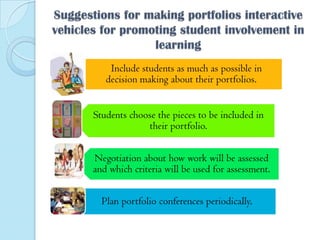
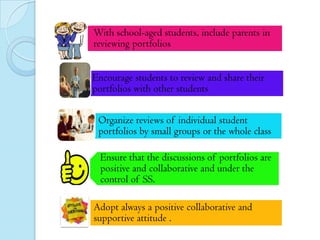
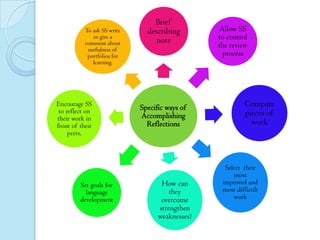
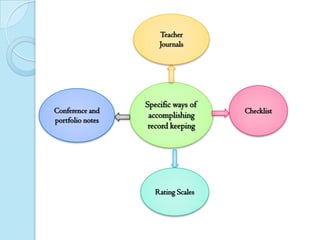
This document discusses portfolios and conferences as assessment tools. It provides definitions and benefits of portfolios and conferences, as well as general guidelines for their use. Portfolios are purposeful collections of student work that demonstrate effort, progress, and achievement. They provide holistic and ongoing records of learning. Conferences allow teachers and students to discuss work, goals, and progress. When used interactively, portfolios and conferences promote student involvement and responsibility for learning.