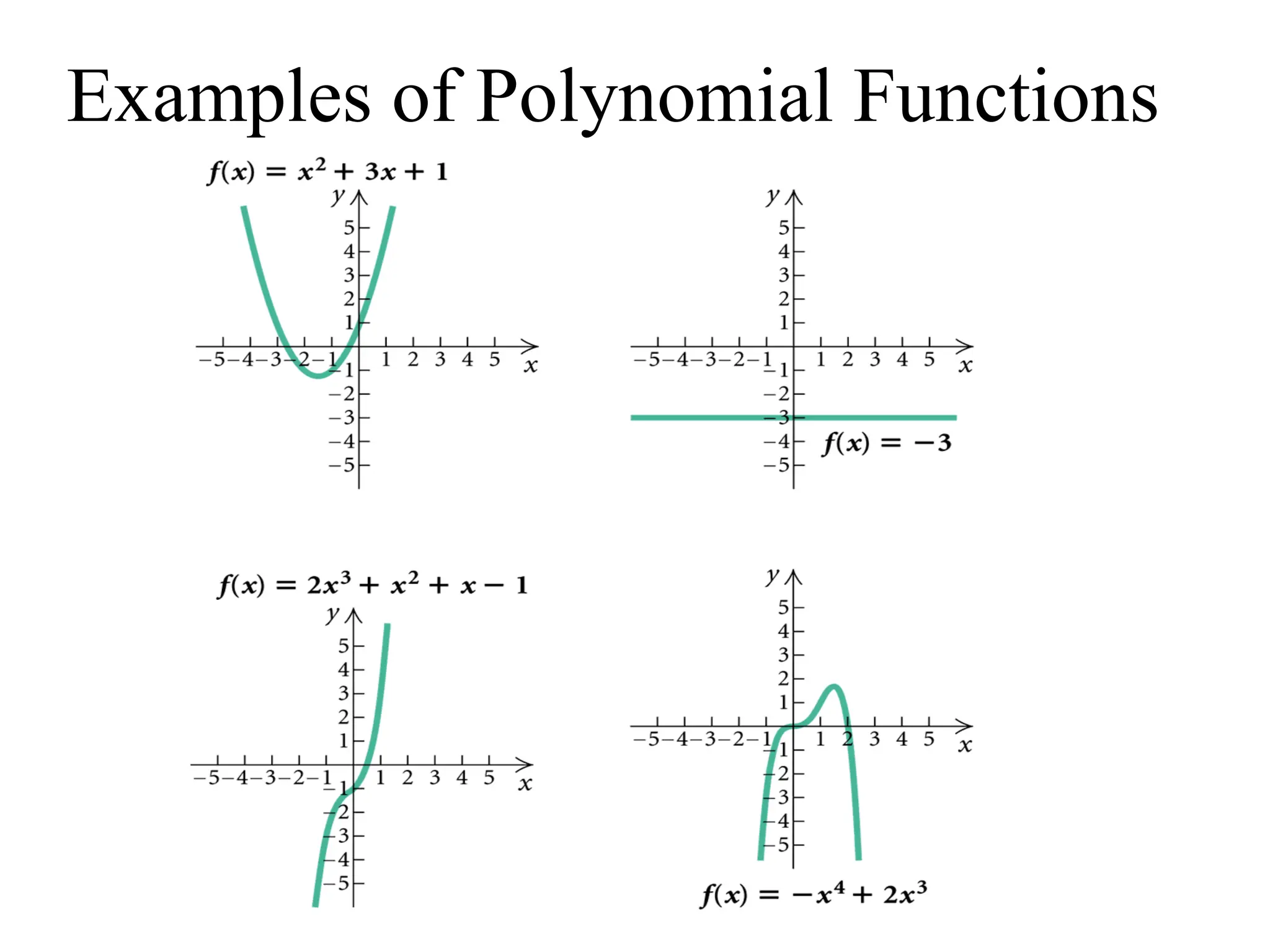
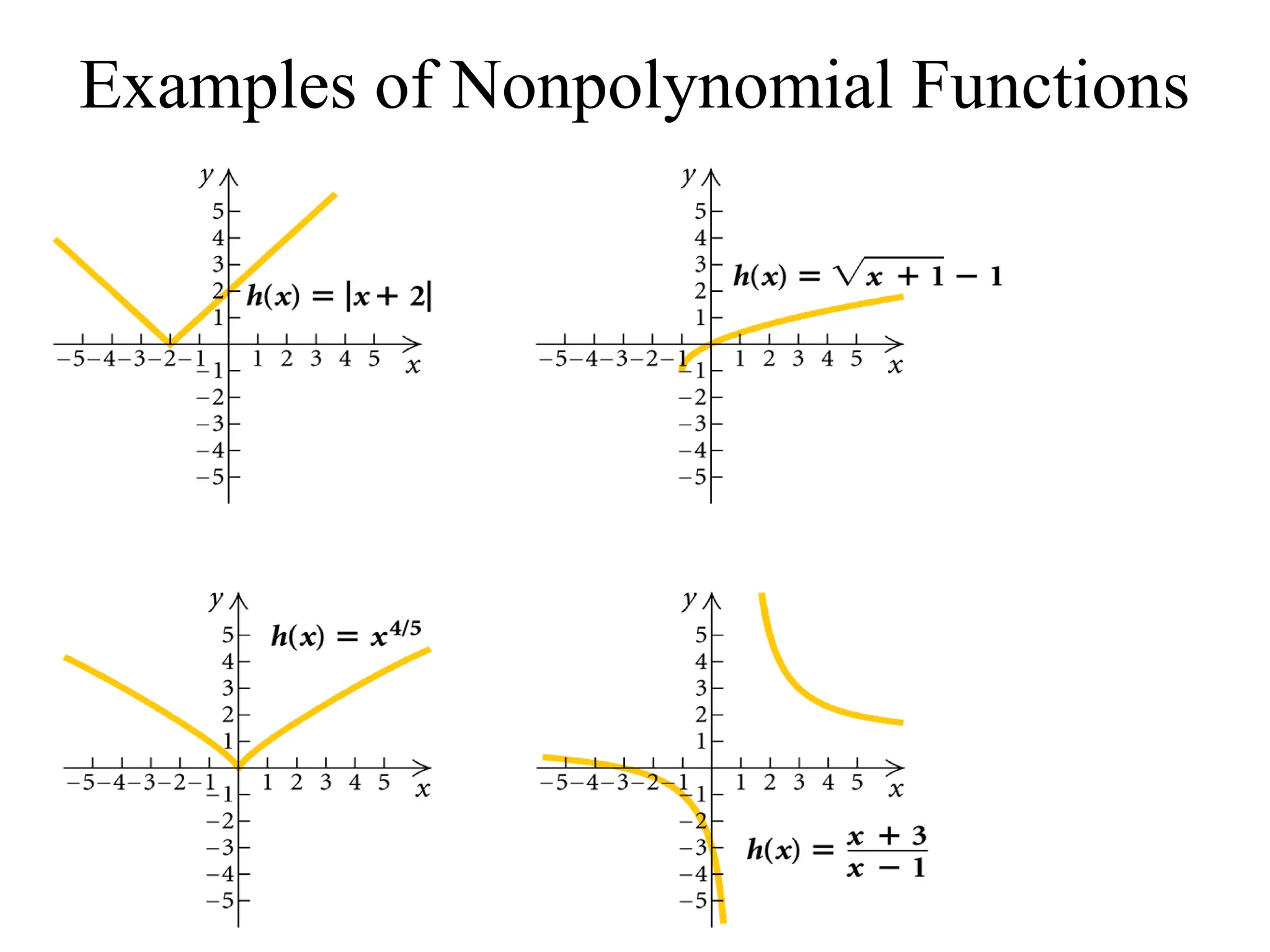
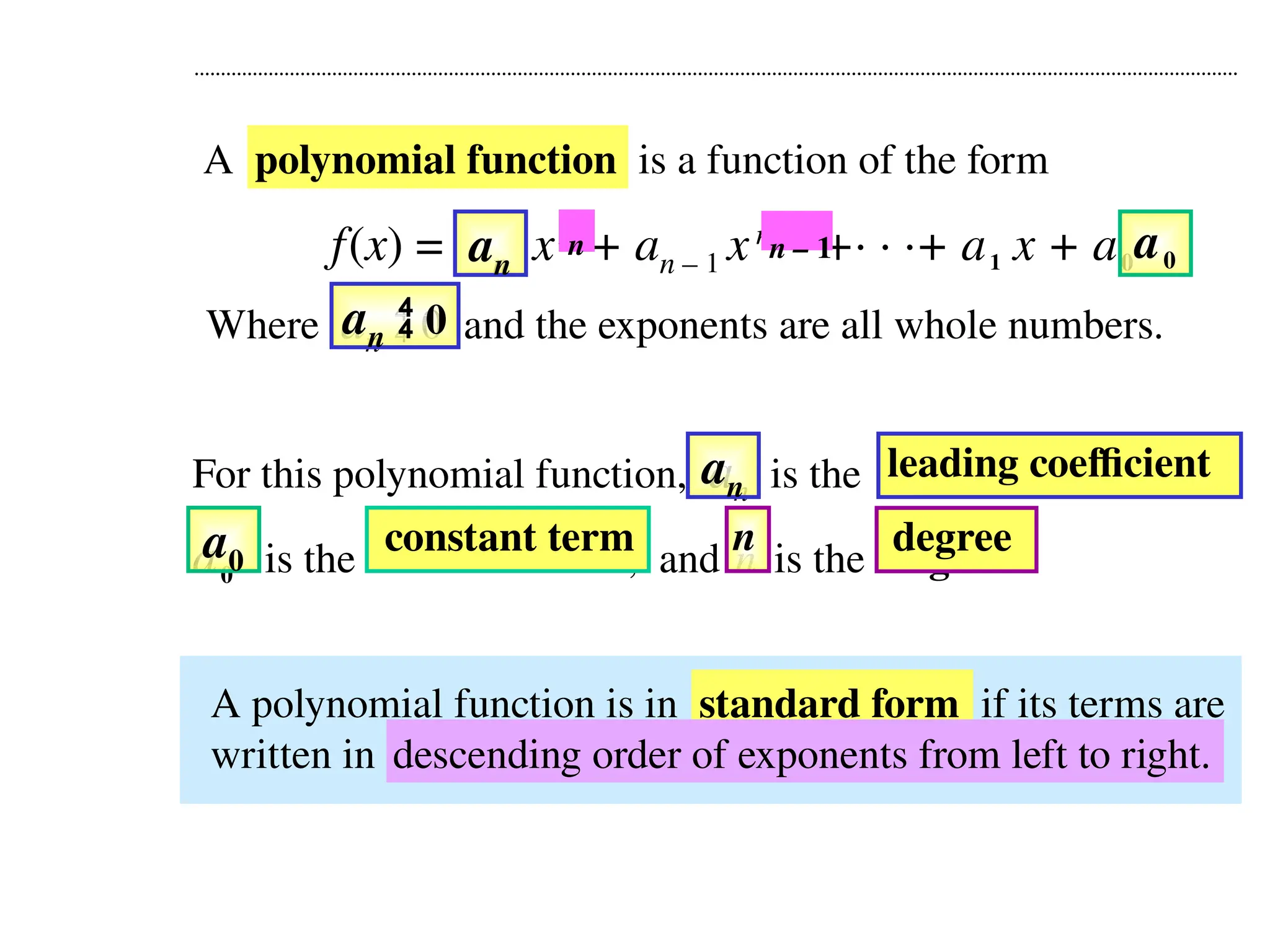
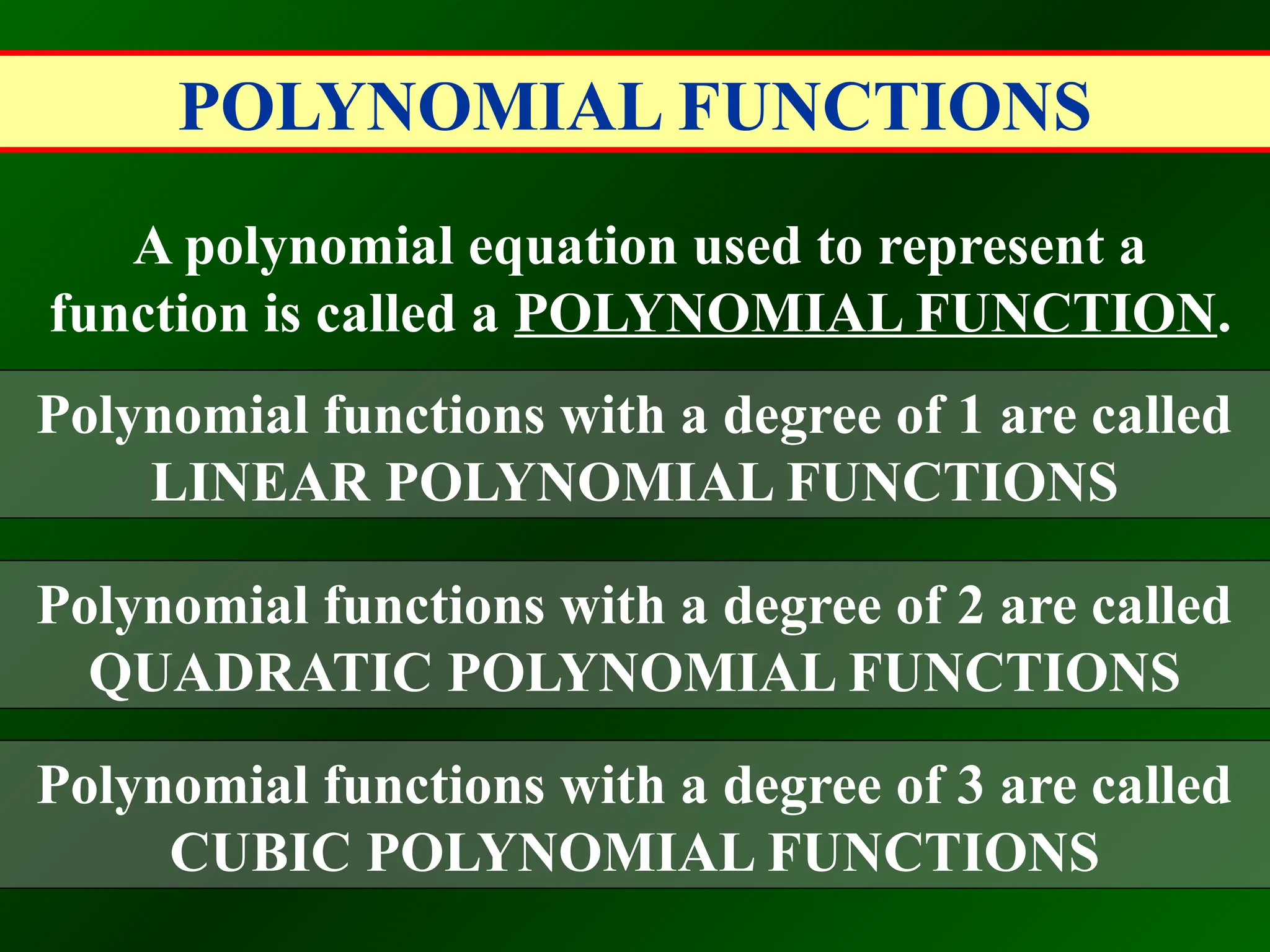
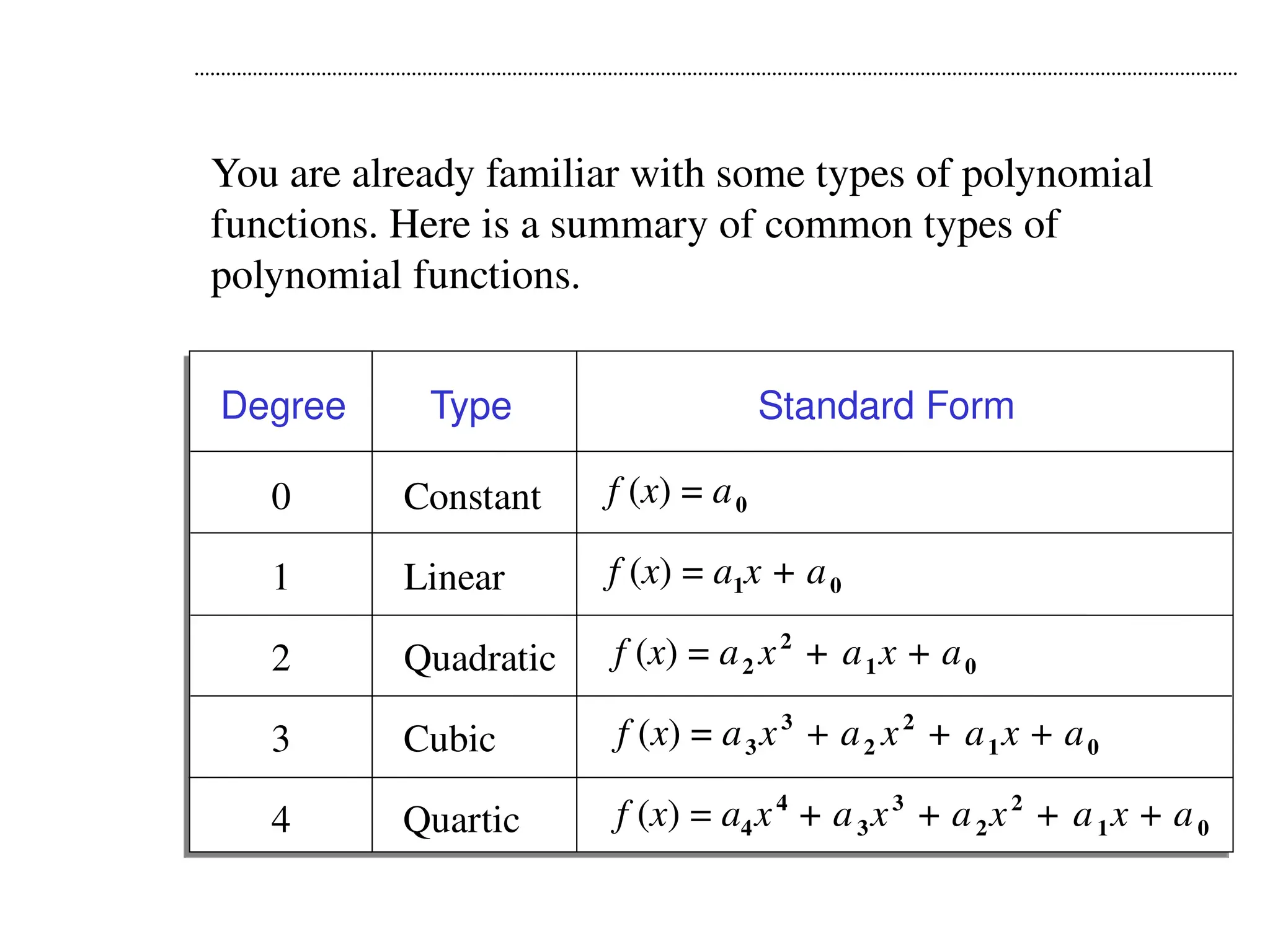
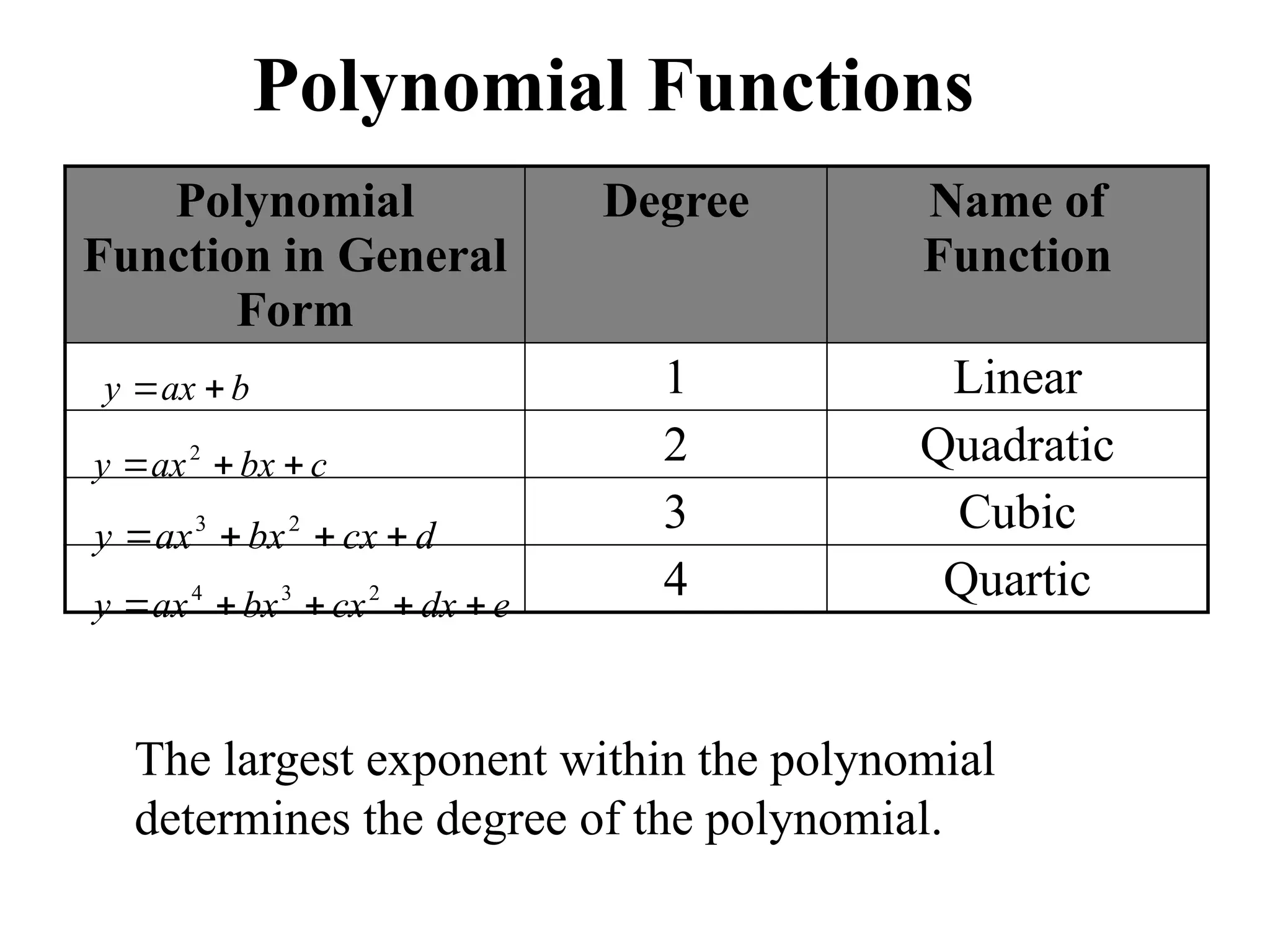
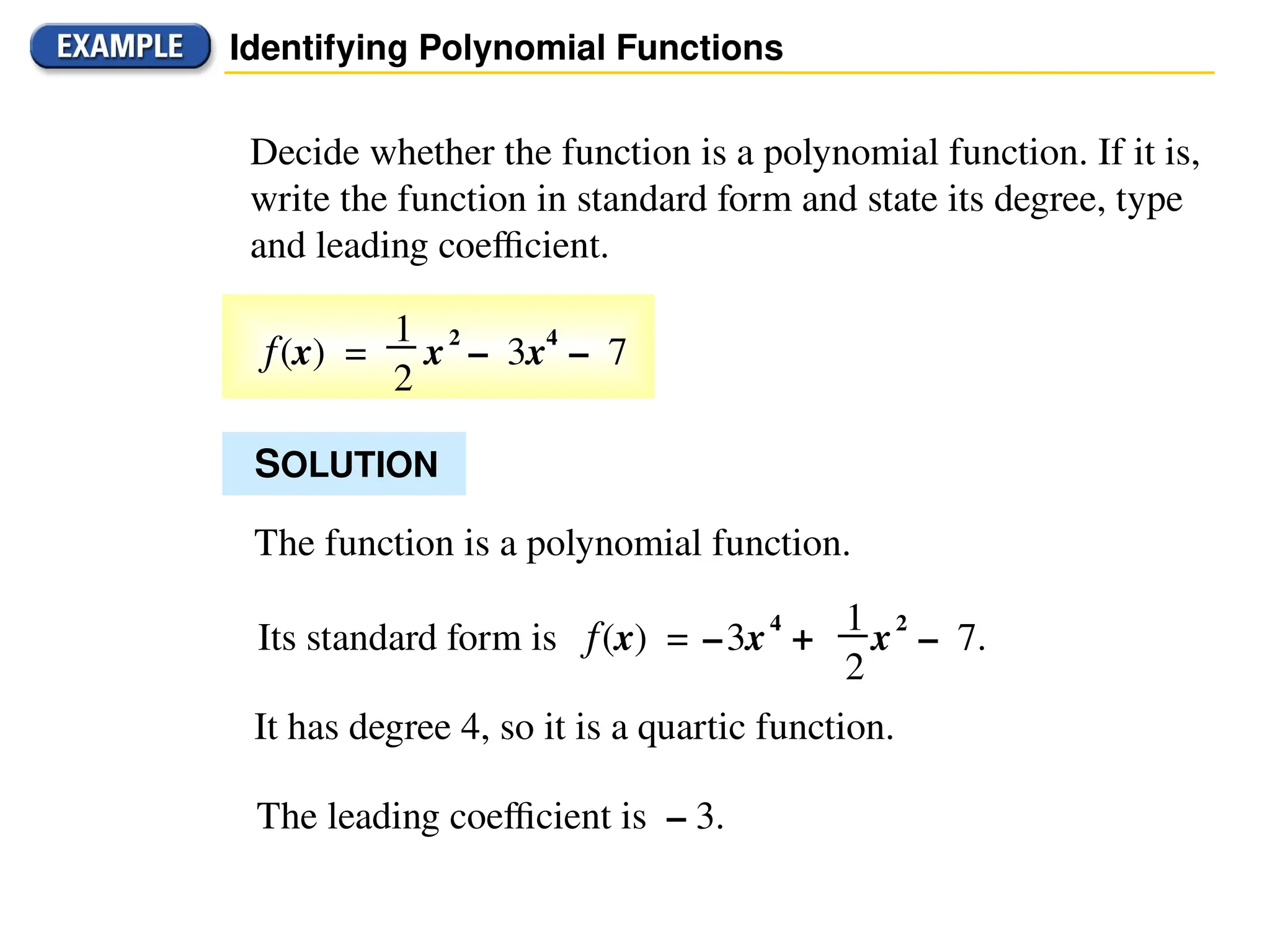
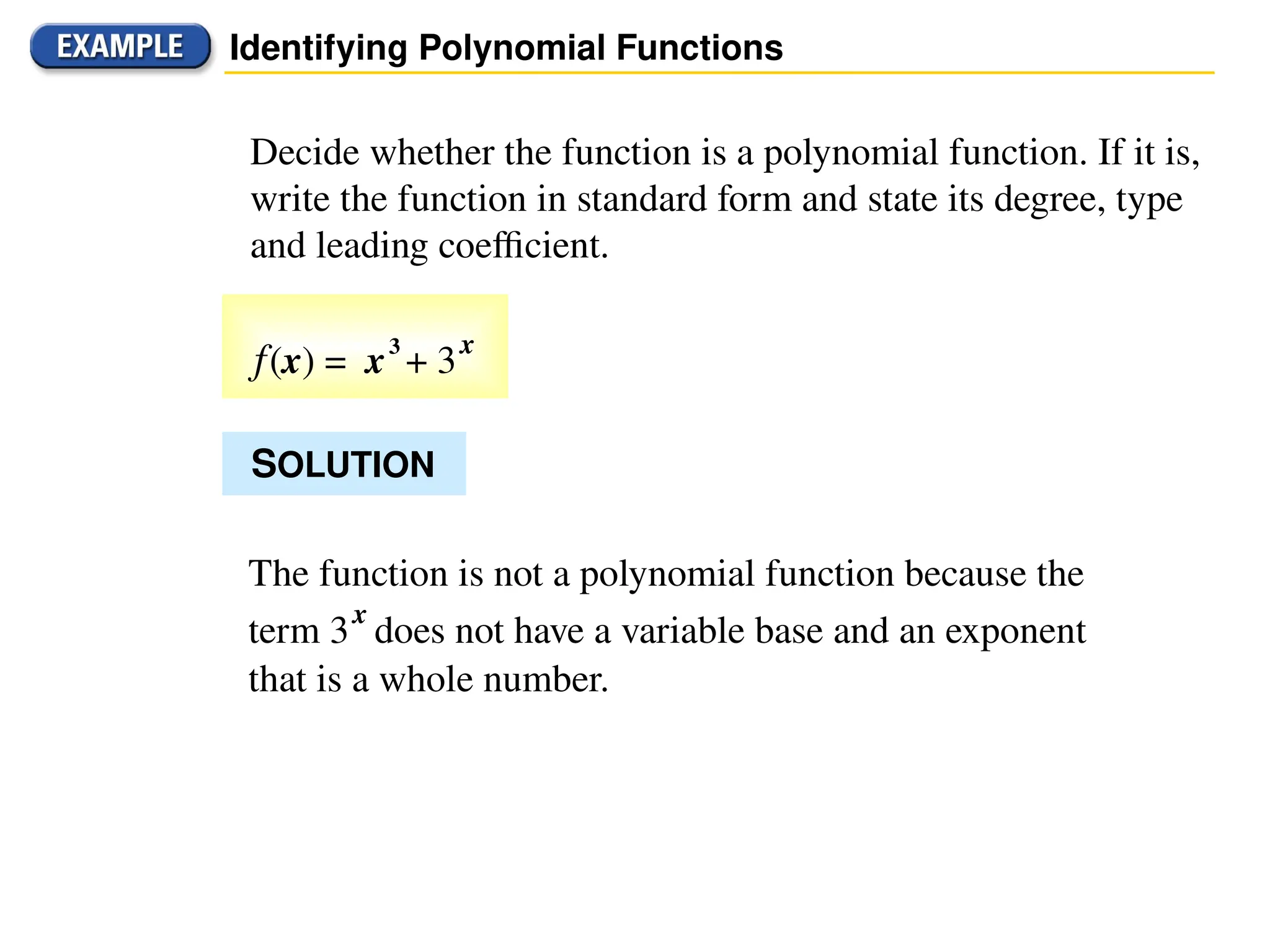
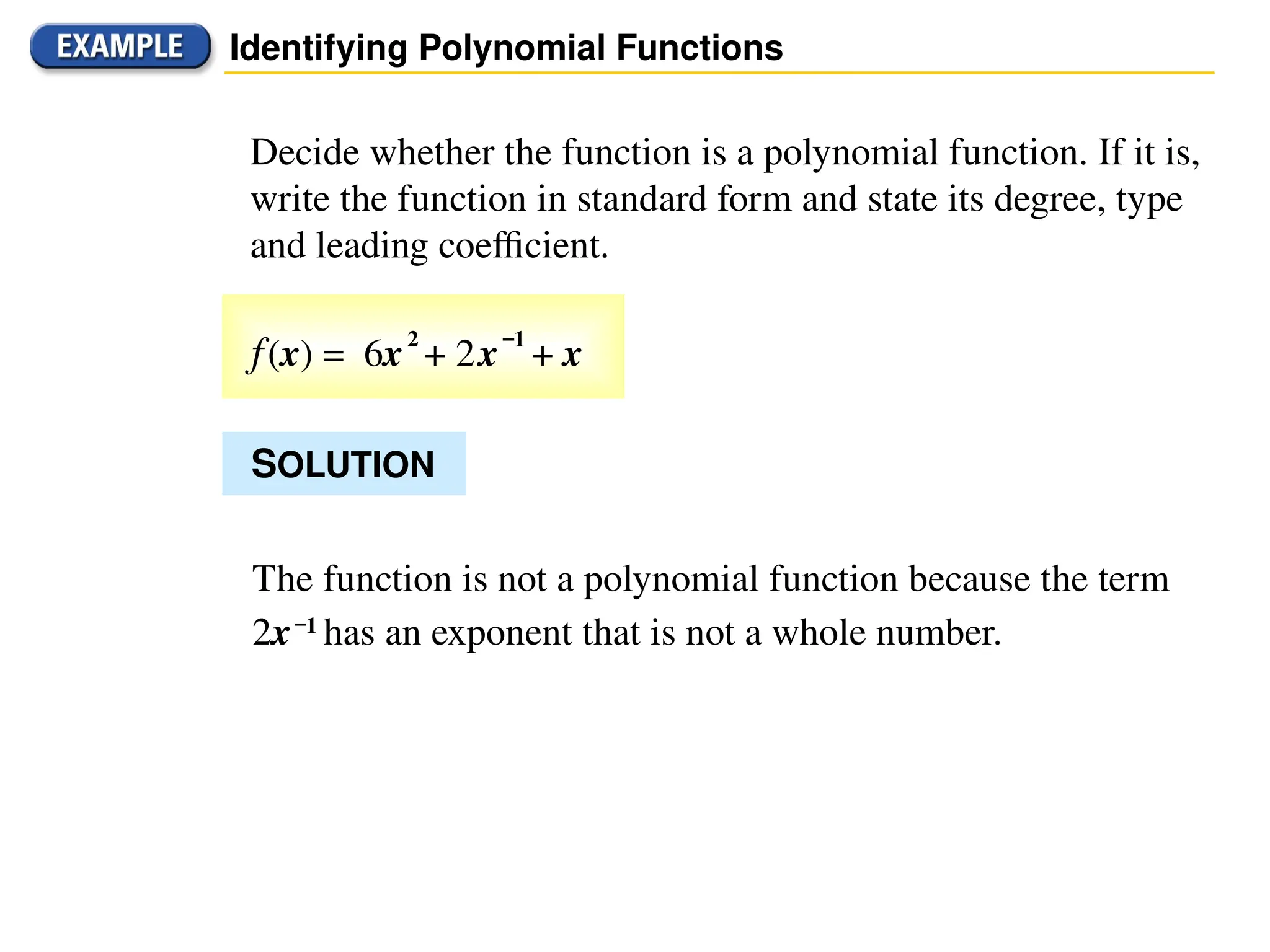
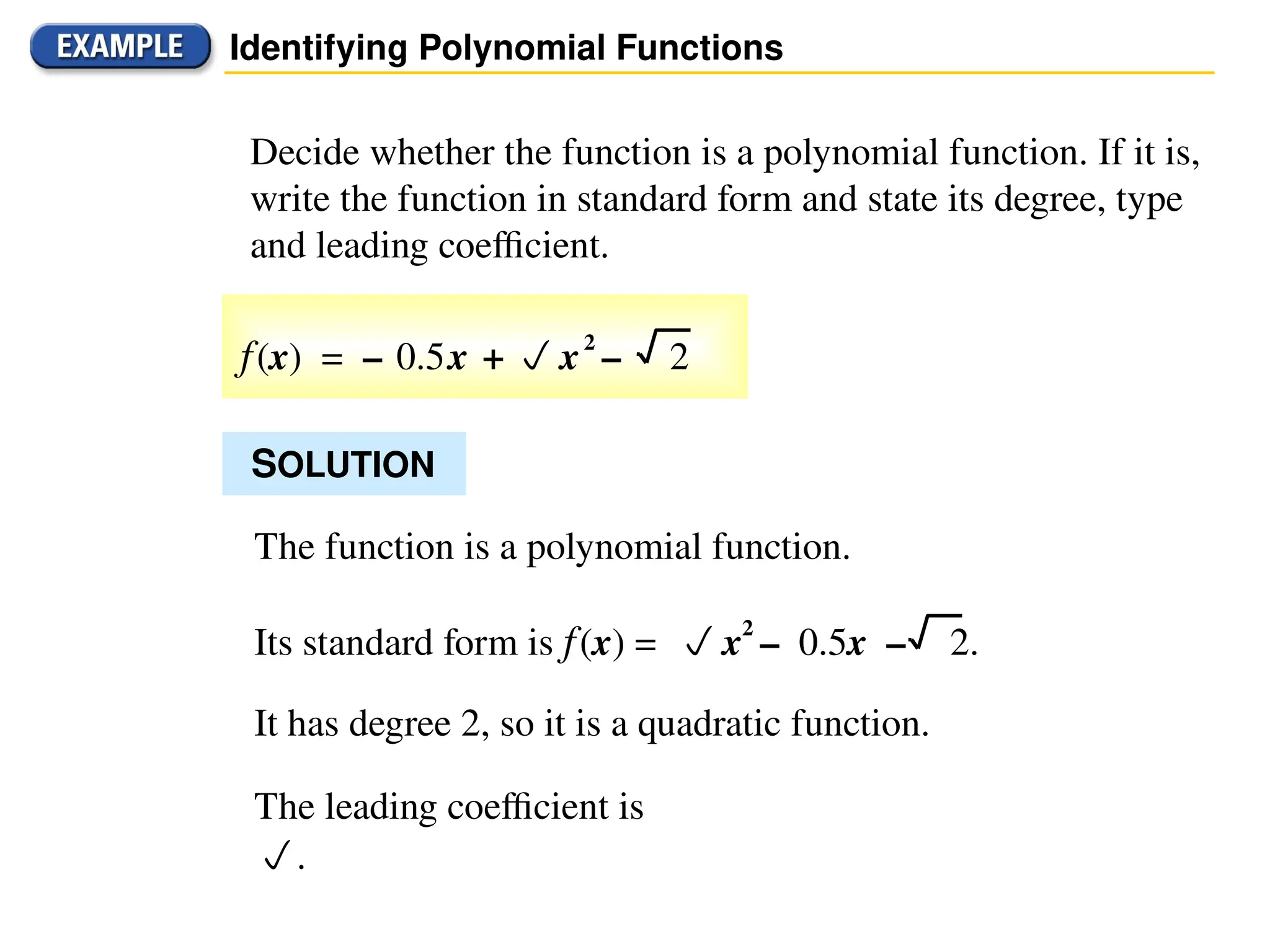
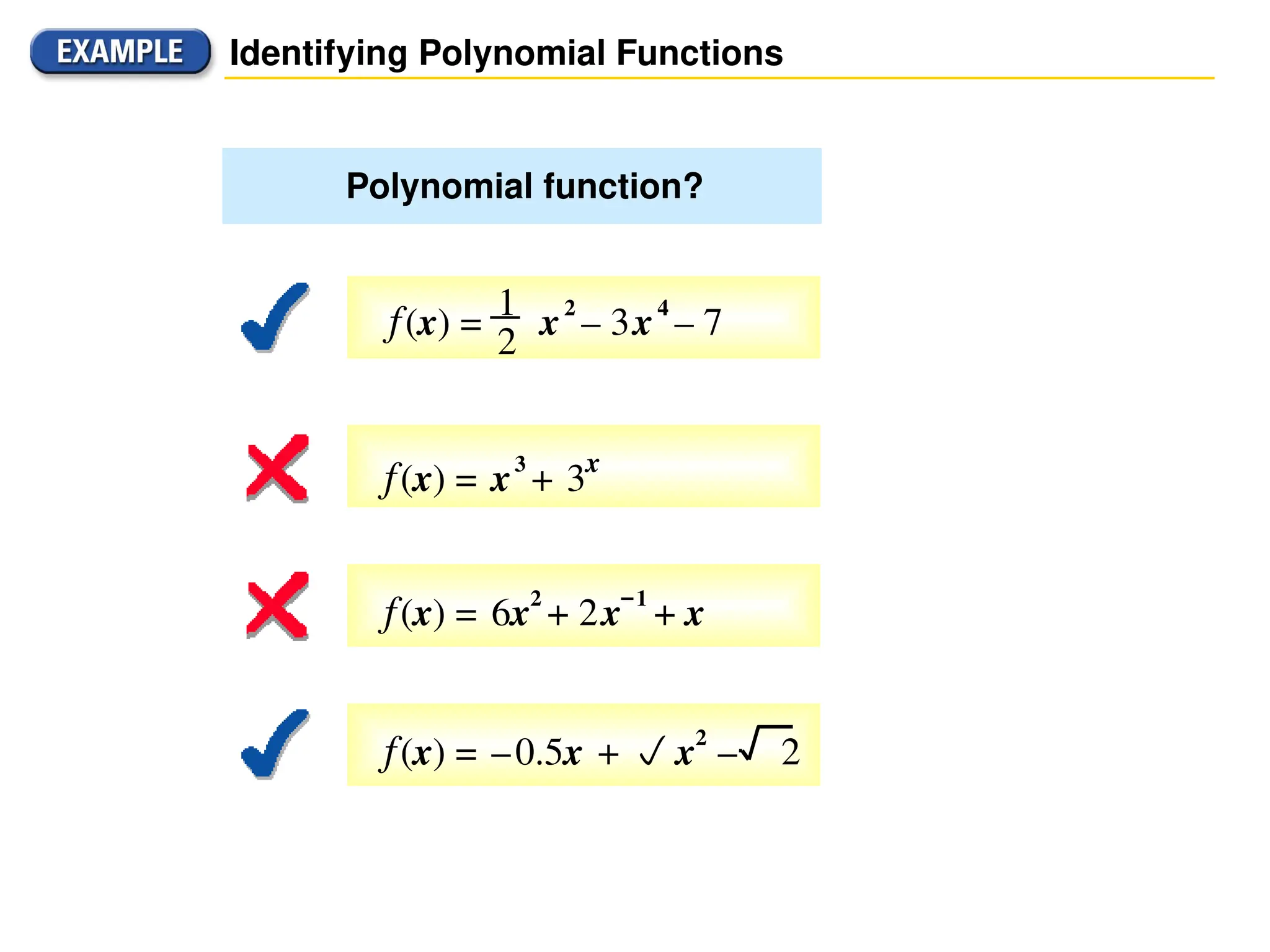
A polynomial is either a monomial or a sum of monomials, represented in functions with terms in descending order of exponents. The degree of a polynomial indicates its highest exponent, with specific names for degrees such as linear (1), quadratic (2), cubic (3), and quartic (4). The document also discusses identifying polynomial functions, determining their degree and leading coefficients, and provides examples of both polynomial and non-polynomial functions.



![POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS
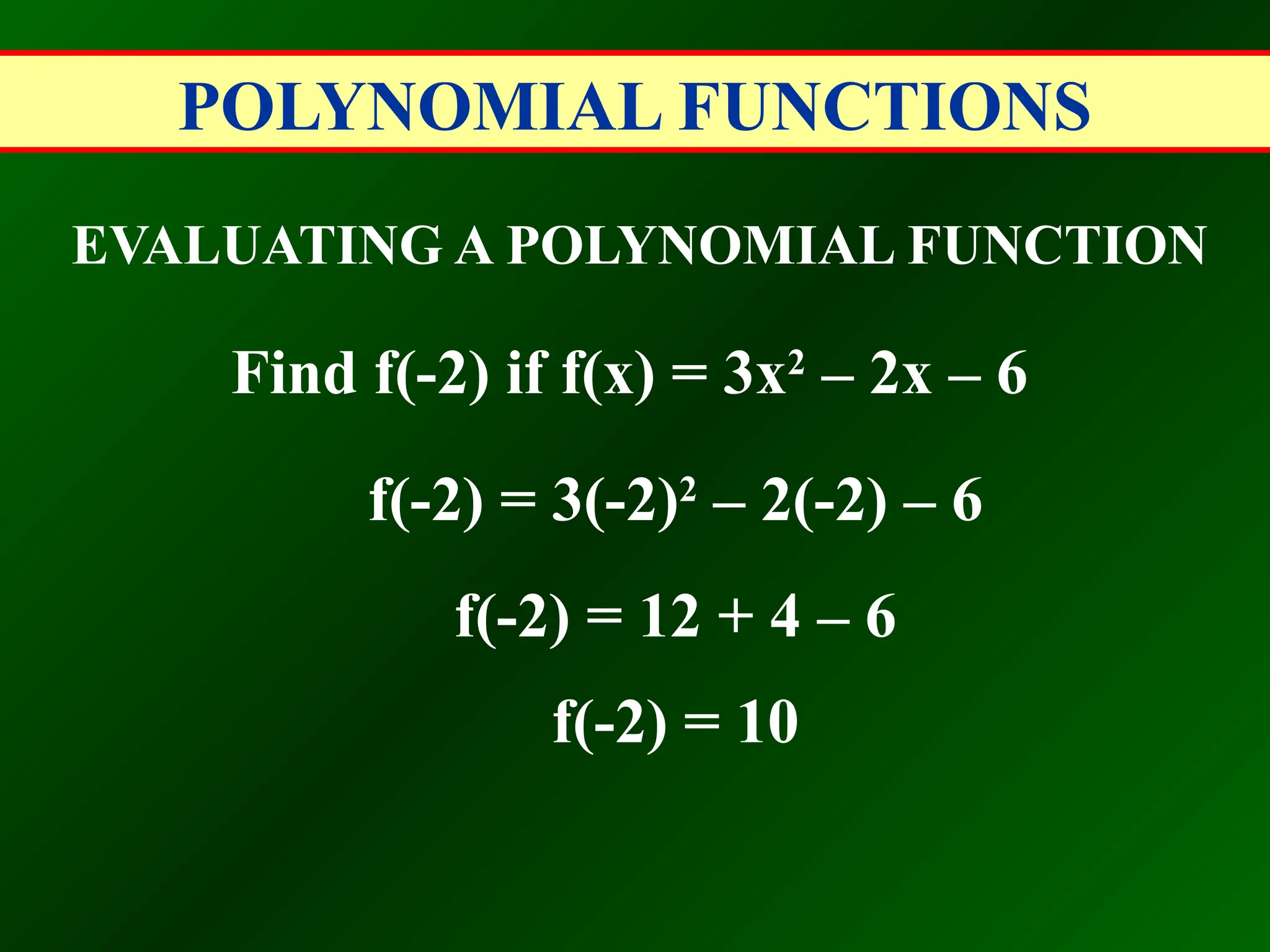
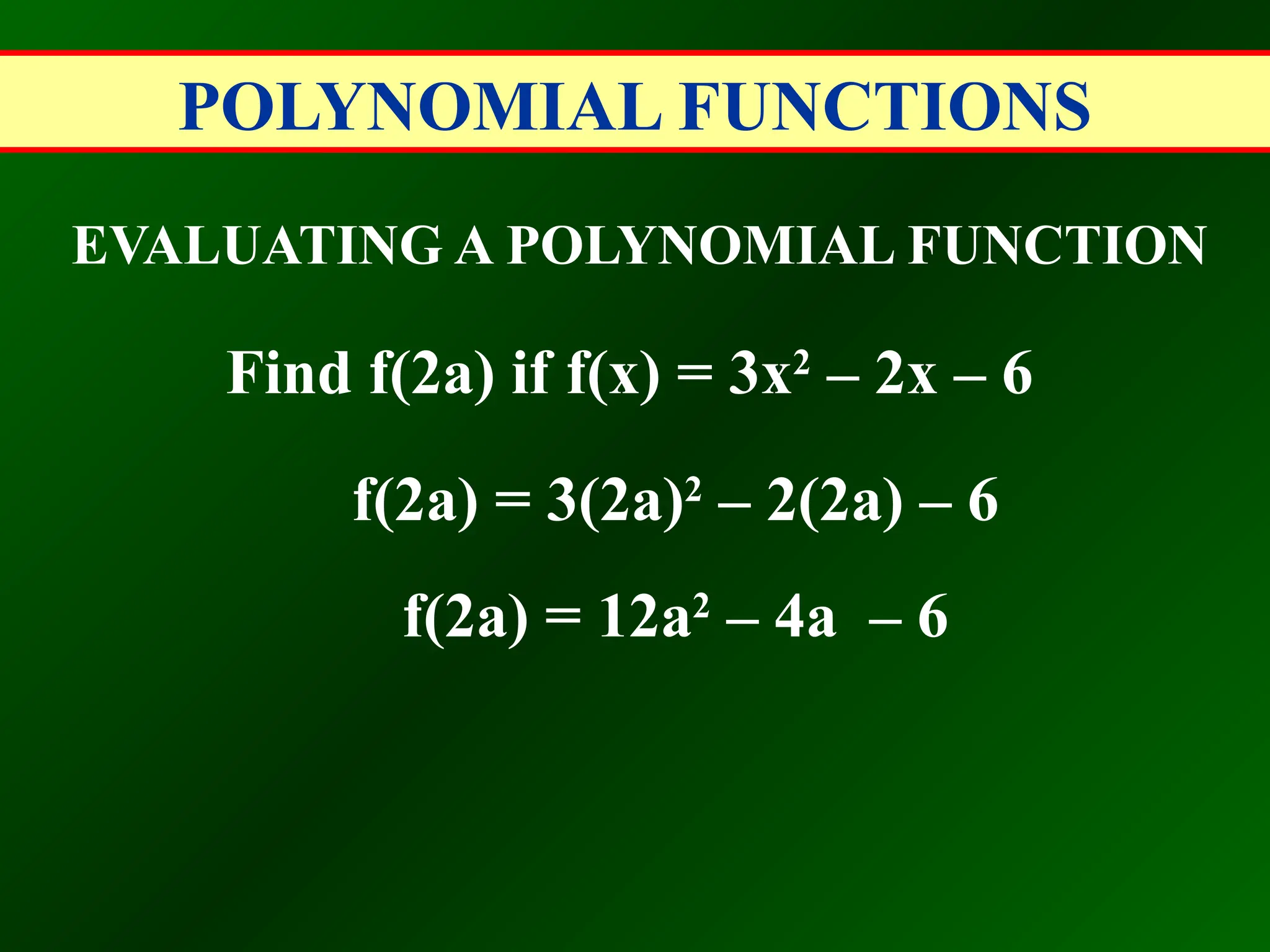
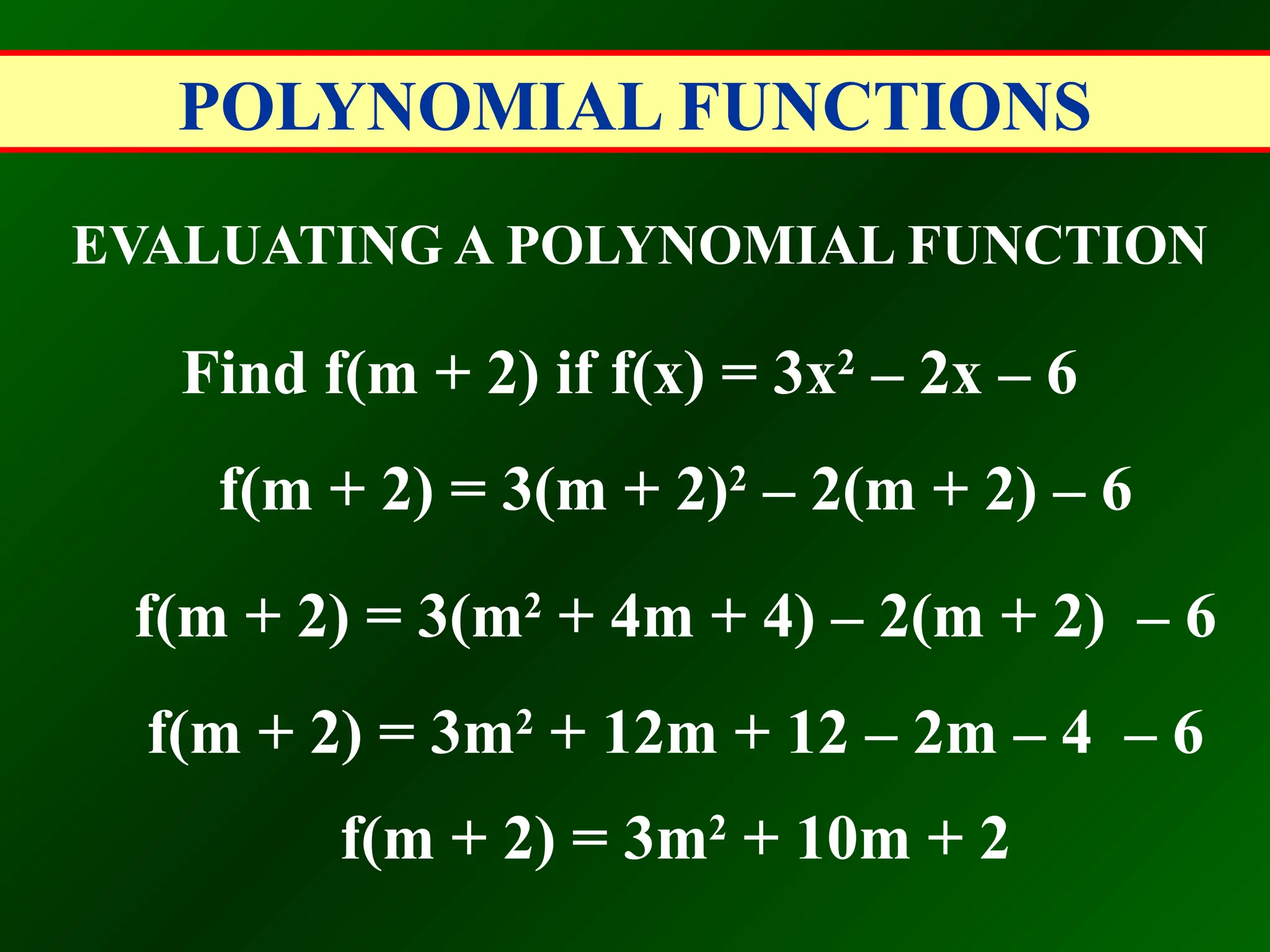
EVALUATING A POLYNOMIAL FUNCTION
Find 2g(-2a) if g(x) = 3x2
– 2x – 6
2g(-2a) = 2[3(-2a)2
– 2(-2a) – 6]
2g(-2a) = 2[12a2
+ 4a – 6]
2g(-2a) = 24a2
+ 8a – 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polynomialfunctions-100630114603-phpapp01-240917044410-de21e67f/75/Polynomialfunctions-100630114603-phpapp01-pptx-16-2048.jpg)