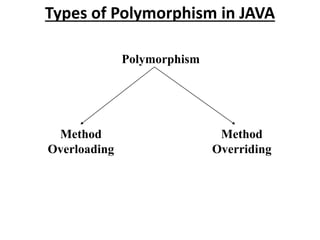
Polymorphism allows objects of derived classes to be treated as objects of base classes. There are two types of polymorphism in Java: method overloading and method overriding. Method overloading involves multiple methods of the same name but with different parameters within a class. Method overriding involves redefining methods in a derived class that are already provided in the base class. This allows derived classes to extend the functionality of methods inherited from the base class.



![class Fruit {
public void show() {
System.out.println("Fruit");
}
}
class Banana extends Fruit {
//method overriden
public void show() {
System.out.println("Banana");
}
public void makeBananaTree() {
System.out.println("Making a tree");
}
}
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Fruit banana = new Banana();
banana.show();
// The following WILL NOT work;
// Variables of type Fruit know only about Fruit methods.
banana.makeBananaTree();
}
} OUTPUT:
Banana
Introduction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphism-230607160648-500218bd/85/Polymorphism-pptx-4-320.jpg)
![class Shape { void draw() { } }
class Circle extends Shape {
private int x, y, r;
Circle(int x, int y, int r) { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.r = r; }
void draw() { System.out.println("Drawing circle (" + x + ", "+ y + ", " + r + ")"); }
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
private int x, y, w, h;
Rectangle(int x, int y, int w, int h) { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.w = w; this.h = h; }
void draw() { System.out.println("Drawing rectangle (" + x + ", "+ y + ", " + w + "," + h + ")"); }
}
class ShapesMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape[] shapes = { new Circle(10, 20, 30),
new Rectangle(20, 30, 40, 50) };
for (int i = 0; i < shapes.length; i++)
shapes[i].draw();
}
}
Introduction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphism-230607160648-500218bd/85/Polymorphism-pptx-5-320.jpg)

![Example 1: Overloading – Different Number of parameters in argument list
When methods name are same but number of arguments are different.
class DisplayOverloading {
public void disp(char c) {
System.out.println(c);
}
public void disp(char c, int num) {
System.out.println(c + " "+num);
}
}
class Sample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
DisplayOverloading obj = new DisplayOverloading();
obj.disp('a');
obj.disp('a',10);
}
}
Output:
a
a 10
Method Overloading (Compile-time
Polymorphism or Static Polymorphism)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphism-230607160648-500218bd/85/Polymorphism-pptx-8-320.jpg)
![Example 2: Overloading – Difference in data type of arguments
In this example, method disp() is overloaded based on the data type, one with char
argument and another with int argument.
class DisplayOverloading2{
public void disp(char c) {
System.out.println(c);
}
public void disp(int c) {
System.out.println(c);
}
}
class Sample2{
public static void main(String args[]) {
DisplayOverloading2 obj = new DisplayOverloading2();
obj.disp('a');
obj.disp(5);
}
}
Output:
a
5
Method Overloading (Compile-time
Polymorphism or Static Polymorphism)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphism-230607160648-500218bd/85/Polymorphism-pptx-9-320.jpg)
![Method Overloading (Compile-time
Polymorphism or Static Polymorphism)
Example3: Overloading – Sequence of data type of arguments
Here method disp() is overloaded based on sequence of data type of arguments
class DisplayOverloading3 {
public void disp(char c, int num) {
System.out.println("I’m the first definition of method disp");
}
public void disp(int num, char c) {
System.out.println("I’m the second definition of method disp" );
}
}
class Sample3{
public static void main(String args[]) {
DisplayOverloading3 obj = new DisplayOverloading3();
obj.disp('x', 51 );
obj.disp(52, 'y');
}
}
Output:
I’m the first definition of method disp
I’m the second definition of method disp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphism-230607160648-500218bd/85/Polymorphism-pptx-10-320.jpg)
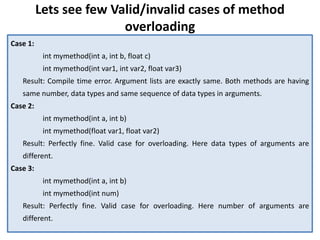
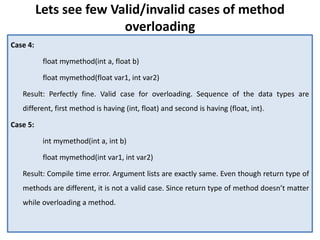

![Guess the answers before checking it at the end
of programs
Question 1 – return type, method name and argument list same.
class Demo {
public int myMethod(int num1, int num2){
System.out.println("First myMethod of class Demo");
return num1+num2;
}
public int myMethod(int var1, int var2) {
System.out.println("Second myMethod of class Demo");
return var1-var2;
}
}
class Sample4 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Demo obj1= new Demo();
obj1.myMethod(10,10);
obj1.myMethod(20,12);
}
}
Answer: It will throw a
compilation error: More than
one method with same name
and argument list cannot be
defined in a same class.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphism-230607160648-500218bd/85/Polymorphism-pptx-14-320.jpg)
![Question 2 – return type is different. Method name & argument list same.
class Demo2 {
public double myMethod(int num1, int num2) {
System.out.println("First myMethod of class Demo");
return num1+num2;
}
public int myMethod(int var1, int var2) {
System.out.println("Second myMethod of class Demo");
return var1-var2;
}
}
class Sample5 {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Demo2 obj2= new Demo2();
obj2.myMethod(10,10);
obj2.myMethod(20,12);
}
}
Guess the answers before checking it at the end
of programs
Answer: It will throw a
compilation error: More than one
method with same name and
argument list cannot be given in a
class even though their return
type is different. Method return
type doesn’t matter in case of
overloading.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphism-230607160648-500218bd/85/Polymorphism-pptx-15-320.jpg)

![class Animal{
public void move(){
System.out.println("Animals can move");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
public void move(){
System.out.println("Dogs can walk and run");
}
}
public class TestDog{
public static void main(String args[]){
Animal a = new Animal(); // Animal reference and object
Animal b = new Dog(); // Animal reference but Dog object
a.move();// runs the method in Animal class
b.move();//Runs the method in Dog class
}
}
Method Overriding (Runtime Polymorphism or
Dynamic Polymorphism )
Output:
Animals can move
Dogs can walk and run](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphism-230607160648-500218bd/85/Polymorphism-pptx-17-320.jpg)
![Consider the following example :
class Animal{
public void move(){
System.out.println("Animals can move");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
public void move(){
System.out.println("Dogs can walk and run");
}
public void bark(){
System.out.println("Dogs can bark");
}
}
public class TestDog{
public static void main(String args[]){
Animal a = new Animal(); // Animal reference and object
Animal b = new Dog(); // Animal reference but Dog object
a.move();// runs the method in Animal class
b.move();//Runs the method in Dog class
b.bark();
}
}
Method Overriding (Runtime Polymorphism or
Dynamic Polymorphism )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphism-230607160648-500218bd/85/Polymorphism-pptx-18-320.jpg)
![Consider the following example :
class Animal{
public void move(){
System.out.println("Animals can move");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
public void move(){
System.out.println("Dogs can walk and run");
}
public void bark(){
System.out.println("Dogs can bark");
}
}
public class TestDog{
public static void main(String args[]){
Animal a = new Animal(); // Animal reference and object
Animal b = new Dog(); // Animal reference but Dog object
a.move();// runs the method in Animal class
b.move();//Runs the method in Dog class
b.bark();
}
}
Method Overriding (Runtime Polymorphism or
Dynamic Polymorphism )
This would produce the following result:
TestDog.java:30: cannot find symbol
symbol : method bark()
location: class Animal
b.bark();
^
This program will throw a compile time error since b's
reference type Animal doesn't have a bark method.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorphism-230607160648-500218bd/85/Polymorphism-pptx-19-320.jpg)
