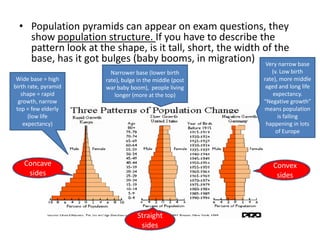
This document discusses factors influencing population changes in the UK, including declining family size, an aging population, and migration trends. The population structure has shifted as birth rates have fallen and life expectancy has increased. Internal migration has seen many move from northern cities to southern England. Internationally, the UK population has been affected by post-accession EU migration from Eastern Europe as well as retirement migration to coastal regions in Spain. Managing the impacts of these demographic changes on public services is an ongoing challenge.