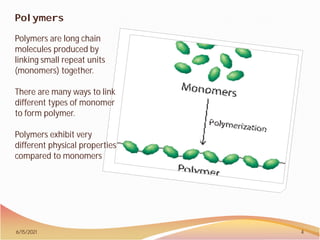
1. The document discusses additive manufacturing and 3D printing of polymers. It notes that polymers are among the cheapest materials for 3D printing and lists some common plastics used, including ABS, PLA, polyamide, and nylon.
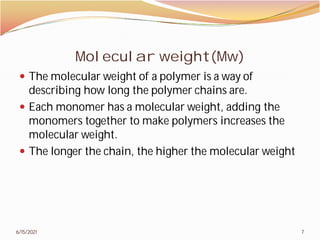
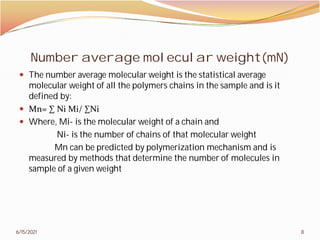
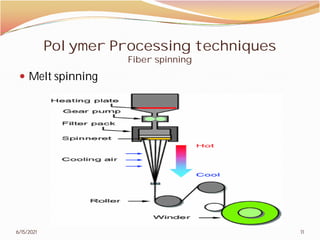
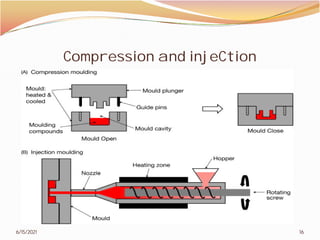
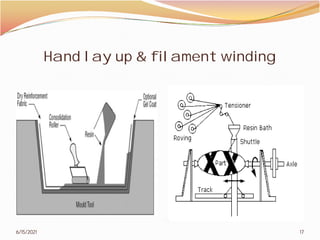
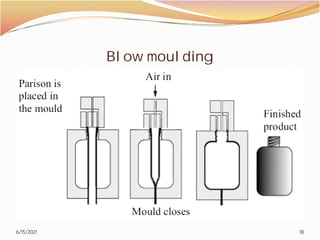
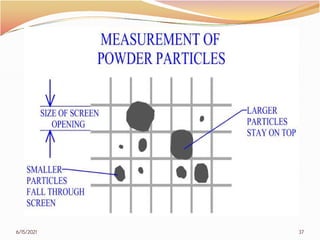
2. The document then covers various topics related to polymers, including classifications of polymers, molecular weight, polymer processing techniques, and metal powder characterization. It provides examples and definitions for these topics.
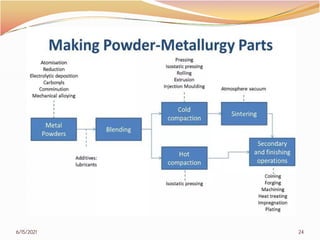
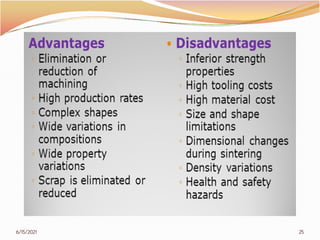
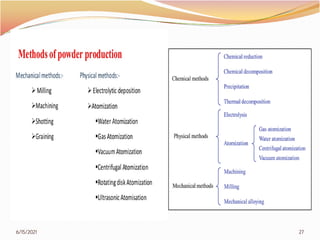
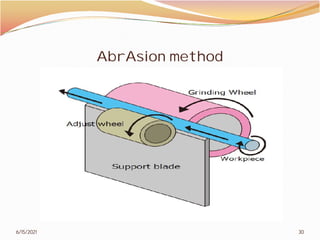
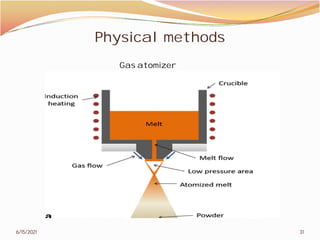
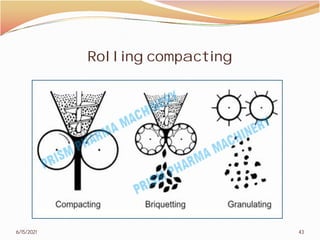
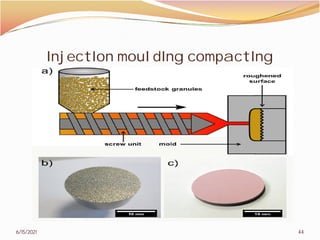
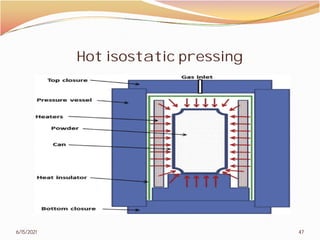
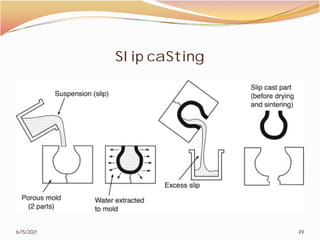
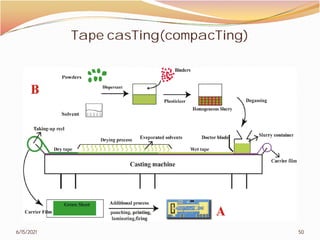
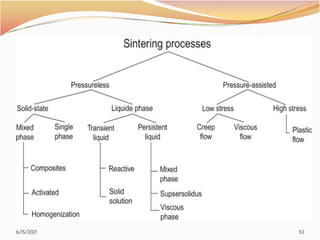
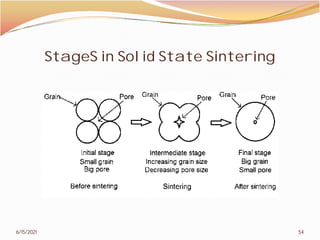
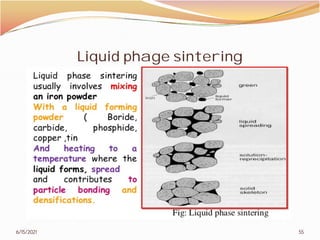
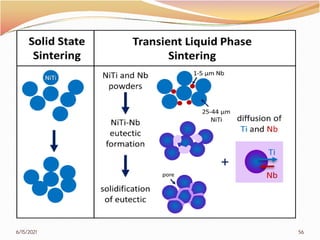
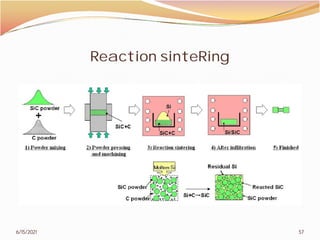
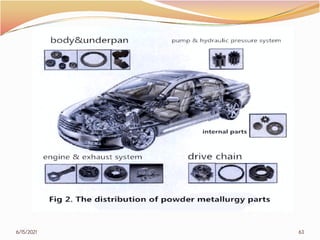
3. The remainder of the document discusses powder metallurgy processing techniques like compaction, sintering, defects in sintering, and applications of powder metallurgy. Processing steps like die pressing, CIP, HIP, slip casting, and